Diamond Tipped Indenting Tool
From DolceraWiki
Revision as of 02:56, 29 October 2009 by Anand.shukla (Talk | contribs) (→Graphical Representation - Tool tip)
Contents
[hide]Agenda
- To introduce and explain the benefits of the patented technology developed by Pratt & Whitney.
- To find out interest of the prospects in acquiring the technology on a licensed basis from Pratt & Whitney.
About Dolcera
- Dolcera is an international services firm specializing in intellectual property and market research services. Our clientele includes several fortune 500 companies and global 100 companies. For more information please visit: www.dolcera.com
- We at Dolcera are partnering with Pratt & whitney to out-license their green technology to replace Ni-Cd coatings used for finishing purposes.
About Pratt & Whitney
- Pratt & Whitney is one of the largest aircraft engine manufacturers in the world with a sales revenue of more than $12 Bn and spends more than $250 Mn in research & development.
- Cutting edge R&D with over a 1000 patents.
- Has always been at the forefront of technologies for turbine, rocket, reciprocating engines, power systems, etc.
Utility
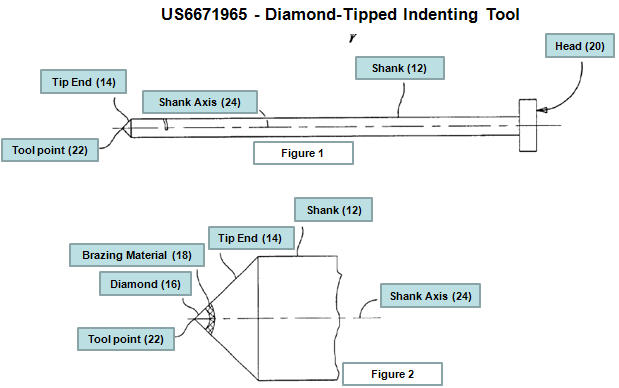
- A Tool using this technology has a diamond at a specified precise orientation affixed to the tip of the shank of the machine Enabling markings on various metal surfaces for
- Identification purposes
- Surface treatment
- Surface condition
- The point of the tool strikes the surface of metal and on impact creates a cold-formed indentation or mark.
Schematic Representation - Indenting Tool
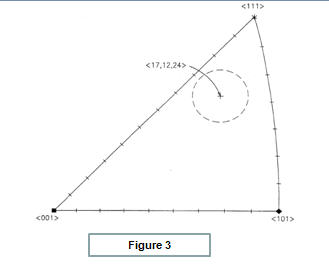
Graphical Representation - Tool tip
- Stereographic projection triangle for the diamond crystal
Represents a 3D orientation spread out on a 2D plane. Figure depicts the orientation of the diamond tip. It Shows the axis of orientation of the diamond crystal w.r.t three standard orientations of the crystal marked by the 3 vertices.The pole of the crystal should lie within the dotted circle to achieve the super wear resistance orientation
Importance of the orientation
- Diamond crystals are anisotropic
- Their mechanical and physical properties vary with their crystallographic orientation
- The orientation of the crystal governs its strength and wear resistance
- This particular super wear-resistant orientation has been discovered and patented by Pratt and Whitney.
Limitations of other technologies
- Carbide and non-oriented diamond indenters have problems such as
- Wear and tear of tool head
- Replacement costs
Advantages of this tool
- Economical
- Low replacement costs because of increased tool life (up too 100 times that of carbide tools)
- Reduced cost per mark
- Quality
- Better reading of 2D markings
- Improved marking reliability and quality
- Physical
- Improved wear resistance
- Less force required to obtain indention depth
Applications
- Aero & Industrial Gas Turbines
- Railway
- Machineries
- Weapon markings
- Punches and Dies
- Cables and Wires
- Weapon markings
- Any metal equipment