Botox - from Medical Procedure to Household Word
Contents
- 1 Objective
- 2 Problem Statement
- 3 Methodology
- 4 Study Goals for Botox
- 5 Study Method to determine 'Expert buzz' required for consumer adoption
- 6 Study Method to determine 'Consumer buzz' for Botox as a market driver
- 7 Data collection and data sources
- 8 Technical overview
- 9 Market overview
- 10 Botox Vs Collagen
- 11 Consumer buzz
- 12 Expert buzz
- 13 Media vehicles used
Objective
- Determining the factors driving the adoption of invasive medical procedures for consumer application
Problem Statement
- To derive the time to market for invasive procedures for consumer applications like
- Nanotechnology for skincare or hair care
- Stem-cell therapy
Methodology
- We decided to follow the 'analogy' method for determining the time it takes for consumer adoption of invasive medical procedures.
- For the purpose of this study, we decided to study the consumer adoption of Botox and apply the learning from Botox story to determine the timescale for consumer adoption of other new invasive procedures.
- Botox was considered appropriate since it is an invasive procedure for skin treatment.
- Botox is similar in that it's adoption is driven by 'expert opinion' which will also be the case for Invasive Nanotechnology therapy and Stem-cell therapy.
Study Goals for Botox
- To determine/measure the 'expert buzz' and 'consumer buzz' required for 'wide scale' adoption of an invasive procedure among experts.
- To determine the market drivers that create the 'expert buzz'
Study Method to determine 'Expert buzz' required for consumer adoption
- Study the number of expert articles published discovering and eulogizing Botox miracle
- Determine the number of experts and the voice required to reach out to them
Study Method to determine 'Consumer buzz' for Botox as a market driver
- Study the number of articles published in consumer media space eulogizing/talking about Botox
- Study the media vehicles in which these articles are published
- Determine from the articles published, the number of media vehicles required and the number of 'voices' (Journalists) required to create a 'consumer buzz'
- Analogy to the internet world will be the number of powerful 'voices' required at the minimum to create a strong 'online buzz' (with a multiplier for the number of powerful voices thrown in to account for media fragmentation)
Data collection and data sources
- We used secondary research for data collection
- Botox procedure data has been taken from ASAPS (American Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons)
- Databases used to search articles are Factiva and Google scholar
- Search query used is:
- botox, botulinum toxin: to find the total number of articles published on botox
- botox and wrinkles, botox and frown, botox and lines: to find skin care articles using botox
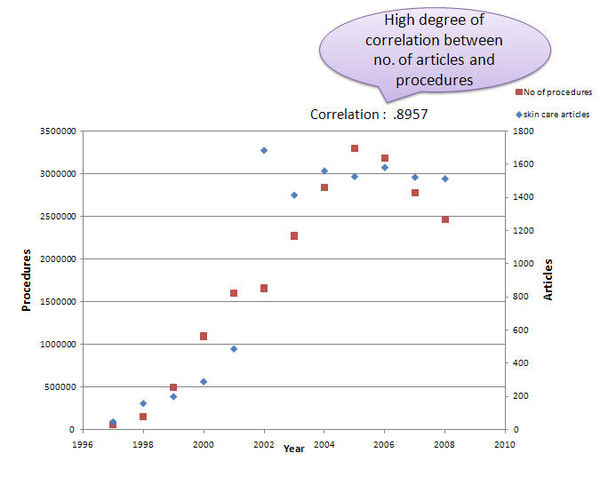
- Determined the correlation between the number of articles published and number of botox procedures
- Analyzed the articles published to determine the market drivers
Technical overview
Botox injection is a diluted form of botulinum toxin type A which is injected into facial muscles to paralyze or weaken the muscles that form wrinkles. Botulinum toxin is a medication and a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is the most toxic protein known with an LD50 of roughly 0.005-0.05 µg/kg.
It is sold commercially under the brand names:
- BTXA, Dysport, Myobloc, Neurobloc and Xeomin which are used in the treatment of muscle spasms.
- Botox Cosmetic and Vistabel are available for cosmetic treatment.
How botox procedure is performed
- Botox procedure usually takes 5-15 minutes and there is no need for any anesthesia.
- The procedure is not entirely painless and the small needle does sting. Some physicians may numb the area with a topical anesthetic prior to the injection.
- Before the injections, all the sites are premarked and cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- The Botox is then injected.
- It generally takes three to seven days to take full effect and it is best to avoid alcohol at least one week prior to treatment.
- Aspirin and anti-inflammatory medications should be stopped two weeks before treatment as well in order to reduce bruising.
- Once the procedure is performed results last anywhere from 4 to 6 months.
Botox Is commonly used to treat
- Forehead lines
- Crow's feet (lines around the eye)
- Frown lines
Side effects of botox
Botox is not without side effects. However, the side effects are minor and resolve rapidly. The most common side effects include:
- Mild nausea
- Flu like symptoms
- Headache
- Redness
- Pain at injection site
No severe side effects have been reported, but the dermatologist or medical practitioner administering botox injection should be experienced.
Market overview
Initially botox was marketed for its medical applications in treating various muscle-related conditions but later its marketing was broadened to include its cosmetic application—smoothing out frown lines between the eyebrows.
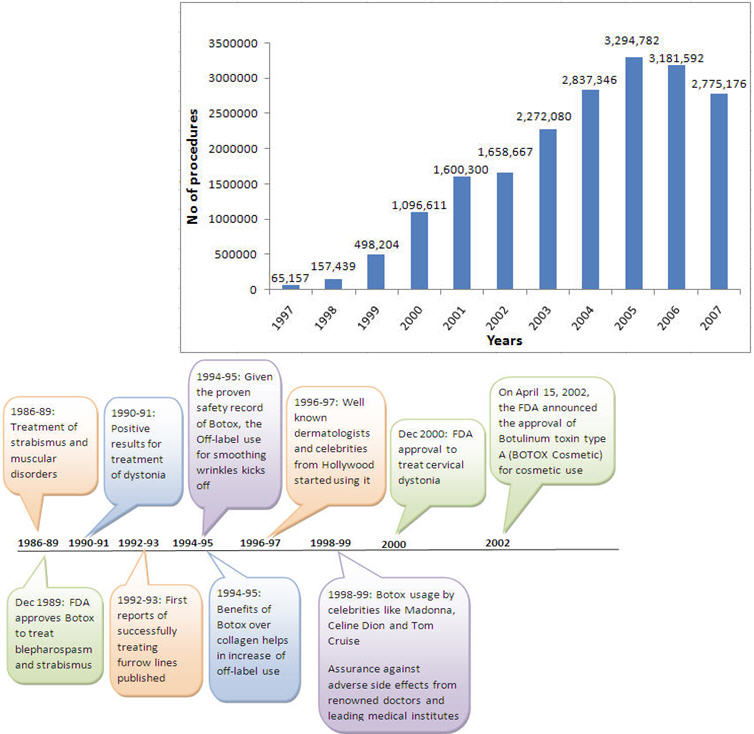
Y-o-Y sale of botox procedures
Conclusions:-
- Safety of botox was proven through invasive muscular and neurological procedures very well till 1992.
- In 1992, a serendipitous discovery showed Botox effect on 'smoothing wrinkles'
- Consumer adoption happened through off label use (6 years before FDA approval for cosmetic use) due to 'Expert Buzz'
- Leading drivers for 'Expert Buzz' were 'safety of Botox' and 'serendipitous discovery' for wrinkle smoothening
- Suddenly experts got a substitute for collagen procedures that took more a few months to show perceptible results (as shown below)
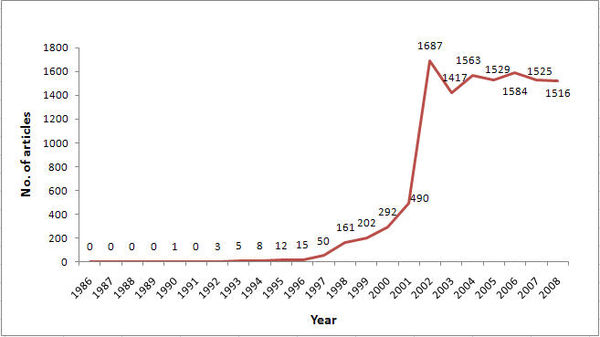
Publication of botox articles for skin care
Correlation among the no. of articles and procedures
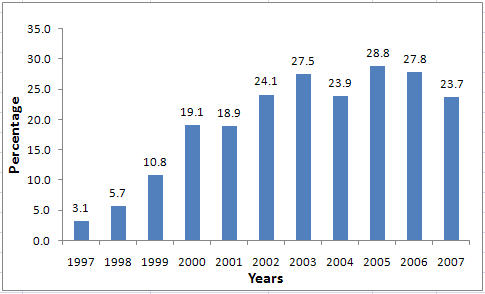
Botox procedures as a percentage of total cosmetic procedures
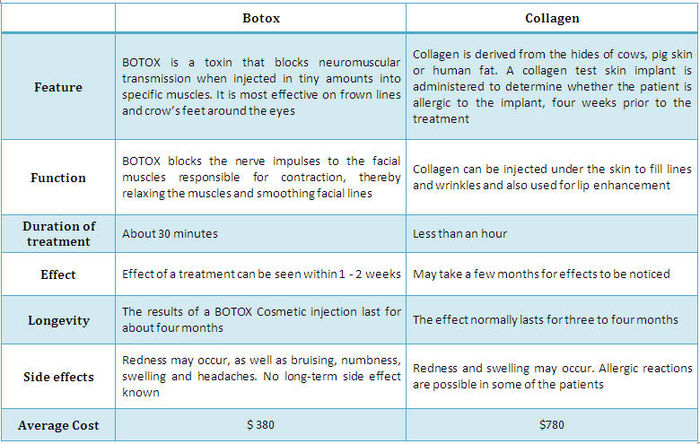
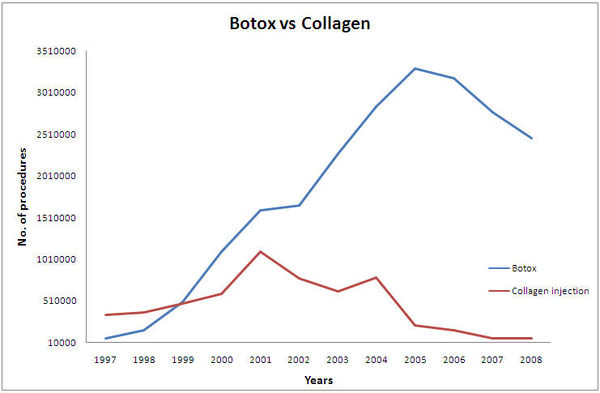
Botox Vs Collagen
Botox and collagen are both invasive procedures used for smoothing of wrinkles and facial lines. With the increase in off-label use and popularity of botox the market share of collagen has decreased.
Comparison of Botox and Collagen
Procedures of Botox Vs Collagen
Consumer buzz
Dcotors, Dermatologists, Surgeons, experts and consumers shared their experiences and gave positive reviews about the use of botox leading to initial buzz.
- Expert Buzz started from 1992 onwards with publication of articles for use of Botox for wrinkle smoothing in leading journals (By Caruthers)
- Consumer Buzz started from 1992 with just 2 articles. But the big jump in Consumer buzz as measured by number of articles published in leading media is 35 in 1997.
- However, by 1997 more than 65,000 Botox procedures had been done. This indicates that the Expert Buzz played a big role in Botox adoption than the Consumer Buzz.
Total no. of articles published in consumer media space till 1997 are: 58
Various distinct experts that gave reviews are:
- Ophthalmologist Jean Carruthers
- Dermatologist Alastair Carruthers
- Dr. Brin
- Dr. William J. Binder
- Dr. Arnold Klein, Hollywood's king of collagen
- Dr. Gerald Imber
- Dr. Alster
- Dr. Davis
- Dr. Kauvar
- Dr. Ian Little
- Dr. Vito Quatela, N.Y.
- Dr. George Brennan, California
- Cosmetic surgeons at the University of Michigan Medical Center
- Dr. Todd Koch, amherst plastic surgeon
- Surgeon Basim Matti
- Dermatologist Rhoda Narins
- Dermatologist Fredric Brandt
- Dermatologist Arsenal
Expert buzz
Medical journals and circulars brought awareness of botox procedures among the dermatologists and surgeons.
Total no. of articles published in medical journals are: 36
Various journals and circulars are:
- American Academy of Neurology
- Journal of Neuroly, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry with practical Neurology
- International Ophthalmology Clinics
- Science and Medicine
- Southern Medical Journal
- Clinical Neuropharmacology
- The Annals of otology, rhinology & laryngology
- Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
- Journal of the American Medical Association
- Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Journal of Dermatological Surgery and Oncology
- Aesthetic Plastic Surgery
- Dermatologic Surgery
- Survey of Ophthalmology
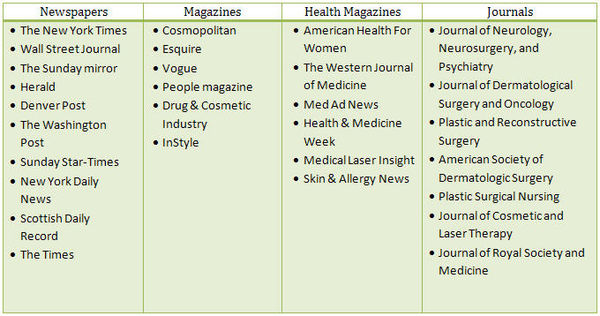
Media vehicles used
Different categories of media created awareness about botox procedures. Total number of unique media publications are 330.
Major media vehicles used are: