LTE
This report presents a brief summary about LTE-MIMO.A detailed taxonomy which covers most of the aspects of LTE is presented. A sample of mapping patents to the standard by using graphical analysis and patent ranking is presented. LTE related ETSI and non-ETSI documents are also shown.
Dolcera Landscape Procedure
- Background study - Background study is done with web search depending on the area of client interest.
- Finding key player/inventors - Web search is carried out to find the products and technologies of key players.
- Patents Search -
- Key patents search.
- Prepared search queries using keywords and classification and finalized these in Micropat/Thompson.
- Patents Classification - Classify all patents by creating taxonomy.
- Specific analysis as required by client like SWOT, SOA, PEST, Claim, and White Space analysis.
- Reporting -
- All necessary data are presented in format of wiki or in form of power point slides.
- Dashboard - Graphical representation of Patents classification.
Contents
- 1 Rationale
- 2 Background description
- 3 Technical details
- 4 LTE architecture
- 5 LTE enabling technologies
- 6 Taxonomy
- 7 Major players in the ETSI list for LTE
- 8 Ranking of ETSI patents
- 9 Relevant Documents for LTE in the ETSI list
- 10 MIMO(Multiple Input Multiple Output)
- 11 Concept table for MIMO
- 12 Control patents
- 13 Search Strategy - MIMO
- 14 Patent mapping by graphical analysis
- 15 Ranking of Non ETSI patents
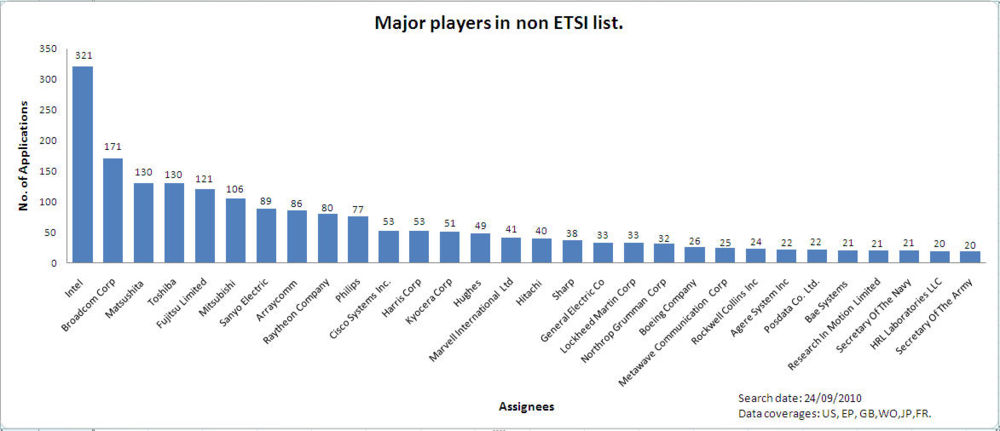
- 16 Major players in the non-ETSI list for MIMO
- 17 Major companies for low cost IP for MIMO
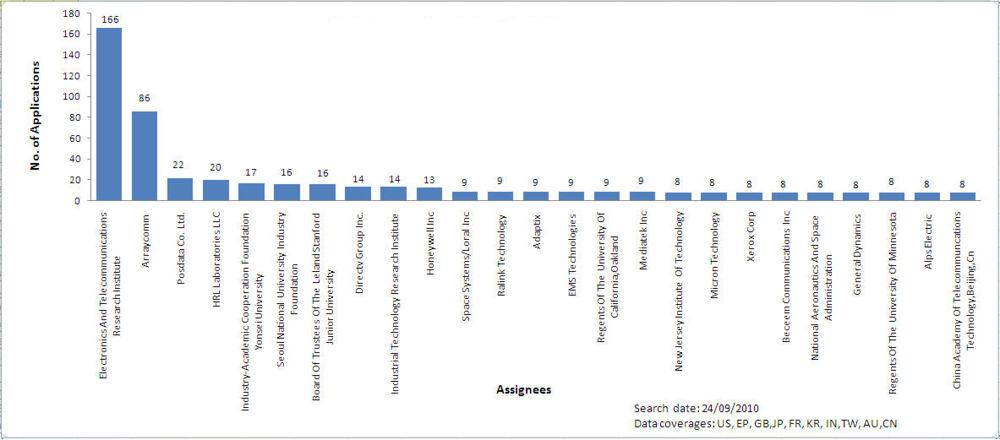
- 18 Most cited documents in non-ETSI list for MIMO
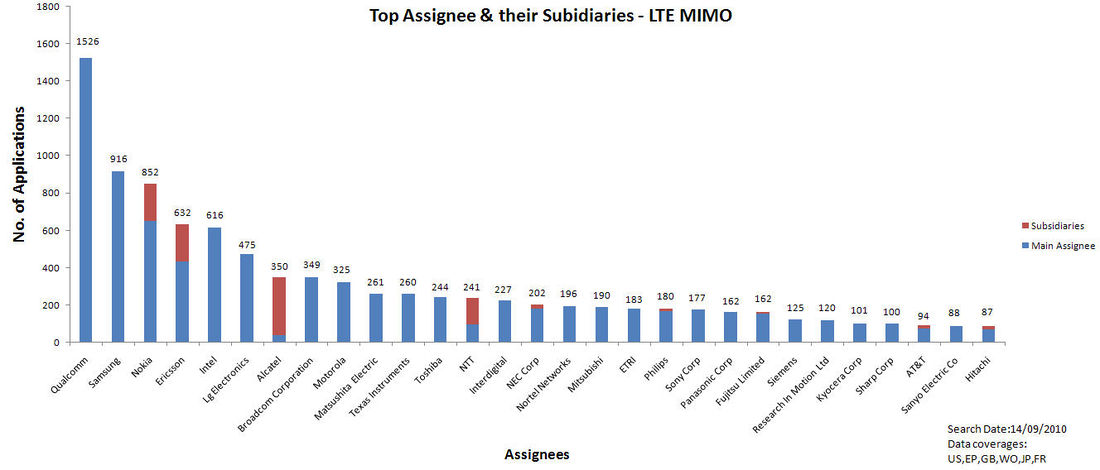
- 19 Company wise distribution of IP
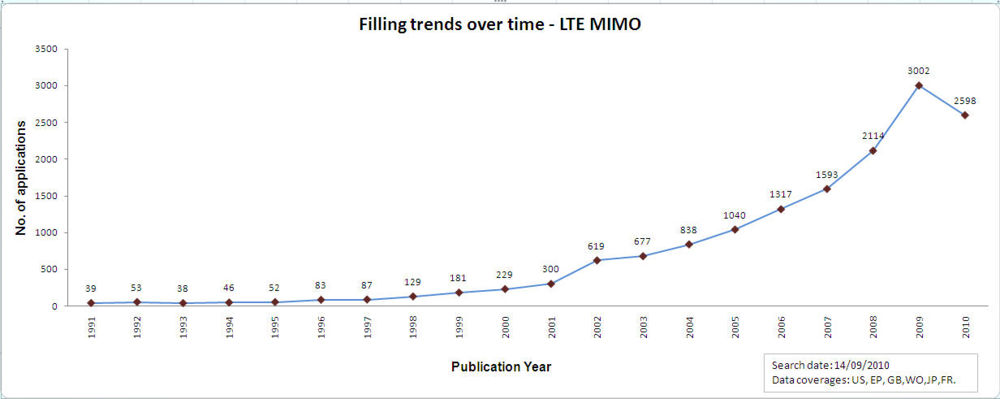
- 20 Filing trends over the years
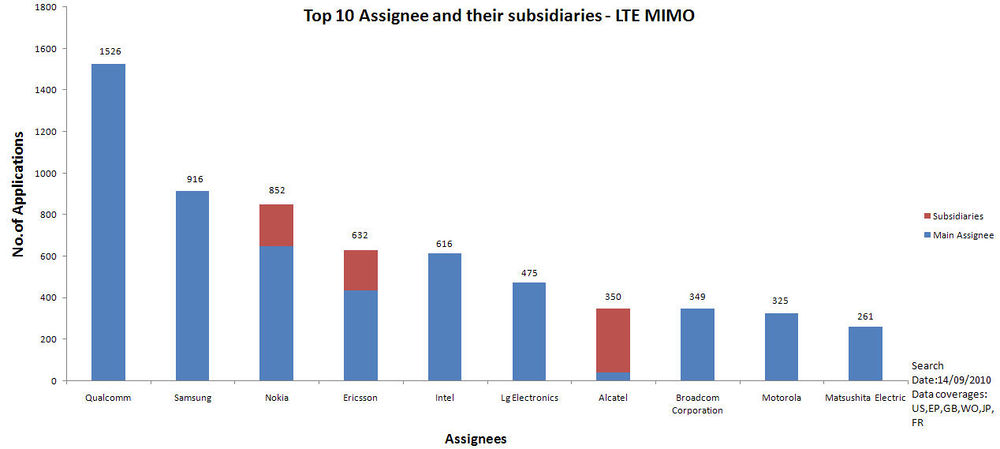
- 21 Filing trends for top 10 companies
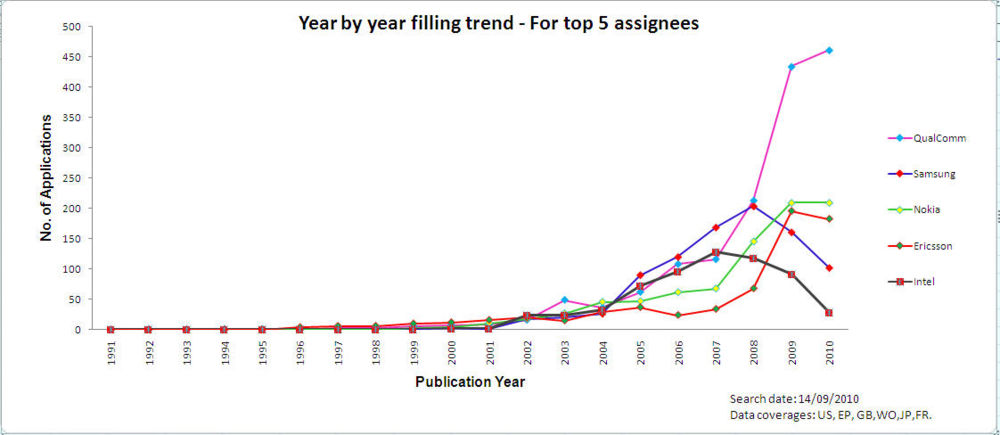
- 22 Year by year trends of top 5 companies
- 23 Interactive Taxonomy
- 24 Dolcera Dashboard
- 25 LTE Release 8
- 26 Meeting minutes
- 27 Like this report?
- 28 References
- 29 Contact Dolcera
Rationale
- LTE is the most suited technology as it provides higher data rates required for the future and is an advancement over widely used GSM/EDGE/HSPA
- A number of corporate giants are looking towards LTE as the technology enabling future communication
- The following factors are expected to be obtained with the realization of LTE
- Reduced cost per bit
- Increased service provisioning - more services at lower cost with better user experience
- Flexibility of use of existing and new frequency bands
- Simplified architecture, Open interfaces
- Allow for reasonable terminal power consumption
Background description
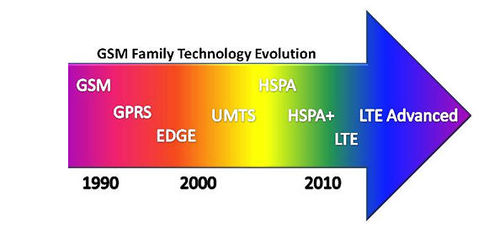
LTE (Long Term Evolution), is the latest standard in the mobile network technology that came into existence because of the growing needs of faster data rates. It is a 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), which realized this technology. LTE is an advancement to previously realized technologies such as GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSxPA etc.Although LTE is often marketed as 4G, first-release LTE is actually a 3.9G technology since it does not fully comply with the IMT Advanced 4G requirements.
Update - LTE-Advanced has been granted 4G compliance given the significant improvement they provide over 3G technologies [1]
Voice traffic will be supported mainly as Voice over IP (VoIP) enabling better integration with other multimedia services.LTE is being designed to be a high data rate and low latency system. LTE is also aimed at minimizing cost and power consumption while ensuring backward-compatibility and a cost effective migration from UMTS systems. LTE tutorial
Technical details
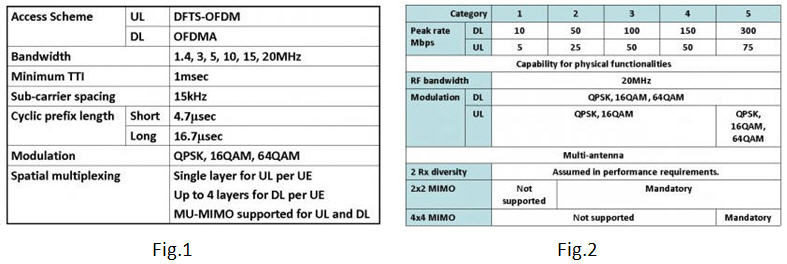
Performance requirements
LTE is expected to support different types of services including web browsing, FTP, video streaming, VoIP, online gaming, real time video, push-to-talk and push-to-view. Therefore, it is being designed to be a high data rate and low latency system as indicated by the key performance criteria shown below.
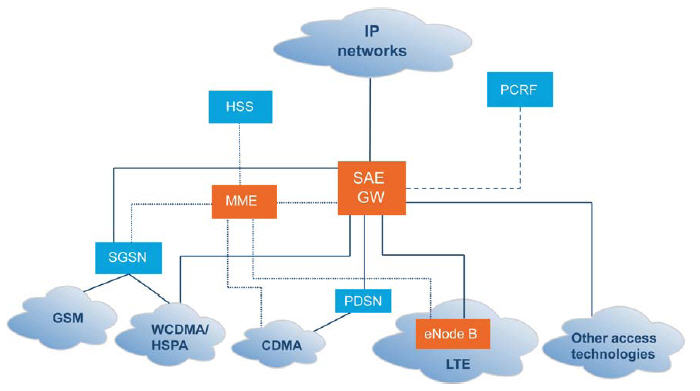
LTE architecture
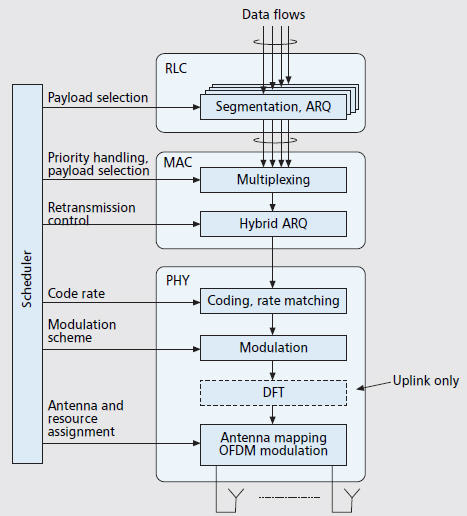
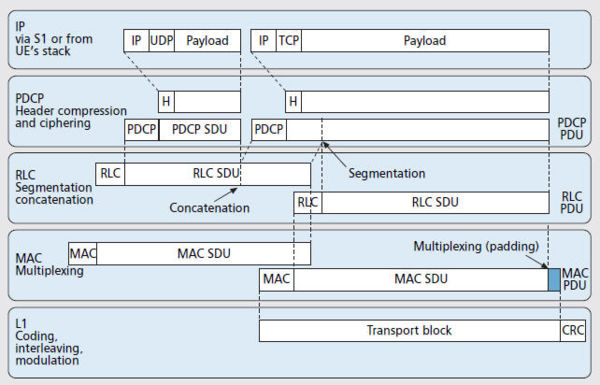
Protocol stack
Data flow
The data flow through protocol stack can be shown as
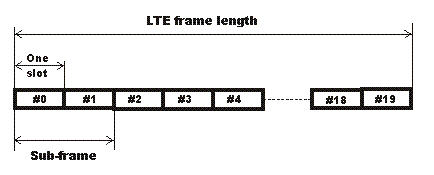
LTE frame structure
In order to maintain synchronization and manage different types of information exchange that need to be carried between the base-station or eNodeB and the User Equipment (UE), LTE system has a defined LTE frame and sub frame structure for the E-UTRA or Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access
There are two types of LTE frame structure:
- Type 1:used for the LTE FDD mode systems
- The basic type 1 LTE frame has an overall length of 10 ms. This is then divided into a total of 20 individual slots. LTE sub frames then consist of two slots - in other words there are ten LTE sub frames within a frame.
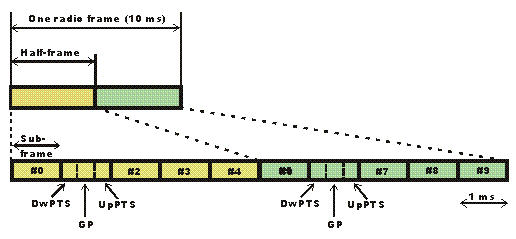
- Type 2:used for the LTE TDD systems
- The frame structure for the type 2 frames used on LTE TDD is somewhat different. The 10 ms frame comprises two half frames, each 5 ms long. The LTE half-frames are further split into five sub frames, each 1ms long.
- The subframes may be divided into standard sub frames of special sub frames. The special sub frames consist of three fields
- DwPTS - Downlink Pilot Time Slot
- GP - Guard Period
- UpPTS - Uplink Pilot Time Slot.
LTE enabling technologies
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)
- It is used in the downlink communication of LTE as it can support high data rates
- SC-FDMA (Single Carrier FDMA)
- It is used in the uplink communication of LTE as it helps in reducing terminal power consumption
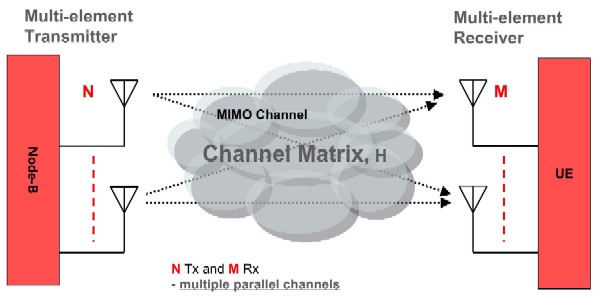
- MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output)
- Helps in obtaining increased data rates with usage of many antennas.
- System Architecture Evolution(SAE)
- New core network architecture to support the high-throughput / low latency LTE access system
- Simplified network architecture
- All IP network
- All services are via PS domain only, No CS domain
- Support mobility between multiple heterogeneous access system
- Fractional frequency reuse
- Helps in reusing the frequency so that spectral efficiency can be improved
Taxonomy
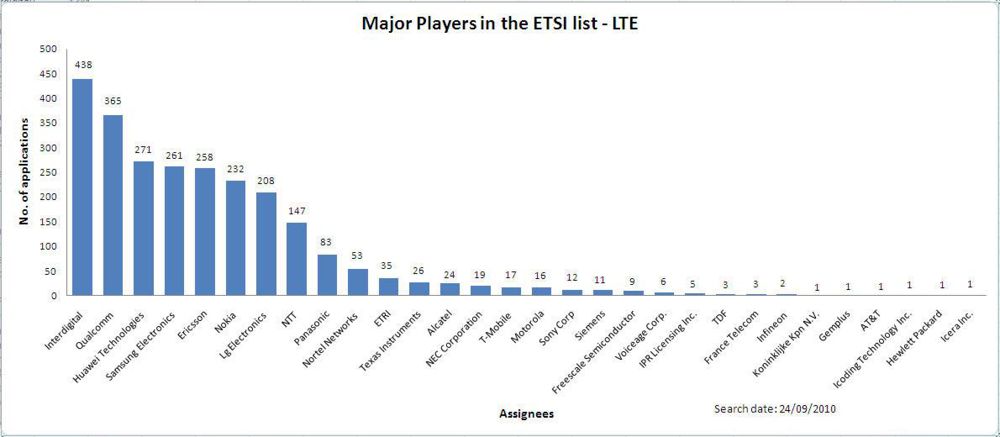
Major players in the ETSI list for LTE
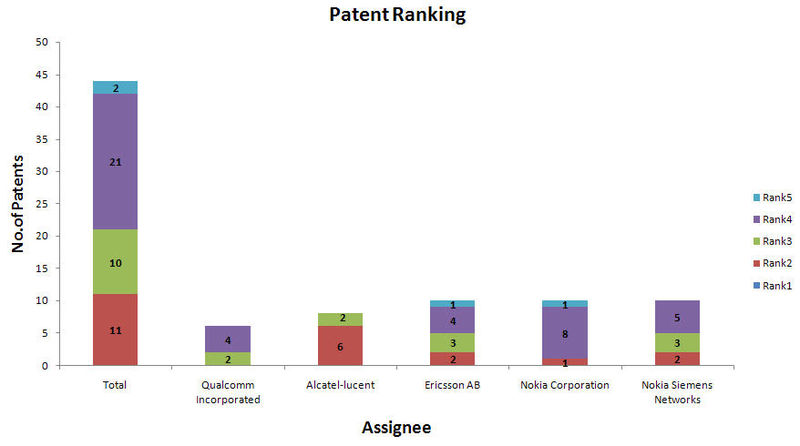
Ranking of ETSI patents
| S.No | Patent/Publication No. | International Class (primary) | Assignee | Title | Publication Year | Priority Year(s) | Legal Status | Rank |
| 1 | US20100182939A1 | H04J000300 | Nokia Corporation | Configuration of multi-periodicity semi-persistent scheduling for time division duplex operation in a packet-based wireless communication system | 2010 | 2008 | 2009 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 2 |
| 2 | EP2181559A1 | H04W003608 | Nokia Siemens Networks | handover of a user equipment with forwarding and reusing a user equipment configuration | 2010 | 2007 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 3 | EP2213034A2 | H04L000118 | Nokia Siemens Networks | Improved ack/nack dtx detection and signalling of not receiving a downlink allocation grant message | 2010 | 2007 | 2008 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 4 | EP2248373A1 | H04W002818 | Ericsson AB | Methods and arrangements for a mobile communications network | 2010 | 2008 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 5 | EP1961141A2 | H04L000100 | Ericsson AB | efficient channel quality reporting and link adaptation for multi-carrier broadband wireless communication | 2008 | 2005 | 2006 | 2006 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 6 | US20110029834A1 | H04L000118 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method for operating harq buffer | 2011 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 2 |
| 7 | US20110090866A1 | H04W003600 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method, user equipment and communication system for inter-rat handover in 3g lte | 2011 | 2008 | 2008 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 2 |
| 8 | US20110093756A1 | H04L000118 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method for dl semi-persistent scheduling harq process allocation and apparatus thereof | 2011 | 2008 | 2008 | Application Dispatched from Preexam, Not Yet Docketed | 2 |
| 9 | EP2248356A1 | H04W000400 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method, user equipment and communication system for inter-rat handover in 3g lte | 2010 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 10 | EP2242322A1 | H04W008000 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method for the harq buffer operation | 2010 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 11 | EP2291019A1 | H04W001610 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method for harq process allocation of dl semi-persistent scheduling and corresponding system | 2011 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 2 |
| 12 | US20090268683A1 | H04W007204 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Partial radio link control status report | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 3 |
| 13 | US20090086710A1 | H04J000324 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method and apparatus for implementing lte rlc header formats | 2009 | 2007 | 2008 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 3 |
| 14 | EP2068505A1 | H04L001256 | Alcatel-Lucent | Method and device for reporting the uplink scheduling request and the emergency status in the wireless networks | 2009 | 2006 | 2007 | 2007 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 15 | EP2180627A1 | H04L000108 | Alcatel-Lucent | A communication method and equipment for controlling the data transmission and retransmission of mobile station at the base station | 2010 | 2007 | 2007 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 16 | EP2198533A2 | H04B000704 | Ericsson AB | Method and arrangements for signaling control information in a communication system | 2010 | 2007 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 17 | EP2220841A1 | H04L002906 | Ericsson AB | Method and system for correlating aaa sessions | 2010 | 2007 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 18 | EP2250856A1 | H04W008400 | Nokia Siemens Networks | Server identifier acquisition based on device location | 2010 | 2008 | 2008 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 19 | EP2263411A2 | H04W007212 | Ericsson AB | Prohibiting unnecessary scheduling requests for uplink grants | 2010 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | Request for Examination Filed | 3 |
| 20 | US20100080152A1 | H04L002902 | Nokia Siemens Networks | Method and apparatus for providing signaling of redundancy versions | 2010 | 2008 | 2009 | Non Final Action Mailed | 3 |
| 21 | US20090268844A1 | H04L002700 | Nokia Siemens Networks | Method and apparatus to link modulating and coding scheme to amount of resources | 2009 | 2008 | 2008 | 2008 | 2009 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 3 |
Click here to see full list of Ranking of ETSI patents
Disclaimer: Patent ranking has been done according to the following logic:
- Rank-1: Granted + LTE related (claims)
- Rank-2: Published + LTE related (claims)
- Rank-3: LTE related (Full spec )
- Rank-4: May be relevant and requires further analysis
- Rank-5: Abandoned or Expired
Note: Here a total of 44 patents from ETSI have been taken, out of which Qualcomm Incorporated has 6 patents, Alcatel-lucent has 8 patents, Ericsson AB, Nokia corporation, Nokia Siemens Networks have 10 each
Relevant Documents for LTE in the ETSI list
| S.No | Publication Number | Title | Filing date | Expiry date | Priority Date | Assignee/Applicant | Count of Cited Refs - Patent | Rating |
| 1 | US5754976A | Algebraic codebook with signal-selected pulse amplitude/position combinations for fast coding of speech | 7/28/1995 | 7/28/2015 | 1990-02-23 | 1992-09-10 | 1995-02-06 | 1995-07-28 | Universite de Sherbrooke,Sherbrooke,CA | 44 | 2 |
| 2 | US6724976B2 | Communication system | 12/21/2000 | 12/21/2020 | 1992-03-26 | 1992-09-25 | 1993-03-25 | 1993-09-27 | 1998-04-22 | 2000-02-16 | 2000-12-21 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co. Ltd.,Osaka,JP | 110 | 3 |
| 3 | US6633600B2 | Traffic lights in a code division multiple access (CDMA) modem | 4/24/2001 | 4/24/2021 | 1995-06-30 | 1996-06-27 | 1998-02-17 | 1999-11-22 | 2001-04-24 | InterDigital Technology Corporation,Wilmington,DE,US | 85 | 3 |
| 4 | US7190966B2 | Method and apparatus for performing an access procedure | 6/29/2005 | 6/29/2025 | 1996-06-27 | 1998-01-06 | 2000-11-22 | 2002-03-01 | 2003-03-26 | 2004-06-14 | 2005-06-29 | InterDigital Technology Corporation,Wilmington,DE,US | 91 | 4 |
| 5 | US7437177B2 | Method employed by a base station for controlling initial power ramp-up using short codes | 3/14/2008 | 3/14/2028 | 1996-06-27 | 1998-01-06 | 2000-11-22 | 2002-03-01 | 2003-03-26 | 2004-06-14 | 2005-06-29 | 2008-03-14 | InterDigital Communications Corp.,Wilmington,DE,US | 190 | 4 |
Disclaimer:
- Rating is given based on claims, no.of cited patents, expiry date and priority date
- Rating is done on a scale from 1 to 5
MIMO(Multiple Input Multiple Output)
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) technologies introduced in LTE such as spatial multiplexing, transmit diversity, and beamforming are key components for providing higher peak rate at a better system efficiency, which are essential for supporting future broadband data service over wireless links.In Long Term Evolution (LTE), MIMO technologies have been widely used to improve downlink peak rate, cell coverage, as well as average cell throughput.
To achieve this diverse set of objectives, LTE adopted various MIMO technologies including transmit diversity, single user (SU)-MIMO, multiuser (MU)-MIMO, closed-loop rank-1 precoding, and dedicated beamforming. MIMO in LTE
Concept table for MIMO
| S.no | MIMO | OFDMA | SCFDMA | Interference | SDMA | HARQ | Multipath | LTE | Others |
| 1 | Multiple adj input* adj multiple adj output* | OFDM | scfdma | interference near3 mitigate* | Space adj2 time adj2 transmit adj2 diversity | HARQ | Multipath near2 effect* | LTE | channel adj2 quality adj2 indication adj2 channel* |
| 2 | Distributed adj transmission adj directional adj reception | (orthogonal adj frequency adj division) near2 multiplex* | SINGLE adj CARRIER adj FREQUENCY adj DIVISION adj MULTIPLE adj ACCESS* | interference near3 cancel* | antenna adj2 multiplex* | Hybrid adj automatic adj repeat adj request | Multipath near2 propagat* | Long term evolution | CQICH |
| 3 | DTDR | ofdma | scfdm | interference near3 reduc* | SDMA | feedback adj2 mechani* | Multipath near2 phenomenon | Evolved packet system | Downlink adj2 Channel adj2 Descriptor adj2 message* |
| 4 | transmission adj2 diversit* | (orthogonal adj frequency adj division) near2 (multiple adj access) | single adj carrier adj frequency adj division adj multiplex* | interference near3 null* | Space adj2 division adj2 multiple adj2 access | Hybrid ARQ | System architecture evolution | adaptive adj2 modulation adj2 coding | |
| 5 | SFBC | discrete adj multi adj tone | SC-FDMA | Space adj2 domain adj2 multiple adj2 access | ARQ | E-UTRA* | pre adj coding*3 | ||
| 6 | Space adj2 frequency adj2 block adj coding | DMT | DFT-spread adj OFDM | plural* near2 (spatial adj streams | automatic adj repeat adj request | Evolved UMTS terrestrial radio access | per adj2 antenna adj2 rate adj2 control | ||
| 7 | SU adj2 MIMO | (adaptive ADJ modulation*) | DFT-S-OFDMA | spatial adj2 adaptation | Automatic Repeat Query | permutation adj2 mode adj2 selection | |||
| 8 | MU adj2 MIMO | sofdm | Interleaved adj FDMA | adaptive adj2 transmi* | |||||
| 9 | space adj2 time adj2 cod* | Interleaved adj Frequency adj Division adj Multiple adj Access | Bell adj2 Labs adj2 Layer adj2 Space adj2 Time | ||||||
| 10 | multiple adj antenna* | IFDMA | spatial adj2 multiplex* | ||||||
| 11 | multi adj antenna* | Discrete adj Fourier adj Transform adj Spread adj Orthogonal adj Frequency adj Multiple adj Access | |||||||
| 12 | multiple adj transmit* adj2 receive* | DFT- SOFDM | |||||||
| 13 | plural* adj2 antenna* | ||||||||
| 14 | atleast adj2 two adj2 antenna* | ||||||||
| 15 | layer adj map*4 | ||||||||
| 16 | beam adj2 steer* | ||||||||
| 17 | smart adj antenna*1 | ||||||||
| 18 | spatial adj multiplex*3 | ||||||||
| 19 | multiple adj transmit* adj antenna*1 | ||||||||
| 20 | multiple adj receive* adj antenna*1 | ||||||||
| 21 | Adaptive adj2 antenna adj2 steer* | ||||||||
| 22 | beam adj2 forming | ||||||||
| 23 | eigenmode adj2 multiplex* |
Control patents
- Control patents are mostly used
- to prepare concepts
- to search classes, and
- to verify the search strategy
- Control patents are found by running a query with narrow keywords, and in this process litigation's and file wrappers are also looked at.
| S.No | Patent/Publication No. | Title | Abstract
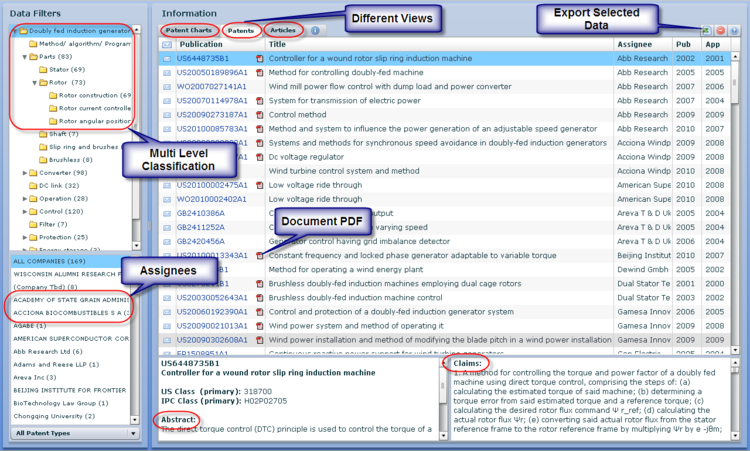
Click here to see full list of LTE control patents Search Strategy - MIMOPatent mapping by graphical analysis
Ranking of Non ETSI patents
Disclaimer: Patent ranking has been done according to the following logic:
Major players in the non-ETSI list for MIMOMajor companies for low cost IP for MIMODisclaimer 1: Here primarily, companies with an average annual revenue less than 400 million USD are considered. In addition to these, some big companies whose primary interest is not LTE and those which provide IP licensing are also considered. Disclaimer 2 :The above graph is based on raw data available with us. Some of the patents may not be relevant Most cited documents in non-ETSI list for MIMO
Company wise distribution of IPNote:
Filing trends over the yearsFiling trends for top 10 companiesYear by year trends of top 5 companies
Interactive Taxonomy
Note:This interactive taxonomy consists of 131 sample documents. Dolcera DashboardDashboard LinkThe Dashboard is Dolcera's visualization platform to present the organized patent landscape
LTE Release 8Meeting minutesClick here for the meeting minutes. Like this report? This is only a sample report with brief analysis
References
Contact Dolcera
|