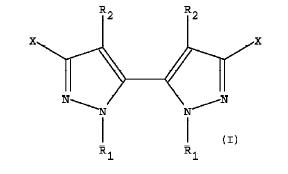
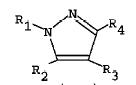
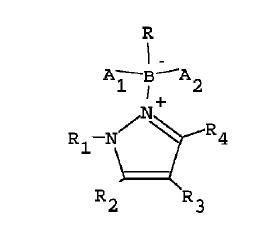
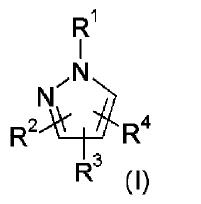
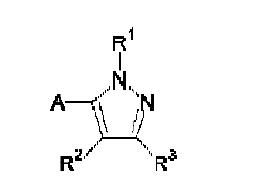
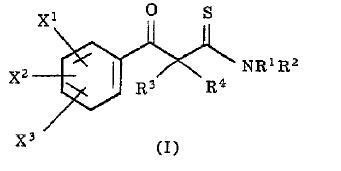
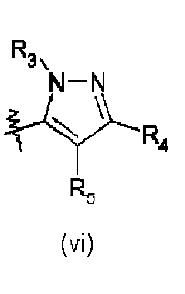
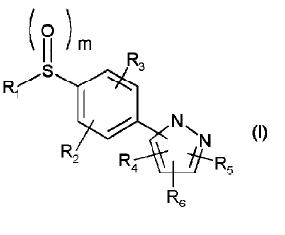
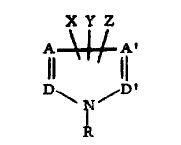
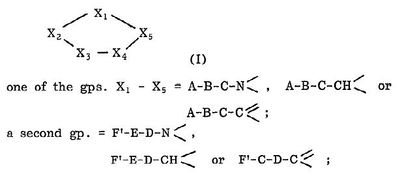Markush Structure Search Sample
Contents
- 1 Patent FTO Search for the Generic compound
- 2 Exact match structures
- 3 Exact match structures but mentioned as optionally substituted at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure
- 4 Relevant structures with missing substituents
- 5 Relevant structures with substituent variation
- 6 Other structures
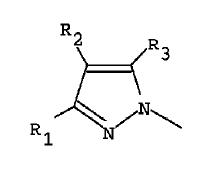
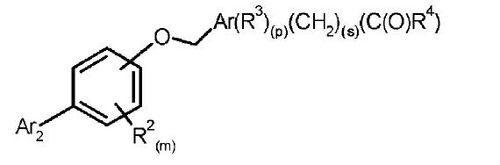
Patent FTO Search for the Generic compound
Exact match structures
Structure-1 (12(doc1))
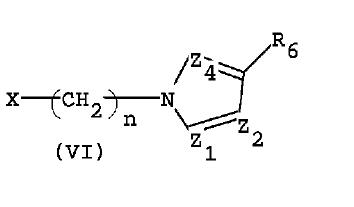
DE4124942
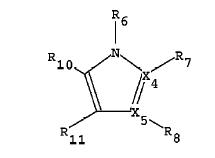
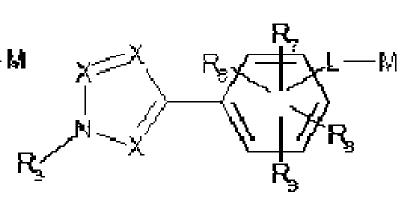
- X1 = A-B-C- C(sp2 carbon), X2 = F-C-D-C(sp2 carbon), X3 = R1-N<, X4 = N, X5 = R2-C(sp2 carbon)
- X1: A =H , B = bond, C = (b) under B which is halo substituted phenylene which completely matches with 4th position substituent of the generic compound
- X2: D = (b) under B is a phenylene(implies a substituted aryl) and F-C- is a substituent on D. It is clear that this will match with R2 (substituent aryl) at the 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- X3: R1 = Q(alkyl) which matches with R1(alkyl) at the 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- X4: N which matches with the 2nd position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- X5: R2 = Cl, Br which matches with R3(halogen) at the 3 rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
Structure-2 (9(doc2))
WO2007081019
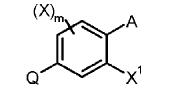
In the above phenyl ring Q is pyrazole.
- R2= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic compound.
- R4 is halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- 4th position of above pyrazole is trihalo substituted aryl which matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic compound .
- 5th position of pyrazole ring is above substituted aryl which matches with R2(substituted aryl) at the 5th position of pyrazole of generic compound.
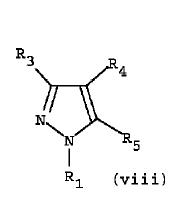
Structure-3 (125(doc2))
JP11130754
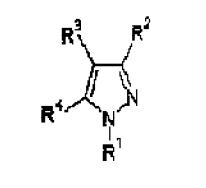
Consider left side ring the pyrazole ring
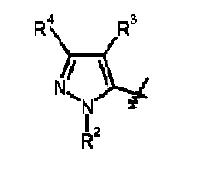
- R1 is 1-4C alkyl which is matching with substituent R1(first position) of the generic structure
- X is Cl so it is matching with the substituent R3 (second position) of the generic structure
- R2 is phenyl substituted by halo, 1-4C alkyl, cyano which is matching with the fourth position of the generic structure
- In the fifth position pyrazole(heteroaryl) is there…which is matching with the substituent R2(fifth position) of the generic structure.
Structure-4 (109(doc2))
WO2006078610
- R2 is 1-6C alkyl which is matching with substituent R1(first position) of the generic structure
- R4 is halo matching with the substituent R3 (second position) of the generic structure
- R3 is heteroaryl or phenyl substituted by 1-8C alkyl, halo, CN, 1-6C alkoxy which is matching with the fourth position of the generic structure
- In fifth position substituted aryl ring there, which is matching with the substituent R2(fifth position) of the generic structure.
Structure-5 (128(doc2))
US5827602
- R1-R6=H, F, 1-4C alkyl, phenyl
- R2= 1-4C alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R5= F which matches with R3(halo)at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R4= phenyl substituted with an electron with drawing group matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure
- R3= substituted aryl which matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
Structure-6 (19(doc2))
US 2007100181
R1-R2= H, -C2H5 which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= 6-25C heteroaryl having 1-3 heteroatoms(N)(could be pyridine) with substituents as halo, OH and alkyl which completely resembles substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
R5= 6-25C heteroaryl having 1-3 heteroatoms(N)(could be pyridine) with substituents which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-7 (88(doc2))
DE19503827
Q-R4
Q= above structure
R4= CR5R6R7 where R5= 1-4C alkyl, R6= H so no need of R7
R4 matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R1= halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R2= alkylaryl substituted by halo matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structures
R3= substituted aryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-8 (86(doc2))
WO9702252
R1-R2= 1-4C alkyl, H matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R3= halogen matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= phenyl substituted with electron withdrawing group(halogens) matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structures
R5= substituted aryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-9 (41(doc2))
JP2005216490
- R1= lower alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R2= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R3= methoxyphenyl which indicates subtituent at 4th position of generic structure
- R4= methoxy phenyl which matches with R2(substituted aryl)at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
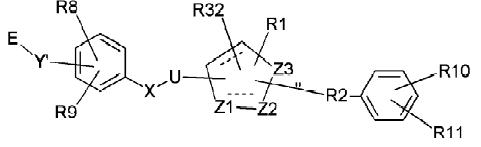
Structure-10 (61(doc1))
WO2004063166
- Z1= C, Z2= N, Z3= N Which indicates pyrazole ring.
- R1= Alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at the 1st position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R32= halo which matches with R3(halogen) at the 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R2(0-8Calkyl) so it may be ’0’C alkyl implies it is simply a bond, bonded to a substituted phenyl ring which matches with R2(substituted aryl) at the 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- U is an aliphatic linker(linker means a bond, aliphatic means saturated. So aliphatic linker means saturated bond which implies a single bond) so it is a bond and X is a single bond linked to substituted aryl with halogens and cycloalkyl as substituents which matches with 4th position of pyrazole of the generic compound.
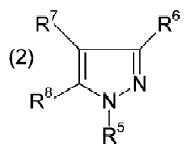
Exact match structures but mentioned as optionally substituted at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-1 (84(doc2))
WO9711952
- R1-R4= 1-8C alkyl, haloalkyl, halo, phenyl(optionally substituted by halo, 1-4C alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxy,)
- R1= 1-8C alkyl which matches with R1(1-4C alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
- R4= halo which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
- R3= phenyl(optionally substituted by halo, alkoxy) which matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R2= phenyl(optionally substituted) which matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
Structure-2 (74(doc2))
WO0130154
- R1= (1-6C)alkyl which matches with R1(1-4C alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R2= halo which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R3= phenyl optionally substituted with halo, 1-6C alkyl, 1-6C alkoxy which matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R4= heterocyclyl containing 1 or 2N and optionally substituted which matches with R2(optionally substituted heteroaryl) at 5th position of the generic compound
Structure-3 (39(doc2))
JP2005272306
- A= substituted heteroaryl which matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R1= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
- R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
- R2= phenyl optionally substituted by Y(1-6C alkyl), 1-6C alkoxy and matches with subtituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-4 (25(doc2))
US2007066822
R1-R2= H, -CH3, -C2H5 which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= 6-25C optionally substituted heteroaryl which resembles substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
R5= optionally substituted 6-25C heteroaryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-5 (23(doc2))
US2007066854
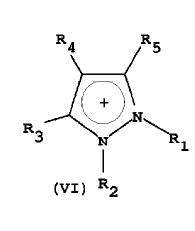
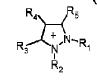
Z+= pyrazolium (substituted at 1-5 R1-R5)
R1= -CH3, -C2H5 which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= 6-25C aryl optionally substituted by C2H5, OH which resembles substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
| R5= optionally substituted 6-25C heteroaryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure |
Structure-6 (90(doc2))
FR2723091
X= halo, n= 2-4
Z1= N, Z2= CR5, Z4= CR7
R4-R7= alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure; halogen matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure; optionally substituted aryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure and matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structures
Structure-7 (92(doc2))
WO9600218
Z= a bond,
R4 is a pyrazole with substituents as 1-4C alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure; halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure; optionally substituted aryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure and matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structures
Structure-8 (95(doc2))
WO9524403
- R1= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R3= halo which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R4= heteroaryl optionally substituted indicating substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R5= optionally substituted heteroaryl which matches with R2(optionally substituted heteroaryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
Structure-9 (98(doc2))
JP6345728
- A= N, B= CR4
- R5= 1-6C alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R4= phenyl(optionally substituted by halo, CN, alkoxy)indicating substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R2= optionally substituted phenyl which matches with R2(optionally substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
Structure-10 (34(doc2))
WO2006084262
It is pyrazolium with substituents
R1-R5= halogen matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure; -C2H5 matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure; 6-20C substituted aryl with substituents as halogen, OH which resembles substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure; R5= optionally substituted 6-20C heteroaryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Relevant structures with missing substituents
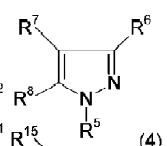
Structure-1
JP09204932
- R6 is 1-3C alkyl which is matching with substituent R1(first position) of the generic structure
- R7 doesn’t exist.. so it is matching with the second position of the generic structure.
- R8 is halogen so it is matching with the substituent R3 (second position) of the generic structure
- R11 is phenyl’’’(substituents are missing)’’’ which is matching with the fourth position of the generic structure
- R10 is phenyl which is matching with the substituent R2(fifth position) of the generic structure.
Structure-2
WO0018741
- Q= pyrazolyl
- In the above structure the substituted aryl bonded to Q(pyrazolyl) matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R1= haloalkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of the generic structure
- R2= aryl optionally substituted with halo, lower alkoxy, CN which matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure.
- But ’’’R3(halogen) of pyrazole of generic structure is missing’’’ in the above structure
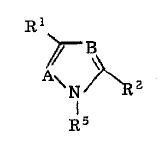
Structure-3
EP335381
D= NR12 , E’’= N, E’= CH, E= CH
R12= alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R7= halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R8= substituted benzene ring matches with substituent at 4th position(but missing substituents) of pyrazole of generic structures
Above pyrazole ring is attached to a substituted aryl matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-4
US5296484
- G= NR20, M= N
- R11= halo, 1-4C alkyl, phenyl
- This structure has substituted aryl at 5th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- At 4th position of pyrazole i.e.,aryl has no substituents compared to generic structure
- One more substituent is missing on the pyrazole ring
Structure-5
US2006122256
- AR2= pyrazol-4-yl optionally substituted by Q(halo, lower alkyl, phenyl)
- Q substituted on AR2(pyrazole) indicates R3, R1 and R5 of pyrazole of the generic structure
- At 4th substituent of pyrazole one substituent is missing and one substituent is varying
Structure-6
JP2004317641
- R5= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R6= halogen which matches with R3(halogen)at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R7= phenyl with no substituents. It represents substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure with substituents missing
- R8= phenyl which matches with R2(aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-7
JP2004317640
- R5= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R6= halogen which matches with R3(halogen)at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R7= phenyl with no substituents. It represents substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure with substituents missing
- R8= phenyl which matches with R2(aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-8
US2005135045
- R= 1-4C alkyl, halogen , phenyl
- R= alkyl which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R= halogen which matches with R3(halogen)at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic structure
- R= phenyl with no substituents. It represents substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structure with substituents missing
- R= phenyl which matches with R2(aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-9
WO2006124776
R1= H, R2= halogen, R3= pyrazole with substituents, R5= H, R6= H
R3 is a pyrazole ring with substituents as:
-CH3 matches with R1(alkyl) of pyrazole of the generic structure
Above ring matches with subtituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
R3 and R2 of pyrazole of generic structure are missing
Structure-10
WO2007038363
R1= H, R2= halogen, R3= pyrazole with substituents, R5= H, R6= H
R3 is defined as 3-25C substituted heteroaryl having 1-3 heteroatoms of N(so can be pyrazole) in which the substituents are -CH3, halogen:
-CH3 matches with R1(alkyl) of pyrazole of the generic structure and halogen matches with R3(halogen) of pyrazole of the generic structure
Above ring matches with subtituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure
R2(substituted aryl) of pyrazole of generic structure missing
Structure-11
US2007100184
R1= H
R2= -C2H5 which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R3= halogen which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= optionally substituted 6-25C heteroaryl with 1-3 of O, N, S or with 1-3 of CH3, C2H5, 3-25, preferably 3-20C straight , branched or cyclic alkane or alkene optionally substituted with halogens which resembles substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of the generic structure but R7 of pyrazole of generic structure is missing
| R5= optionally substituted 6-25C heteroaryl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure |
Structure-12
US2005020646
Ra= pyrazolyl optionally substituted with 1-3 substituents of R11 or 1-4C alkyl
R11 is defined as halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure; pyridyl which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure; pyridyl matches with substituent at 4th position of pyrazole of generic structures but R7 of generic structure is missing
Structure-13
EP548680
X1= het
Het = pyrazolyl with substituents alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure; halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure; phenyl matches with substituent at 4th position(but missing substituents) of pyrazole of generic structures
Above aryl ring is a substituent on X1 which resembles R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-14
WO2003087062
G= above pyrazole
R3= alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R4= halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R5= phenyl matches with substituent at 4th position(but missing substituents) of pyrazole of generic structures
Above given aryl matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
Structure-15
WO200066562
R4= alkyl matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of pyrazole of generic structure
R5= halo matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of generic structure
R6= optionally substituted aryl matches with substituent at 4th position(but missing substituents) of pyrazole of generic structures
Above given aryl matches with R2(substituted aryl) at 5th position of pyrazole of generic structure
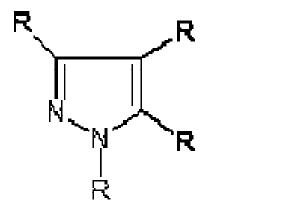
Relevant structures with substituent variation
Structure-1
EP0080051
- In the above structure D is N & A,A’,D’ are considered as carbons…so it is forming a pyrazole ring.
- In the first position substituent R is 3-iodopropargyl, so it is matching with the substituent R1( first position) of the generic structure.
- X is Cl, so it is matching with the substituent R3 (third position) of the generic structure.
- Y is 3-chloro-2-nitrophenyl which is matching with the ring of the fourth position of the generic structure but here ’’’substituent variation’’’ is there.
- Z is phenyl, so it is matching with the substituent R2 (fifth position) of the generic structure.
Structure-2
US2005159470
- First position: R3 is alkyl, so it is matching with the substituent R1 (first position) of the generic structure.
- Second position: X is N, so it is matching with second position of the generic structure.
- Third position: X is CR5 , R5 is halo so it is matching with the substituent R3 (third position) of the generic structure.
- Fourth position: In fourth position substituted aryl ring is present’’’(but it contains five substituents)’’’, is matching with fourth position of the generic structure.
- Fifth position: X is CR5, R5 is heteroaryl, so it is matching with substituent R2 (fifth position) of the generic structure.
Other structures
WO2007070607
- R1-H,
- R2 is –C2H5 which matches with R1(alkyl) at 1st position of the generic structure
- R5 is halo which matches with R3(halogen) at 3rd position of pyrazole of the generic compound
- R4 is heteroaryl substituted by C2H5(one substituent is missing) matches with substituent at 4th position of the generic structure.
- R3 is substituted heteroaryl which is matching with the substituent R2(fifth position) of the generic structure