Rationale
- “Medication for men plagued by hair loss has become a topic of interest in Japan since a drug company began marketing it at the end of last year." March 5th, 2006 – [1]
- “An increasing number of companies are apparently turning the Chinese fear of a bald spot into big bucks with some doing so well they are branching out into other countries.” February 16, 2006 – [2]
Introduction
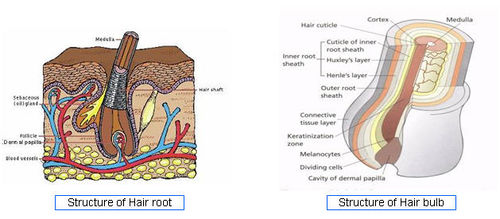
Hair Basics
- Hair is a complex and delicate part of the body
- Keeping it healthy and beautiful is a challenge
Reasons for Hair loss
Both men and women lose hair for similar reasons. Hair loss in men is often more dramatic, and follows a specific pattern of loss which has been termed “Male Pattern Baldness” (Androgenetic Alopecia).
Main reasons
- Hormonal effect of androgen
- Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle
- Deactivation of hair matrix cells
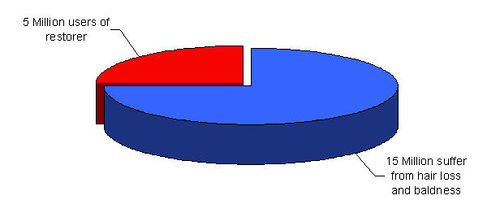
Some facts from Japan
- Market size: ¥ 30 Billion
- Number of products: more than 100
(JICST-EPlus - Japanese Science & Technology)
Goals
- Summarize IP activity over the years
- Identify major players
- Conduct patent analysis
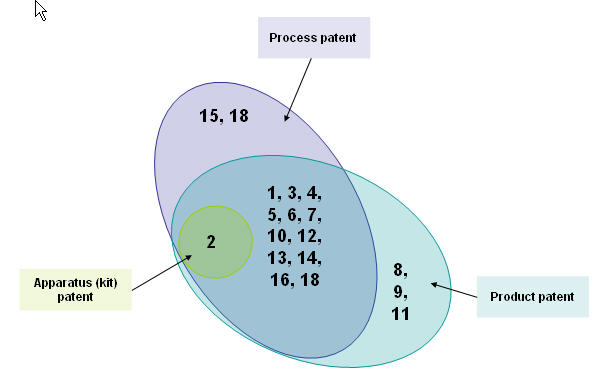
a) Composition b) Nature c) Action
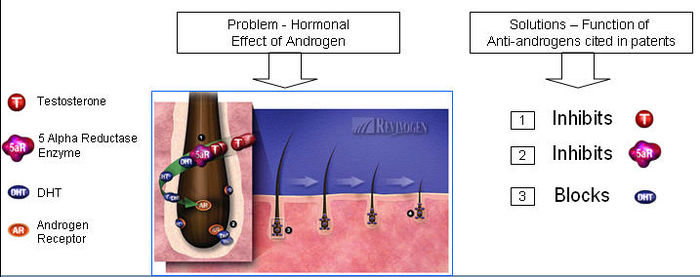
Alopecia occurs, due to
- Hormonal effect of androgens
- Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle
- Deactivation of hair matrix cells
And then
- Analyze patents pertaining to high sebum activity
Approach
Broad search conducted on hair loss patents.
Patent information sourced through SIP.
Patents selected randomly for analysis.
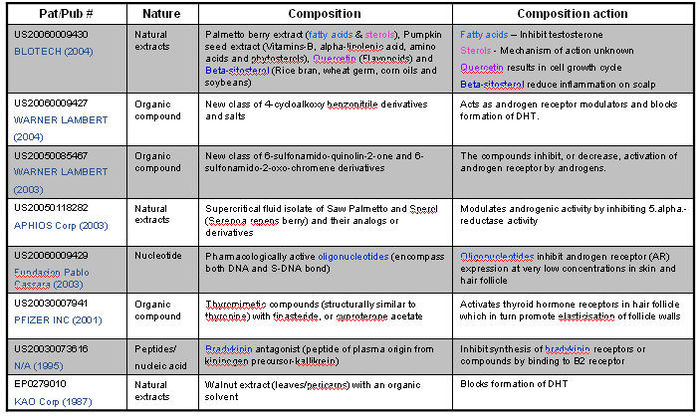
Composition of treatment for causes identified and categorized as follows:
- Anti-androgen
- Minoxidil
- Double action (Anti-androgen + Mindoxidil)
- Hair matrix cells activator
- Sebum production inhibitor
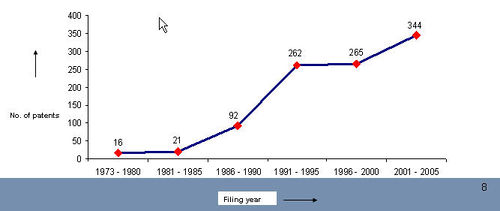
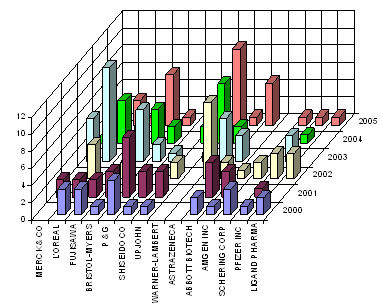
IP activity over years
The graph indicates:
- Number of patents filed every 5 years (except for first 7 years).
- First solution proposed in 1973.
- Filing trend indicates steep rise in activity recently.
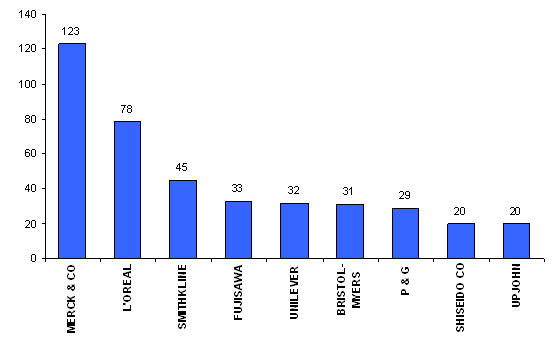
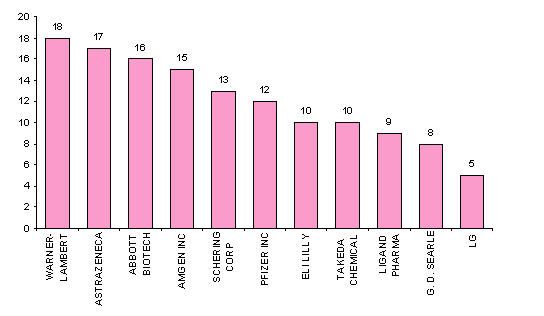
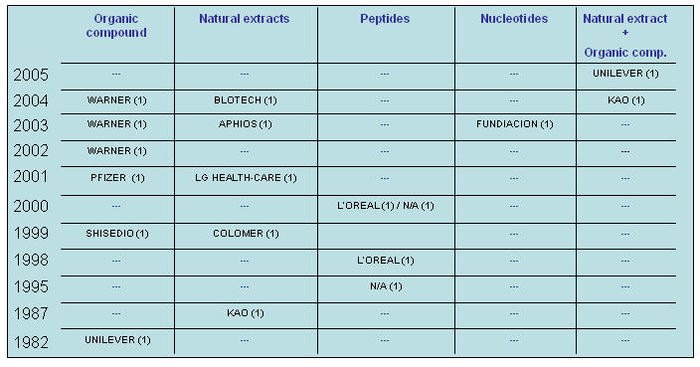
Major Players
- Assignees with more than 20 patents to their credit
- Assignees with less than 20 patents to their credit
- Active Assignees
Assignees currently active with more than 5 patents to their credit during 2000-2005, among them following are the leaders of 2005-
WARNER with 9 patents,
BRISTOL with 6 and
ABBOTT with 5.
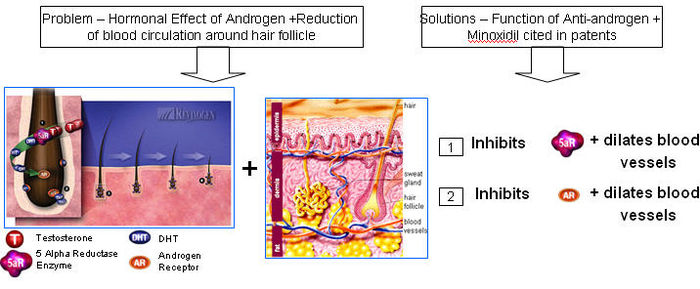
Anti-androgens
- Anti-androgen is a substance that inhibits biological effects of androgenic hormones
- 5-alpha reductase + Testosterone = Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
- DHT attaches to an Androgen Receptor.
- DHT causes increase in hair loss and gradual miniaturization of the follicle, which eventually dies resulting hair loss
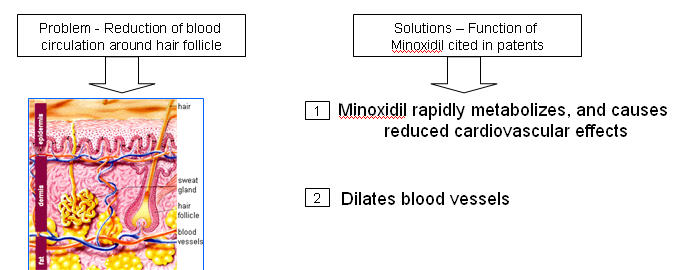
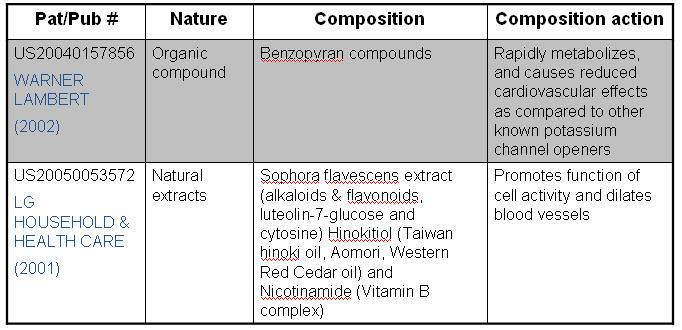
Minoxidil
- A thick network of tiny veins and arteries lines the outer wall of the follicle. Blood pumps through the bulb and hair via this network
- Minoxidil dilates blood vessels; which is also called as “potassium channel opener”
- Minoxidil sulfate (MS) appears to be the active metabolite responsible for hair growth stimulation.
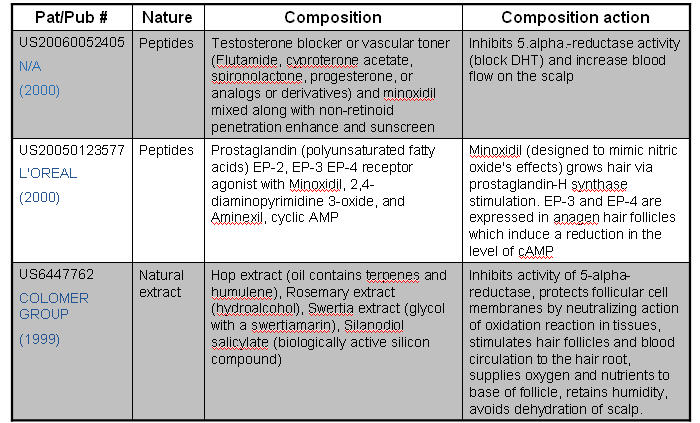
Double action (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil)
- Combination of Minoxidil + Anti-androgen (double action) composition for effective treatment of Male-Pattern Baldness
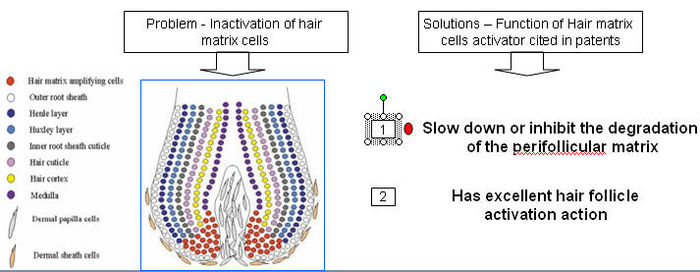
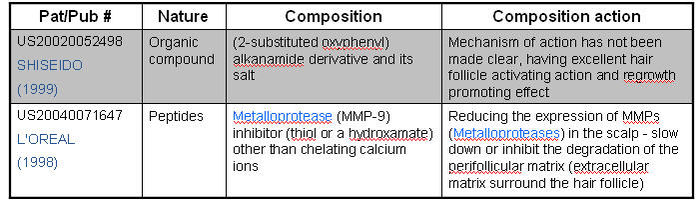
Hair matrix cell activator
- Stem cells of the hair follicle are gathered in the basal layer of the outer root sheath bulge.
- It is from these cells that matrix cells are formed.
- Growth and differentiation of the matrix cells are under the influence of substances produced by cells of the dermal papilla.
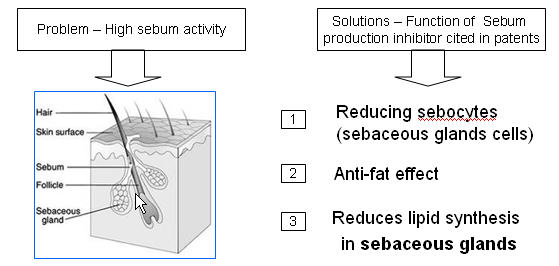
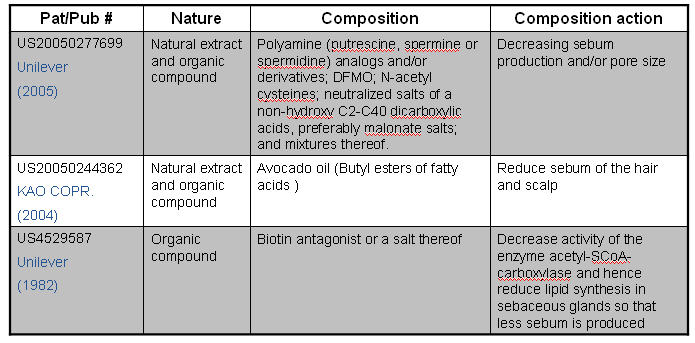
Sebum Production Inhibitor
- Sebum, a complex mixture of lipid substances, is secreted from sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles.
- The inhibitor blocks the excessive sebum production produces greasy effect on hair and scalp and also responsible for thinning and loosing of hair.
Composition nature matrix
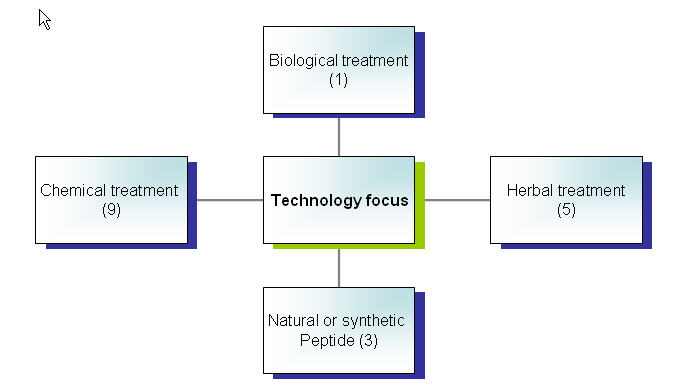
Focus on different aspects
Distribution on different aspects
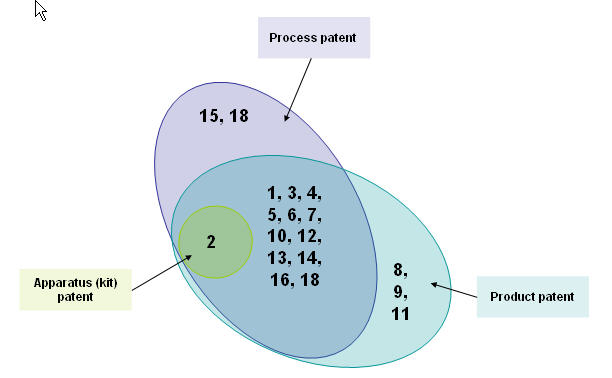
Distribution based on patent types
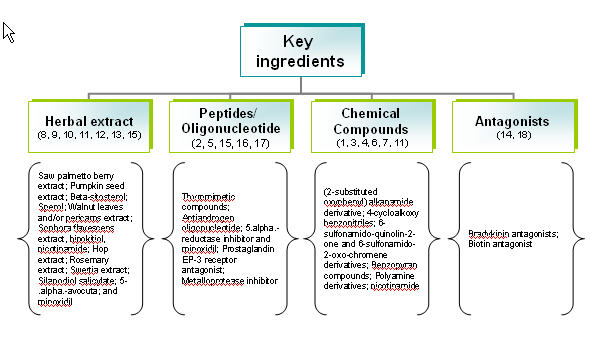
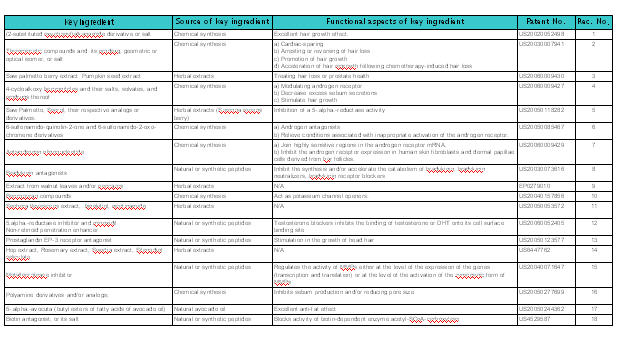
Distribution of key ingredients
Other attributes of the key ingredients
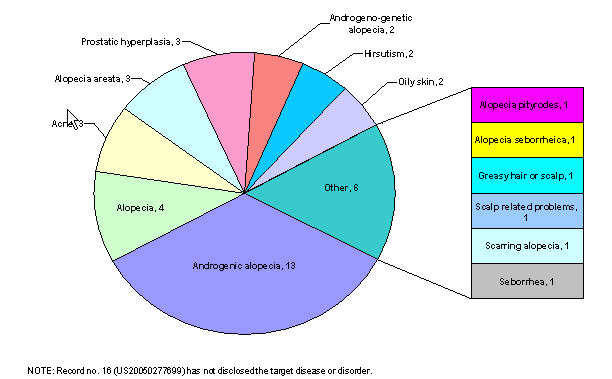
Distribution based on target diseases
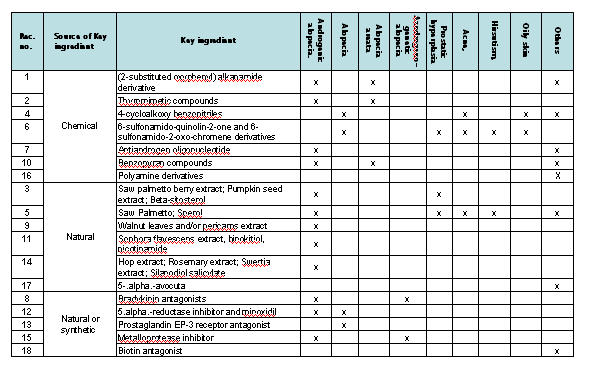
Key ingredients vs. Target disease/disorder
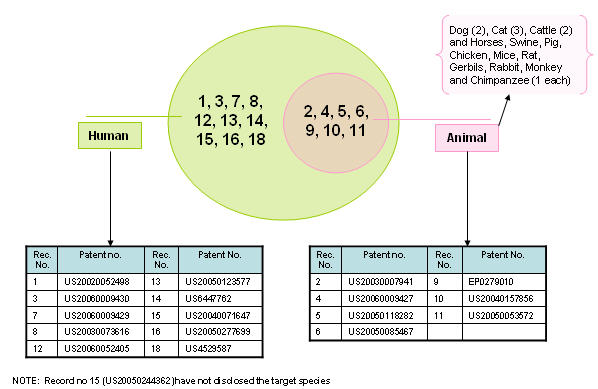
Target species
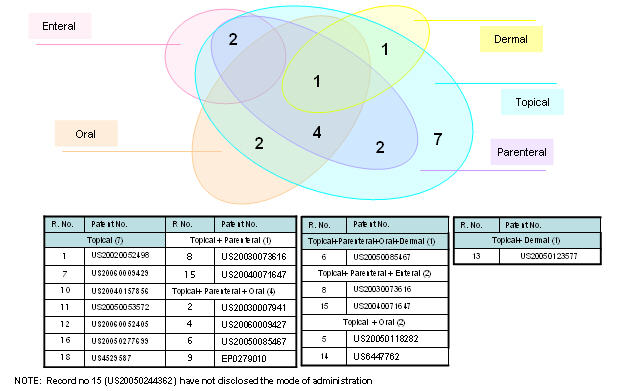
Mode of administration
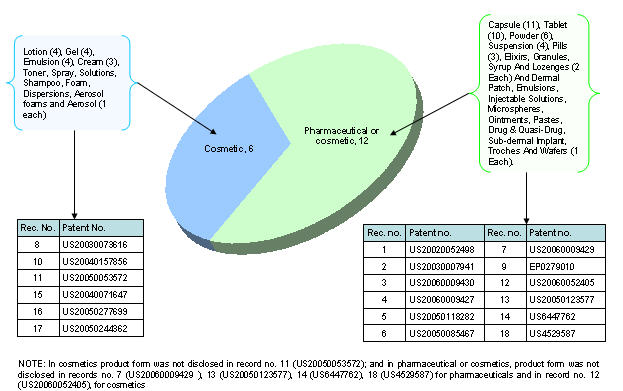
Product type vs. Product form
Distribution of patents based on different aspects
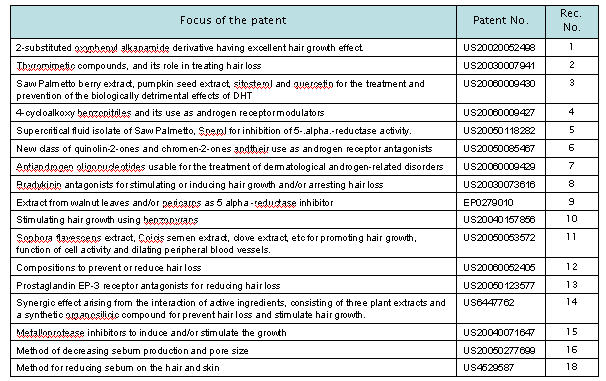
List of patents
Distribution of patents based on target diseases
Distribution of patents based on application
Questions Dolcera Answers
What’s hot?
- What compositions/ approaches are the most promising?
- What can I license?
- Can you map blockbuster products to their patents?
Can you save me some time?
- What combinations/ compounds have already been tried?
- Is any empirical data available?
- Can you tell me the side effects?
Where should I focus my R&D investment?
- What are the most promising approaches?
- Where’s the ‘white space’ for me to play in?
Any hints for research?
- Are there any combinations I could develop?
What should I do in this geography?
- What are my competitors up to in this geography?
- What are my strengths/ weaknesses here?
What’s my competition up to?
- What’s my top competitor investing in?
- Are there any loopholes in their patents?
- When are their patents expiring?
- Will a competitor emerge from nowhere and surprise me?
- What are the crowded areas?
How do I play defense?
- What should my blocking/reactive strategies be?
New Combinations based on IP study?
Yes, new Combinations can be made with natural products based on IP study
- Walnut extract containing
 inhibitor (as anti-androgen) and Flavnones (for vasodilation).
inhibitor (as anti-androgen) and Flavnones (for vasodilation). - Sophora Flavnones (for vasodilation) in combination with Saw Palmetto berry (as anti-androgen).
Note: The above combinations are based on limited study and are only possible examples
IP studies provides
Technology trends
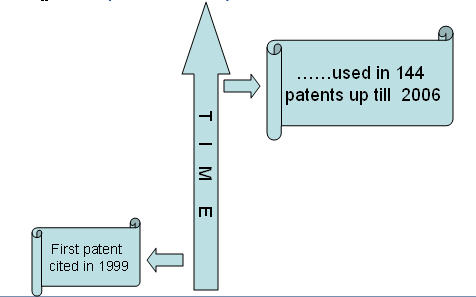
- Use of saw palmetto berry for treating alopecia was first patented in 1996.
- Since then, 144 patents (including family patents) have been filed till 2006.
- Most patents use saw palmetto berry in combination with other products.
New opportunities
Yes, the IP studies provide new opportunities in the following area.
- Sophora Flavescens contain flavnoids.
- Natural extract Sophora Flavescens cited in LG patent of 2001.
- Research shows fewer than 7 patents based on Sophora Flavescens for hair loss or alopecia.
Conclusions
- Hair loss medication is a very active area of research and intellectual property development.
- One of the most promising areas of development is the area of Anti-androgens.
- The top companies are Merck, L’Oreal and Smithkline.