Overview
- Cloud computing is a style of computing in which dynamically scalable and often virtualized resources are provided as a service over the Internet.
- Users need not have knowledge of, expertise in, or control over the technology infrastructure in the "cloud" that supports them.
- Cloud computing services often provide common business applications online that are accessed from a web browser, while the software and data are stored on the servers.
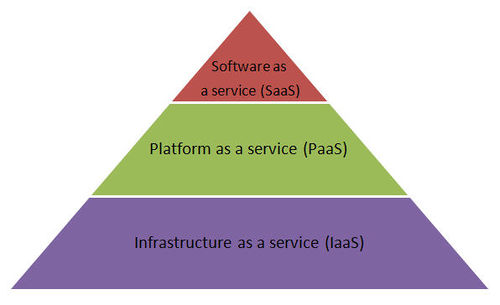
The concept generally incorporates combinations of the following:
Market overview
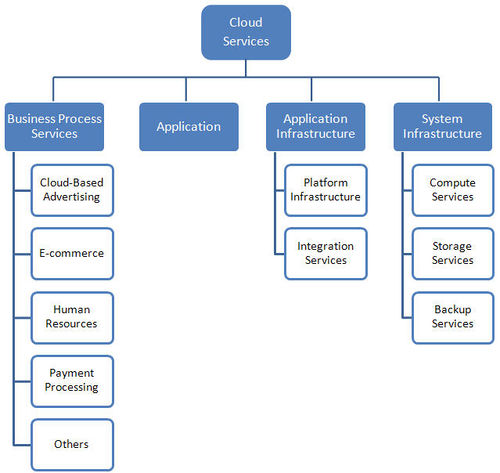
Cloud services provided worldwide are:
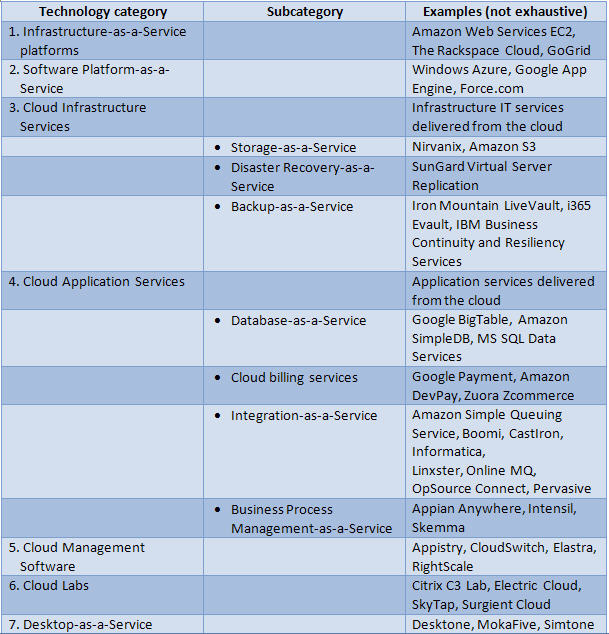
Companies providing cloud computing technology
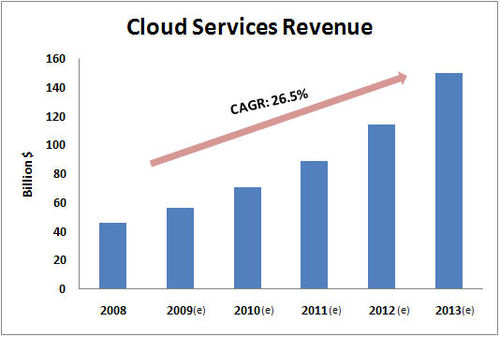
Y-on-Y revenue from cloud services
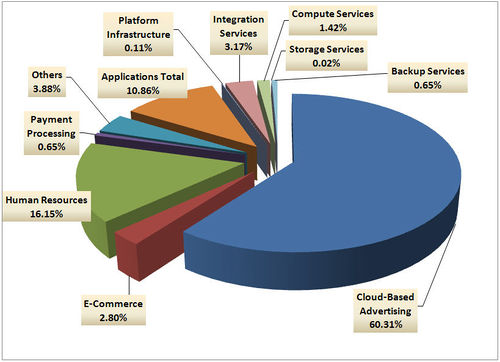
Cloud services - revenue breakup
Pros and cons of cloud computing
Technical overview
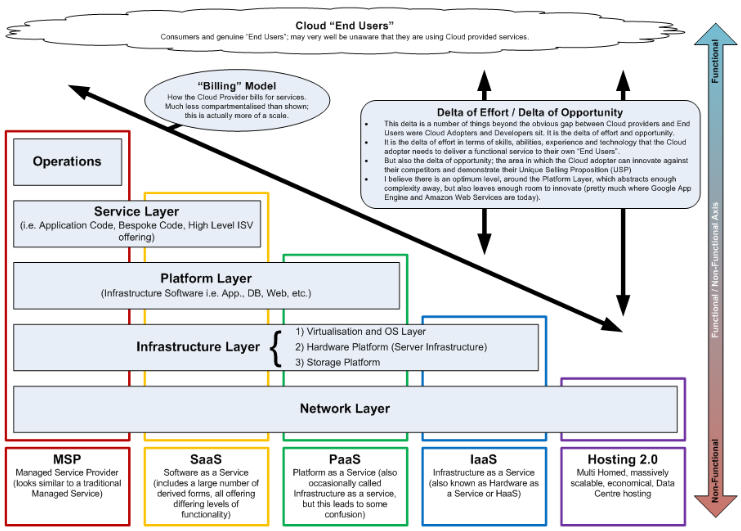
Cloud computing architecture
Three major participants in cloud:
- Cloud Providers; building out clouds, for instance Google, Amazon, etc. effectively technology providers.
- Cloud Adopters / Developers; those developing services over the Cloud and some becoming the first generation of Cloud ISVs.
- Cloud "End" Users; those using Cloud provisioned services, often without knowing that they are cloud provisioned, e.g. Facebook users have no idea that their favorite FB app is running on AWS.
Various architectural layers:
- Operations: it supports functional business processes rather than supporting the technology itself.
- Service layer: it is made up of application code, bespoke code, high-level ISV offerings.
- Platform layer: it is made up of standard platform software i.e. app. servers, DB servers, web servers, etc., and an example implementation would be a LAMP stack.
- Infrastructure layer: it is made up of
- (i) infrastructure software (i.e.virtualisation and OS software)
- (ii) the hardware platform and server infrastructure
- (iii) the storage platform
- Network layer: it is made up of routers, firewalls, gateways, and other network technology.
Delta of Effort / Delta of Opportunity
The gap between the cloud providers and the end cloud users is known as the delta of effort and also the delta of opportunity.
It is the delta of effort in terms of skills, abilities, experience and technology that the cloud adopter needs to deliver a functional service to their own “End Users”. This will be potentially a major area of cost to the cloud adopters. But it's also the delta of opportunity in terms of 'room' to innovate.
Cloud Adoption Strategy
Some of the steps which need to be followed in order to identify the relevant business scenario relevant for leveraging cloud are:
1. Access:
- a. Application portfolio to identify core and non-core applications
- b. Map the scenarios relevant for cloud adoption
- c. Identify business processes which are more suitable for cloud adoption
- d. Evaluate the cloud vendors for strategic and tactical use scenarios
2. Validate:
- a. Justify the cost benefits and business case
- b. Perform pilots and proof of concepts to identify functional gaps and assess user experience
3. Technology:
- a. Changes to be done on the organizations policies and procedures
- b. Governance and operations
- c. Standardization across various cloud projects
4. Execute:
- a. Migration and Integration
- b. Co-existence and switchover planning
Cloud computing applications in different industry segments
Hospitality
Cloud computing is used in hospitality industry to provide
- Disaster recover infrastructure for mission critical applications
- For online reservation system
- Purchase of a dedicated pool of computing resources and allocating them as needed
- Facilitating in responding to real-time situations
- e.g. Preferred Hotel Group is using Terremark's Enterprise cloud services
Web applications
Cloud computing is used in various web applications such as Microsoft's Hotmail, Google's Gmail and YouTube, and Yahoo's Flickr photo-sharing service etc
- Consumers run only their browsers on local computers
- The rest of the software along with users' email messages, photos or videos are on remote machines the user can't see and doesn't have to know anything about it
- e.g. Microsoft's Hotmail is using Azure (cloud computing platform from Microsoft) and Google's Gmail is using Google Apps
- Google Docs - online versions of word processor and spreadsheet applications is also using cloud computing
Consumer electronics
Cloud computing is being used in consumer electronics at various levels:
- In Laptop computers for Wireless communication and access to the Internet
- Laptops require minimum hardware to reduce cost and a internet connection
- Gaming industry, that will allow iPhones and other thin-client devices to have really high-end graphics without having a big, expensive hot video card in them that draws battery life
- e.g Netbook, a general purpose laptop, works on cloud computing and is available at a price of US$400 and some even in US$50-100 range.
Retail
- Cloud services allow retailers to plan for demand peaks in online services dynamically without worrying about provisioning for high availability
- Pay-as-you-model helps them save cost rather than paying for expensive hardware to meet these peaks while they are under used for the rest of the year
- Increases productivity and help companies serve their customers better.
- e.g. Amazon is using cloud computing for its online retail services
Telecommunication
- Enterprises use various operating systems to create virtual private data centers for business lines or applications
- A virtual private data center is functionally equivalent to a co-location facility
- It allow users to define custom application infrastructures using just a browser
- Operating system then creates and maintains the infrastructure for the user on the grid
- It simplify data center design and operations and helping enterprises meet requirements such as high availability and disaster recovery
- e.g. British Telecom is using AppLogic, product of 3Tera, for utility computing services