OLED Background
From DolceraWiki
OLED Components
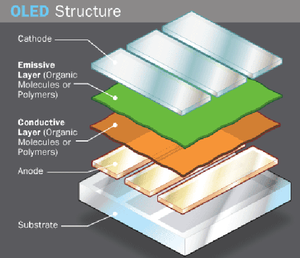
An OLED consists of the following parts:
- Substrate (clear plastic, glass, foil) - The substrate supports the OLED.
- Anode (transparent) - The anode removes electrons (adds electron "holes") when a current flows through the device.
- Organic layers - These layers are made of organic molecules or polymers.
- Conducting layer - This layer is made of organic plastic molecules that transport "holes" from the anode. One conducting polymer used in OLEDs is polyaniline.
- Emissive layer - This layer is made of organic plastic molecules (different ones from the conducting layer) that transport electrons from the cathode; this is where light is made. One polymer used in the emissive layer is polyfluorene.
- Cathode (may or may not be transparent depending on the type of OLED) - The cathode injects electrons when a current flows through the device.source
To see details on working of OLED's click here
OLED Types
There are several types of OLEDs
- Passive-matrix OLED
- Active-matrix OLED
- Transparent OLED
- Top-emitting OLED
- Bottom-emitting OLED
- Foldable OLED
- White OLED
For more details click here
To view details on OLED Advantages and Disadvantages click here