Alopecia - Hair Loss
Contents
- 1 Rationale
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Goals
- 4 Approach
- 5 IP activity over years
- 6 Major Players
- 7 Anti-androgens
- 8 Minoxidil
- 9 Double action (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil)
- 10 Hair matrix cell activator
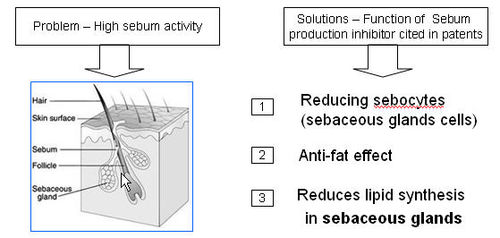
- 11 Sebum Production Inhibitor
- 12 Composition nature matrix
- 13 Focus on different aspects
- 14 Distribution on different aspects
- 15 Distribution of patents based on different aspects
- 16 Questions Dolcera Answers
- 17 New Combinations based on IP study?
- 18 IP studies provides
- 19 Conclusions
- 20 Useful links
Rationale
- “Medication for men plagued by hair loss has become a topic of interest in Japan since a drug company began marketing it at the end of last year." March 5th, 2006 – [1]
- “An increasing number of companies are apparently turning the Chinese fear of a bald spot into big bucks with some doing so well they are branching out into other countries.” February 16, 2006 – [2]
Introduction
Hair Basics
- Hair is a complex and delicate part of the body
- Keeping it healthy and beautiful is a challenge
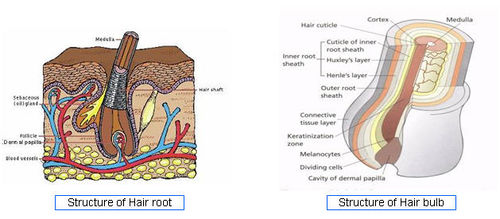
- Structure of Hair root - [3]
- Structure of Hair bulb - [4]
Reasons for Hair loss
Both men and women lose hair for similar reasons. Hair loss in men is often more dramatic, and follows a specific pattern of loss which has been termed “Male Pattern Baldness” (Androgenetic Alopecia).
Main reasons
- Hormonal effect of androgen
- Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle
- Deactivation of hair matrix cells
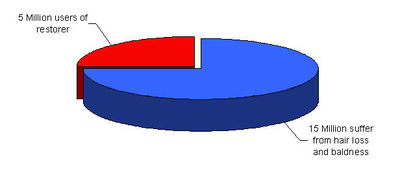
Some facts from Japan
- Market size: ¥ 30 Billion
- Number of products: more than 100
(JICST-EPlus - Japanese Science & Technology)
Goals
- Summarize IP activity over the years
- Identify major players
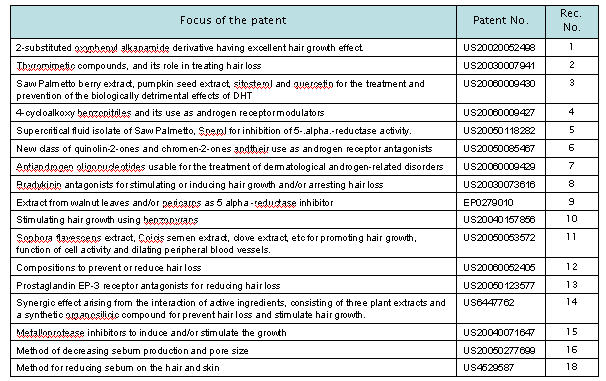
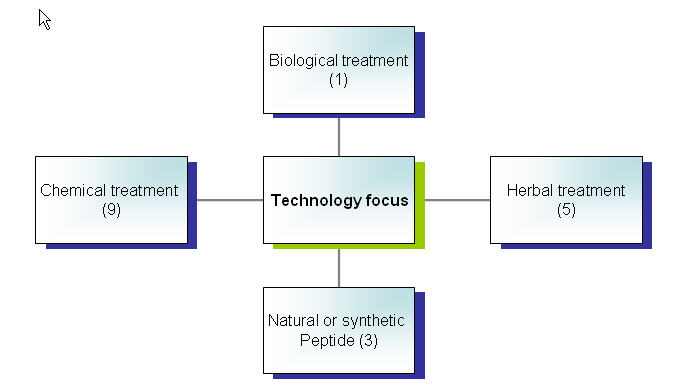
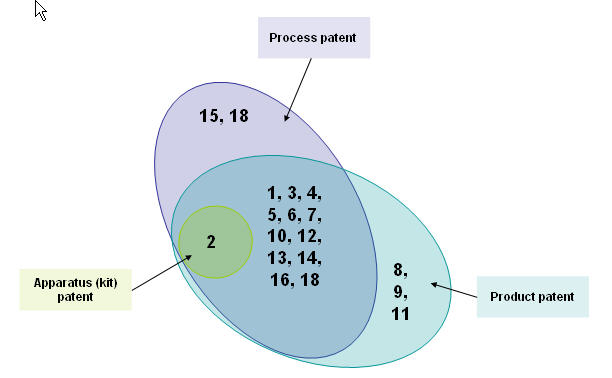
- Conduct patent analysis
a) Composition b) Nature c) Action
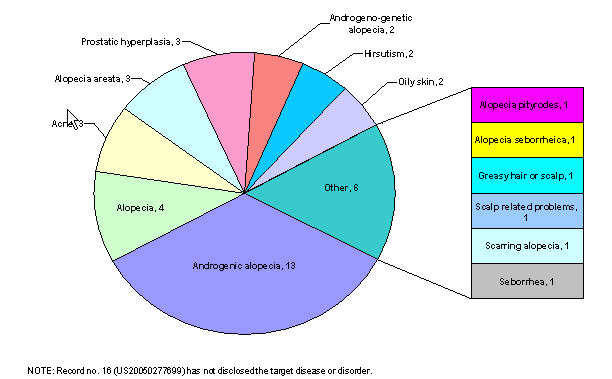
Alopecia occurs due to
- Hormonal effects of androgens
- Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle
- Deactivation of hair matrix cells
And then
- Analyze patents pertaining to high sebum activity
Approach
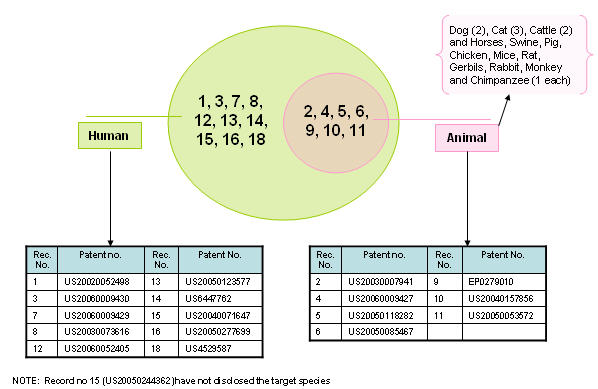
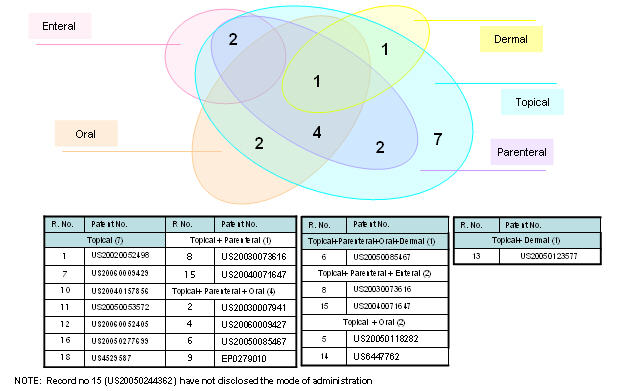
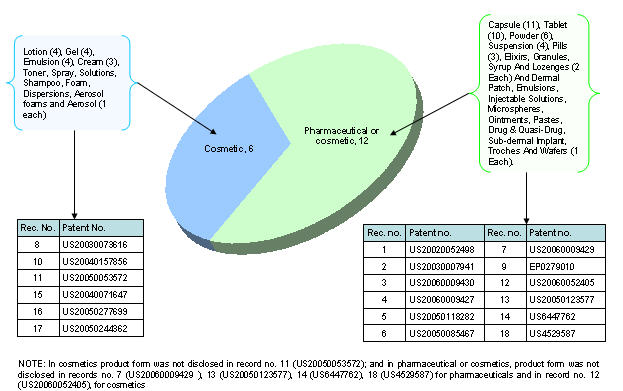
Broad search conducted on hair loss patents.
Patent information sourced through SIP.
Patents selected randomly for analysis.
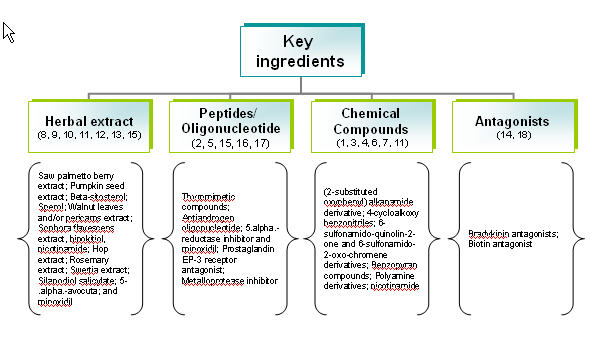
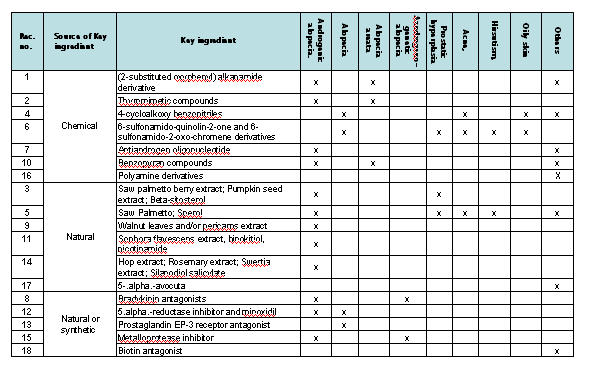
Composition of treatment for causes are identified and categorized as follows:
- Anti-androgen
- Minoxidil
- Double action (Anti-androgen + Mindoxidil)
- Hair matrix cells activator
- Sebum production inhibitor
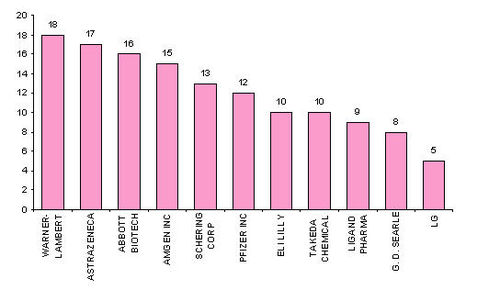
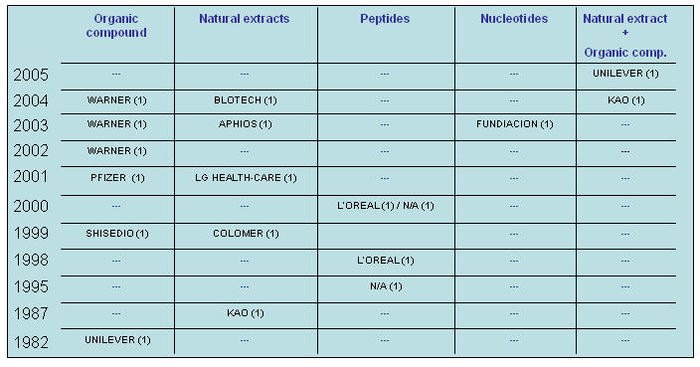
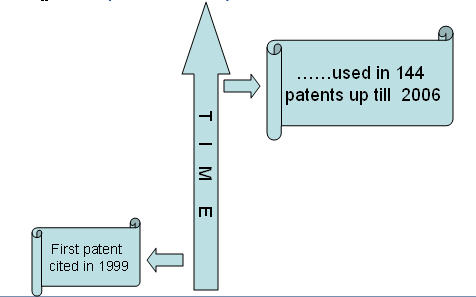
IP activity over years
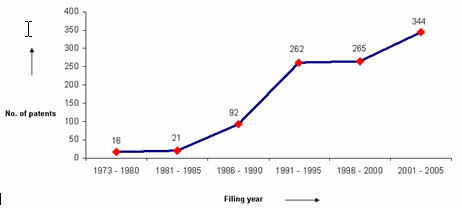
The graph indicates: -
- Number of patents filed every 5 years (except for first 7 years).
- First solution proposed in 1973
- Filing trend indicates steep rise in activity recently.
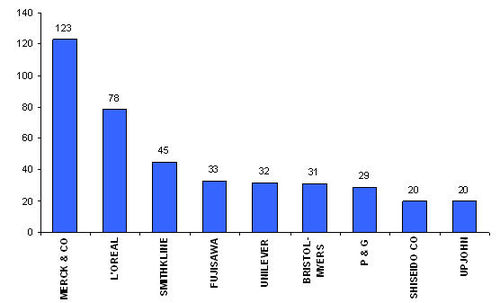
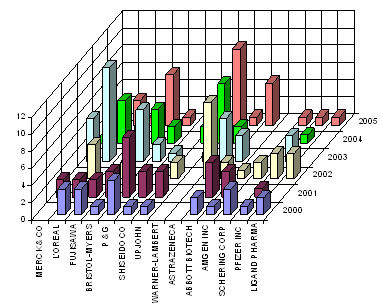
Major Players
- Assignees with more than 20 patents to their credit
- Assignees with less than 20 patents to their credit
- Active Assignees
Assignees currently active with more than 5 patents to their credit during 2000-2005, among them following are the leaders of 2005-
WARNER with 9 patents,
BRISTOL with 6 and
ABBOTT with 5.
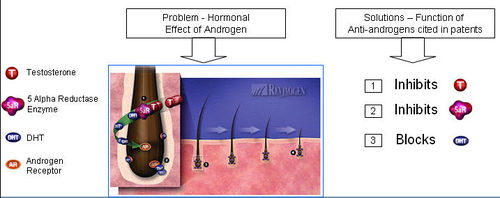
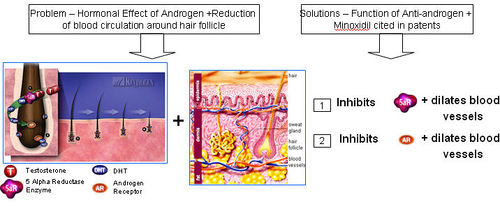
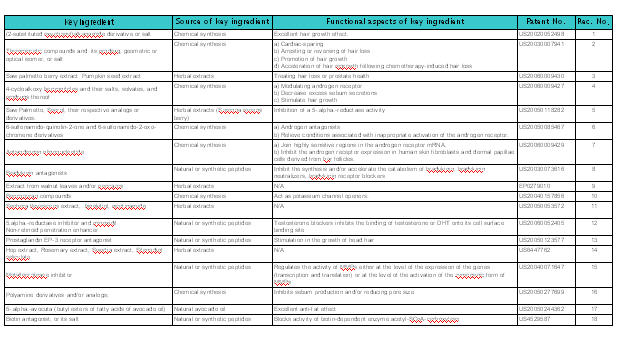
Anti-androgens
- Anti-androgen is a substance that inhibits biological effects of androgenic hormones
- 5-alpha reductase + Testosterone = Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
- DHT attaches to an Androgen Receptor.
- DHT causes increase in hair loss and gradual miniaturization of the follicle, which eventually dies resulting hair loss
Functions of Anti-androgen
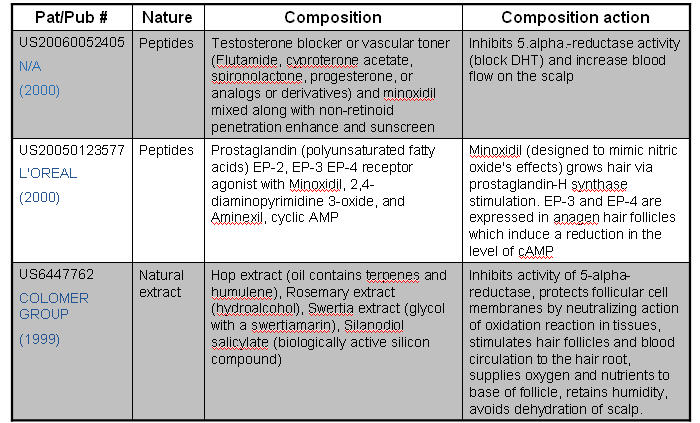
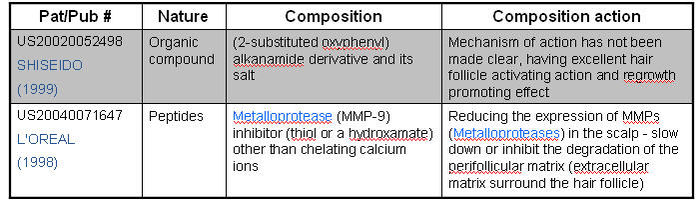
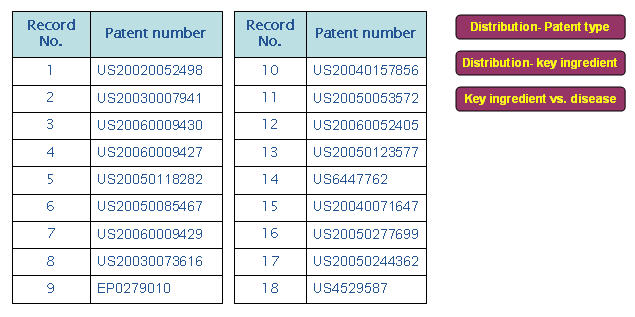
IP Map for Anti-androgen
| Pat/Pub# | Nature | Composition | Composition action |
|---|---|---|---|
| US20060009430
BLOTECH (2004) |
Natural extracts | Palmetto berry extract (fatty acids & sterols), Pumpkin seed extract (Vitamins-B, alpha-linolenic acid, amino acids and phytosterols), Quercetin (Flavonoids) and Beta-sitosterol (Rice bran, wheat germ, corn oils and soybeans) | Fatty acids – Inhibit testosterone
Sterols - Mechanism of action unknown. Quercetin results in cell growth cycle. Beta-sitosterol reduce inflammation on scalp |
| US20060009427
WARNER LAMBERT(2004) |
Organic compound | New class of 4-cycloalkoxy benzonitrile derivatives and salts | Acts as androgen receptor modulators and blocks formation of DHT. |
| US20050085467
WARNER LAMBERT(2004) |
Organic compound | New class of 6-sulfonamido-quinolin-2-one and 6-sulfonamido-2-oxo-chromene derivatives. | The compounds inhibit, or decrease, activation of androgen receptor by androgens. |
| US20050118282
APHIOS Corp (2003) |
Natural extracts | Supercritical fluid isolate of Saw Palmetto and Sperol (Serenoa repens berry) and their analogs or derivatives. | Modulates androgenic activity by inhibiting 5.alpha.-reductase activity. |
| US20060009429
Fundacion Pablo Cassara (2003) |
Nucleotide | Pharmacologically active oligonucleotides (encompass both DNA and S-DNA bond) | Oligonucleotides inhibit androgen receptor (AR) expression at very low concentrations in skin and hair follicle |
| US20030007941
PFIZER INC (2001) |
Organic compound | Thyromimetic compounds (structurally similar to thyronine) with finasteride, or cyproterone acetate | Activates thyroid hormone receptors in hair follicle which in turn promote elasticisation of follicle walls and hair follicle |
| US20030073616
N/A (1995) |
Peptides/nucleic acid | Bradykinin antagonist (peptide of plasma origin from kininogen precursor-kallikrein) | Inhibit synthesis of bradykinin receptors or compounds by binding to B2 receptor |
| EP0279010
KAO Corp (1987) |
Natural extracts | Walnut extract (leaves/pericarps) with an organic solvent | Blocks formation of DHT |
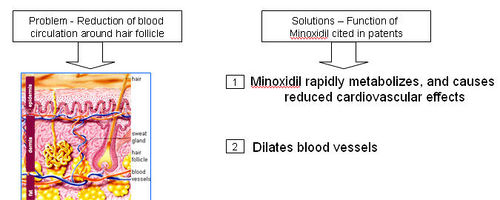
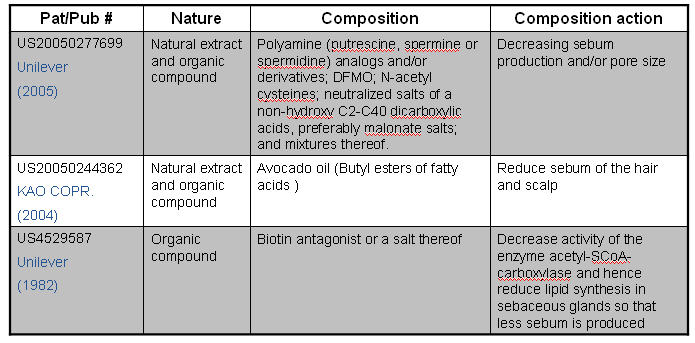
Minoxidil
- A thick network of tiny veins and arteries lines the outer wall of the follicle. Blood pumps through the bulb and hair via this network
- Minoxidil dilates blood vessels; which is also called as “potassium channel opener”
- Minoxidil sulfate (MS) appears to be the active metabolite responsible for hair growth stimulation.