Electric Vehicles
Back to Wireless Power Transmission
Electric vehicles first came into existence in the mid-19th century, when electricity was among the preferred methods for motor vehicle propulsion, providing a level of comfort and ease of operation that could not be achieved by the gasoline cars of the time. During the last few decades, environmental impact of the petroleum-based transportation infrastructure, along with the peak oil , has led to renewed interest in an electric transportation infrastructure.
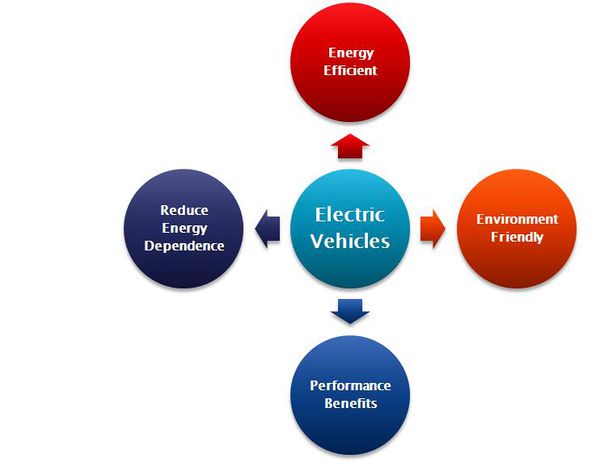
Electric vehicles (EVs) are propelled by an electric motor (or motors) powered by rechargeable battery packs. Electric motors have several advantages over internal combustion engines (ICEs):
- Energy efficient. Electric motors convert 75% of the chemical energy from the batteries to power the wheels—internal combustion engines (ICEs) only convert 20% of the energy stored in gasoline.
- Environmentally friendly. EVs emit no tailpipe pollutants, although the power plant producing the electricity may emit them. Electricity from nuclear-, hydro-, solar-, or wind-powered plants causes no air pollutants.
- Performance benefits. Electric motors provide quiet, smooth operation and stronger acceleration and require less maintenance than ICEs.
- Reduce energy dependence. Electricity is a domestic energy source.
Contents
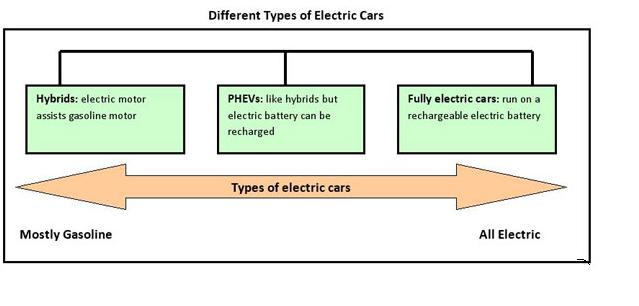
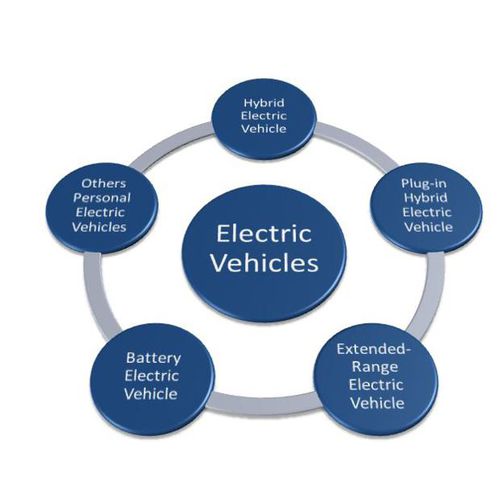
Major Types of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
- Extended Range Electric Vehicles
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Other Personal Electric Vehicles
For More details, please click Types of Electric Vehicles
Status of EV Market
California created regulations specifying a share of electric vehicles to be sold in California to be 10% after GM announced its intention to produce Electric Vehicles, in 1990. Several manufacturers produced and field tested several EVs, predominantly using Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH).
Moreover, as a result of the sharp rise in oil prices, and considerable technological progress in lithium ion (Li-ion) battery chemistries, a new wave of enthusiasm for electric vehicles (EVs) has emerged.
Santini and Vyas (2009) for the U.S. and Golob and Brownstone (2005) for California have shown that the proportion of cars in the vehicle population increases as population density increases. Thus, EVs that are under development are “City” cars, or “City EVs”. They are generally small, even among cars.
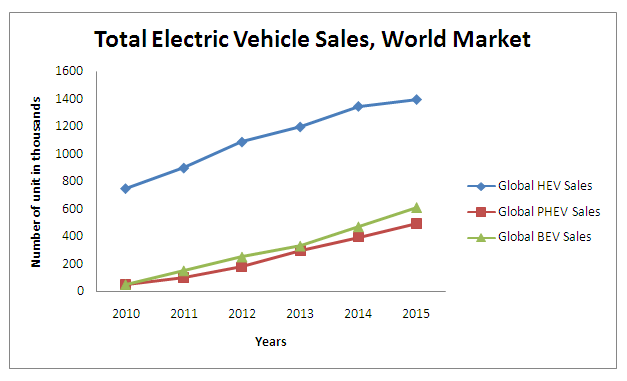
Total Electric Vehicle Sales, World Market: 2010 to 2015
Source Green Car Congress-Sept.2010
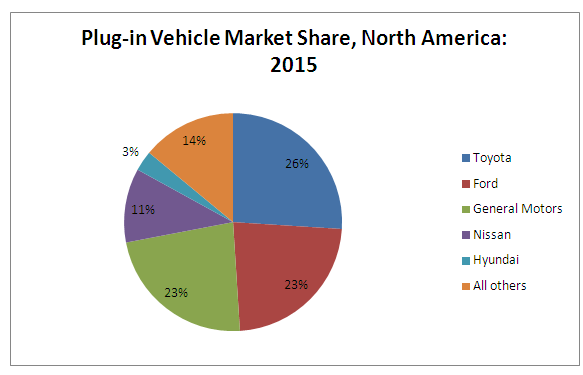
Source Pike Research: North American Plug-in Vehicle Market Share, 2015
Source VW joins rush into electric vehicles:source JD Power
Major EVs in the Market
- BMW is developing an EV version of its Mini, which becomes a two-seater when the battery is included.
- DaimlerChrysler is developing an electric version of the “ForTwo”, a small two-seater now available in the U.S.
- Mitsubishi has developed the i-MiEV, a “Lilliputian four passenger EV with 16 kWh battery packs that may be priced at upwards of $45000”. Mitsubishi plans more models and will have a cooperative agreement with Peugeot of France to produce EVs for Peugeot.
- Tesla Motors, which has developed the extremely high performance two seat electric Tesla Roadster, plans to produce a sedan seating 5 adults and two small children, the Model S. Tesla has sold 700 roadsters, which use Li-ion batteries, at prices above $100,000.
- The all-electric car, Leaf by Nissan Motors, having four doors and a hatchback, which was launched in US IN 2010. It is recommended that consumers have a home charging station, made by Aerovironment, installed for an average cost of $2,200, according to Nissan. The all-electric Leaf has a driving range of about 100 miles
- General Motors designed the Chevy Volt with a large battery pack and a gasoline engine. It was also launched in 2010. Thus, unlike the Leaf the Volt has a gas engine to fall back on. It generates power to spin the electric motor when the battery is depleted.
- Toyota introduced its first hybrid gas-electric vehicle, Prius, in 2000. In January 2011, Toyota debuted the Prius v, which goes on sale in third quarter of 2011. It is a mid-size vehicle that provides more than 50 percent additional interior cargo space than the current Prius. In early 2012 Prius will launch two more Prius family members – the Prius c compact hybrid vehicle and the Prius Plug-in Hybrid vehicle.
- Ford joins GM, Nissan and Toyota in mass-producing plug-in cars. In January 2011, Ford unveiled electric Ford Focus. Ford's electric car has no gasoline engine for backup. It can drive from 80 to 100 miles on a full charge. The car even communicates with smart phones, so a driver can call his car remotely and order it to charge immediately, or wait for utility rates to drop at nighttime. Ford is also planning new electric, hybrid and plug-in vehicles by 2015.
| Car Company | PHEV | BEV | Models | Timeline | Planned Production Output |
| BMW | No | Yes | Mini-E, Active-E, Megacity | Megacity-2013 Mini-E, Active-E on pilot lease |
Unknown |
| Chrysler-Fiat | No | Yes | Fiat 500 | 2012 | Unknown |
| Daimler | No | Yes | Smart ED Fortwo | 2012 | 1,500 globally in 2011, series production in 2012 |
| Mitsubishi | Yes | Yes | iMiEV, PX-MiEV | i-MiEV: 2011 PX-MiEV: 2013 |
Unknown |
| Tesla | No | Yes | Roadster, Model S | Roadster: in serial production Model S: 2012 |
Roadster: 1,200 annually Model S: 20,000 annually |
| Nissan | No | Yes | LEAF, NV200, Infiniti EV | LEAF: In serial production | LEAF: 500,000/year globally by 2012 |
| GM | Yes | No | Volt | In serial production | 2011: 10-15,000 units 2012: up to 60,000 units |
| Ford | Yes | Yes | Focus BEV, Transit Connect Electric, unnamed PHEV | Transit Connect Electric: began in late 2010 Focus BEV: 2011 Unnamed PHEV: 2012 |
Transit Connect Electric: 600-700 annually beginning in April 2011 Focus BEV: 5,000-10,000 units annually13 |
| Toyota | Yes | Yes | Prius PHEV, Unnamed BEV | 2012 | Prius PHEV: 10000 units annually |
Source Plug-in Electric Vehicles: A Practical Plan for Progress February 2011, School of Public and Environmental Affairs at Indiana University
Number of EV Models Expected to be Introduced 2011 to 2015
| Type | Already in Market | Model year 2011 | Model Year 2012 | Model Year 2013 | Model Year 2014 | Model Year 2015 | Total Models By 2015 |
| HEVs | 22 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 52 |
| PHEVs | 0 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 18 |
| BEVs | 1 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 32 |
| FCVs | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| Total | 23 | 27 | 24 | 11 | 14 | 9 | 108 |
SourceFall 2010 Electric Vehicle Forecast Summary Prepared by Baum and Associates September 2010
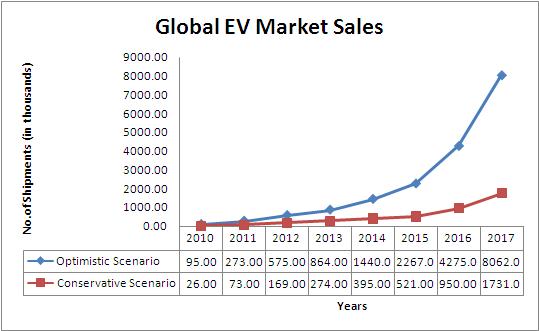
Estimated Sales of EVs: 2011 TO 2017
Patent Valuation-Auckland Uniservices
Wireless Chargers for Electric Vehicles
Sources
Electric Vehicle Primer-Types of EVs
Pike Research: North American Plug-in Vehicle Market Share, 2015
VW joins rush into electric vehicles:source JD Power
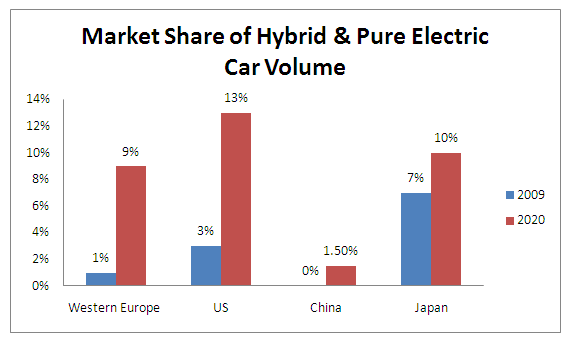
EV Market Development, May 2010
Fall 2010 Electric Vehicle Forecast Summary Prepared by Baum and Associates September 2010
Back to Wireless Power Transmission