Introduction
- Toxicology is the science that investigates the adverse effects of chemicals on health.
- It describes the relationship of the body’s response to different amounts of an agent such as a drug or toxin
- Routes of Entry : Ingestion,Inhalation,Dermal absorption,Ocular, etc.,
- Bio-monitoring is done for some toxic exposures such as blood lead levels or metabolites of chemicals (biomarkers).
- Threshold levels refers to the amount of a substance necessary to cause a response in the body.
- Toxicity can be generally broken down into two categories:
- Acute toxicity refers to the rapid development of symptoms/effects after the intake of relatively high doses of the toxicant.Acute toxicity refers to immediate harmful effects generated by sufficiently large doses.
- Chronic toxicity refers to the harmful effects of long-term exposure to relatively low doses of toxicant. This would include traces of pesticides in foods, air pollution, etc.A single compound may generate both acute and chronic toxic effects depending on the dose and duration of exposure.
- Drugs are taken voluntarily and often under the supervision of a licensed health care provider.Hazardous chemical exposures are most often involuntary.
- Host factors may impact the therapeutic or toxic effect of a drug or chemical.Age,Genetics,Weight,Drugs that a person may be taking,Pregnancy status and others
- The scientific pursuit of toxicology is typically divided between Observational studies looking at what effects result from exposure to a particular substance and Mechanistic studies which attempt to understand and explain the basis for such effects.These two activities form the basis of toxicology
Branches of Toxicology
- Clinical toxicologyInvolves the application of toxicological principles within a diagnostic setting, usually to determine whether a presenting adverse effect or disease or injury is due to some type of chemical exposure. This area of toxicology is typically practiced by a physician, nurse or other clinician, often times in consultation with the experimental toxicologist, who is in a position to better explain certain published experimental findings and whether they would be applicable to the case at hand.
- Regulatory toxicology- Relies on risk assessment and experimental data to determine the risk and benefits, or the costs and benefits of exposure to certain chemicals, to determine whether such chemical will be allowed in the public sphere and to what extent its use and exposure will be regulated. This field of toxicology probably has the greatest effect on our daily lives of all the different fields of toxicology. Deciphers and analyzes toxicological data for risk estimation, Solvent vapor thresholds in industry and Safe level for human drugs
- Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology- Determining mode of action of chemicals at the molecular level , Effect of chemicals on DNA,Cancer genes
- Product Development Toxicology - Service and pre-clinical toxicology for product development, Evaluation of full toxic potential of chemicals destined for drug use and Establishing safe dose for people
- Risk assessment - Determining probabilistically, outside the laboratory, the likelihood of an adverse effect based on a particular exposure scenario. This is not experimental activity, involves much more uncertainty about its findings and is as much art as science. It is conducted quantitatively, relying on mathematics and computer modeling, or qualitatively, relying more on experience and similar scenarios that have been previously looked at. Source
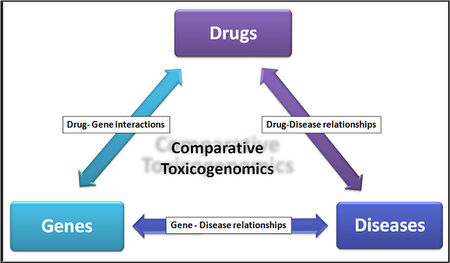
Comparative Toxicogenomics
- It describes the relationships between Drugs,genes and human diseases.
- To study the effects of environmental chemicals on human health.
- The etiology of many chronic diseases involves interactions between environmental factors and genes that modulate important physiological processes. Chemicals are an important component of the environment. Conditions such as asthma, cancer, diabetes, hypertension, immunodeficiency, and Parkinson's disease are known to be influenced by the environment; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying these correlations are not well understood. Comparative Toxicogenomics database may help resolve these mechanisms.Source
Databases
- National Gene Vector Laboratories (NGVL)toxicology Reports
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Chemical effects in biological systems
- Toxnet
- The Carcinogenic Potency Database
- National Toxicology program database
- DssTox public database network
- European chemical substances information system
- European centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of chemicals
- Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry
- Comparative Toxicogenomics database
Sample Example
| Summary of Primary Pharmacokinetic, Toxicokineticand Toxicology Studies | ||||||
| Species (Strain) | Study Type | Route | Dose (mg/kg) | No. of Animals per Sex | GLP? | |
| M | F | |||||
| Rat (Sprague Dawley) | Single Dose Pharmacokinetic | i.v. | 10 | 9 | - | No |
| oral | 1 | 9 | - | |||
| 5 | 9 | - | ||||
| 10 | 9 | - | ||||
| Single Dose Acute Toxicity | Oral | 0 | 5 | 5 | Yes | |
| 50 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| 100 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| 300 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| 14-Day Toxicity/Toxicokinetic | Oral | 0 | 15 + 9 TK | 15 + 9 TK | Yes | |
| 10 | 10 + 9 TK | 10 + 9 TK | ||||
| 50 | 10 + 9 TK | 10 + 9 TK | ||||
| 100 | 15 + 9 TK | 15 + 9 TK | ||||
| Single-Dose Pharmacokinetic and ToxicokineticParameters | ||||||||||
| Species (Strain) | Study | Route | Dose (mg/kg) | No. of Animals | AUC0-∞(ng∙hr/mL) | t1/2(hr) | Cmax(ng/mL) | Tmax(hr) | F (%) | |
| M | F | |||||||||
| Rat (Sprague Dawley) | Single Dose PK | i.v. | 10 | 9 | - | 10735 | 2.34 | 14500 | 0.083 | - |
| Oral | 1 | 9 | - | 494 | 1.09 | 262 | 0.5 | 46.0 | ||
| 5 | 9 | - | 1638 | 1.23 | 590 | 0.5 | 30.5 | |||
| 10 | 9 | - | 2435 | 1.12 | 739 | 0.5 | 22.7 | |||
| 14-Day Toxicity/TK | Oral | 10 | 9 | - | 2413 | 1.51 | 612 | 1.00 | - | |
| - | 9 | 1843 | 3.74 | 682 | 0.50 | - | ||||
| 50 | 9 | - | 7671a | ND | 1517 | 2.00 | - | |||
| - | 9 | 7055 | 3.08 | 1131 | 2.00 | - | ||||
| 100 | 9 | - | 11749 | 3.30 | 1763 | 1.00 | - | |||
| - | 9 | 9129a | ND | 1175 | 4.00 | - | ||||
| Selected Hematology Data from Rat Single-Dose -Escalating Toxicology Studies | |||||||||||||
| Species (Strain) | Sex | Dose (mg/kg)a | Red Blood Cell Count(1x106/μL) | Hemoglobin (g/dL) | Hematocrit(%) | Mean Corpuscular Volume (femtoliter) | Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (pg) | Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Conc. (g/dL) | Reticulocytes(1x103/μL) | Platelets (1x103/μL) | White Blood Cell Count (1x103/μL) | Neutrophils (1x103/μL) | Lymphocytes(1x103/μL) |
| Rat (Sprague Dawley)b | M | 0 | 6.94±0.221 | 14.3 ±0.48 | 44.5 ±1.89 | 64.1 ±1.52 | 20.6 ±0.36 | 32.2 ±0.33 | 544.5 ±30.82 | 1448 ±288.8 | 7.15 ±0.885 | 0.71±0.214 | 6.19 ±0.984 |
| 300 | 7.27 ±0.537 | 14.7 ±0.70 | 48.0 ±3.02 | 63.4 ±2.37 | 20.2 ±0.81 | 31.9 ±0.80 | 503.3 ±67.80 | 1228 ±201.6 | 6.42 ±1.189 | 0.79 ±0.338 | 5.32 ±1.153 | ||
| F | 0 | 7.29 ±0.150 | 14.8 ±0.23 | 44.7 ±0.58 | 61.2 ±0.58 | 20.3 ±0.25 | 33.2 ±0.24 | 353.2 ±10.97 | 1328 ±104.2 | 6.24 ±1.442 | 0.75 ±0.233 | 5.15 ±1.443 | |
| 300 | 7.55 ±0.185 | 15.2 ±0.28 | 45.6 ±1.11 | 60.4 ±4.41 | 20.1 ±0.52 | 33.3 ±0.38 | 333.0 ±52.44 | 1245 ±166.6 | 7.66 ±1.944 | 0.63 ±0.374 | 6.70 ±1.693 | ||
| Safety Pharmacology Studies | |||||||
| Species (Strain) | Study Type | Route | Dose (mg/kg) | No. of Animals | GLP? | Results | |
| M | F | ||||||
| Rat (Sprague Dawley) | Central Nervous System | Oral | 0 | 6 | 6 | Yes | Cyclopropavirhad no effect on clinical signs, body weight or Irwintest results |
| 10 | 6 | 6 | |||||
| 50 | 6 | 6 | |||||
| 100 | 6 | 6 | |||||
| Selected Clinical Chemistry Data from Rat Single-Dose Escalating Toxicology Studies | ||||||||||||
| Species (Strain) | Sex | Dose (mg/kg) | Urea Nitrogen (mg/dL) | Creatinine(mg/dL) | Total Protein (g/dL) | Albumin (g/dL) | Globulin (g/dL) | Albumin Globulin Ratio | Calcium (mg/dL) | Phosphorus (mg/dL) | Sodium (mmol/L) | Potassium(mmol/L) |
| Rat (Sprague Dawley)a,b | M | 0 | 14 ±1.1 | 0.5±0.00 | 5.7 ±0.24 | 4.0 ±0.12 | 1.7 ±0.05 | 2.4 ±0.09 | 10.8 ±0.11 | 11.0 ±0.51 | 147 ±1.3 | 5.8 ±0.31 |
| 300 | 13 ±1.3 | 0.5 ±0.00 | 5.8 ±0.43 | 4.1 ±0.12 | 1.7 ±0.11 | 2.4 ±0.13 | 10.9 ±0.28 | 10.6 ±0.27 | 148 ±1.6 | 5.8 ±0.37 | ||
| F | 0 | 15 ±1.3 | 0.6 ±0.05 | 6.0 ±0.18 | 4.4 ±0.05 | 1.7 ±0.18 | 2.7 ±0.31 | 11.1 ±0.30 | 9.5 ±0.40 | 147 ±1.0 | 5.4 ±0.4 | |
| 300 | 15 ±2.3 | 0.5 ±0.04 | 6.1 ±0.18 | 4.6 ±0.08 | 1.6 ±0.17 | 3.0 ±0.35 | 11.3 ±0.11 | 9.7 ±0.72 | 147 ±2.3 | 5.5 ±0.5 | ||