Difference between revisions of "Smart miniature drug delivery systems"
From DolceraWiki
(→'''Taxanomy''') |
Manikandan (Talk | contribs) (→Dashboard link) |
||
| Line 225: | Line 225: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Contact Dolcera== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Samir Raiyani''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''201 A South Delaware St. #306''' | ||
| + | '''San Mateo, CA 94401 USA''' | ||
| + | '''Phone: +1-650-269-7952''' | ||
| + | '''Fax: +1-866-690-7517''' | ||
| + | '''info@dolcera.com''' | ||
Revision as of 00:56, 30 April 2009
Contents
[hide]Background
Introduction
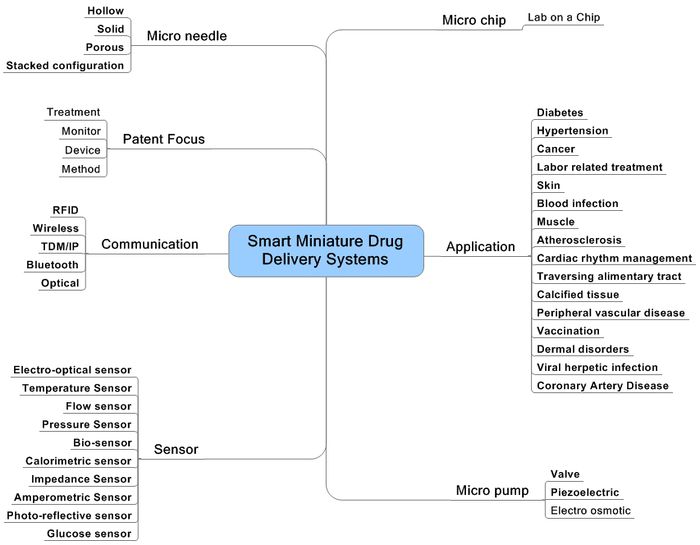
- The smart miniature drug delivery sytem is for delivering the drugs to the host.Biological information is detected by biological sensors, the information is analyzed and drug delivery system is actuated to deliver the drug based on the information.
- This system utilizes MEMS or NEMS technology based drug pumps, micro-pumps, micro-needles, micro-osmotic pumps, Nano-pumps.
- It also includes sensors or communication systems to activate or control pumps.
- Microsystems technologies are changing the Life Sciences industry. New in vitro diagnostic systems, new therapy strategies, genetic diseases treatment, targeted and intelligent drug delivery, artificial pancreas, drug discovery processes are health improvement promised to the future generations, enabled by semiconductor and MEMS technologies. The Life Sciences industry already faces critical challenges to take its way to its expected market.
- The bar graph below gives details of the MEMS component for lifescience market
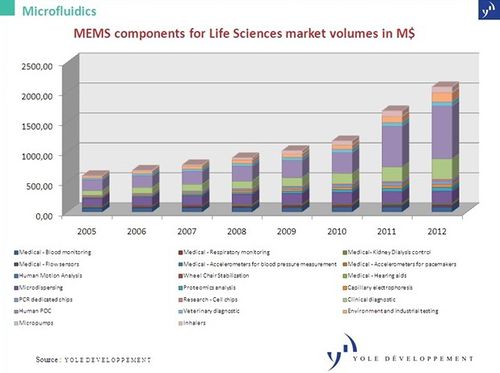
MEMS component lifescience market Source
- Micro- and nano-electromechanical systems (MEMS or NEMS)-based drug delivery devices offer opportunities to address unmet medical needs related to dosing. Such devices should be considered when conventional dosing methods perform suboptimally in terms of safety, efficacy, pain, or convenience. In addition, applications of these technologies may create totally new drug delivery paradigms. MEMS technologies may create new therapies with existing molecular entities.
Some of the MEMS based drug delivery systems are listed below
Micropumps
- Although any kind of small pump is often referred to as micropump, a more accurate and up-to-date definition restricts this term to pumps with functional dimensions in the micrometre range. Such pumps are of special interest in microfluidic research, and have become available for industrial product integration in recent years. Their miniaturized overall size, potential cost and improved dosing accuracy compared to existing miniature pumps fuel the growing interest for this innovative kind of pump.
- Micropumps can be grouped into mechanical and non-mechanical devices: Mechanical systems contain moving parts, which are usually actuation and valve membranes or flaps. The driving force can be generated by utilizing piezoelectric, electrostatic, thermo-pneumatic, pneumatic or magnetic effects. Non-mechanical pumps function with electro-hydrodynamic, electro-osmotic or ultrasonic flow generation.Source

Micropump Source
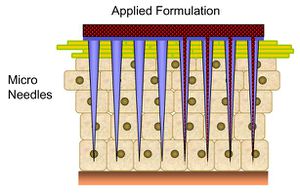
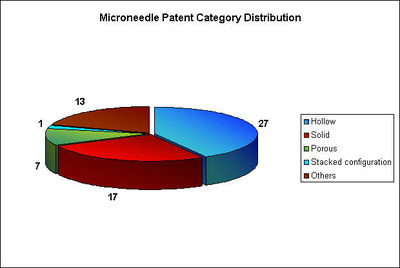
Microneedles
- Microneedles were first developed as a method for transdermal drug delivery . The microneedles
are long enough to penetrate the stratum corneum, which often acts as the primary barrier to drug transport across the skin, but are short enough to avoid the nerves located in the dermis, potentially offering a painless method for drug delivery.
- The microneedles can be divided into "In-Plane" and "Out of plane" microneedle based o fabrication methods and as "Hollow" and "Solid" Microneedles based on their physical aspects.
Taxonomy
Search concepts
| Sr. No | Concept 1 | Concept 2 | Concept 3 | Concept 4 | Concept 5 | Concept 6 |
| 1 | MEMS | NEMS | DRUG | SENSOR | COMMUNICATION | DELIVERY |
| 2 | Microelectromechanical Systems | Nanoelectromechanical systems | Medicament | Biosensor | Bioinformation technology | Inject*4 |
| 3 | Microsystem Technology | BioNems | Pharmaceutic*2 | Smartsensor | Telemetry | Perfus*3 |
| 4 | BioMems | Nanoneedle | Medic*5 | Microsensor | Infus*3 | |
| 5 | Micropump | Nanopump | Diffus*3 | |||
| 6 | Microneedle | Releas* | ||||
| 7 | Mems Drugpump | |||||
| 8 | Microosmotic pump | |||||
| 9 | Lab on a chip | |||||
| 10 | Lab micro chip |
Search strategy
| Micropat | |||||
| Sr. No | Concept | Search Query | Scope | Year | Hits |
| 1 | MEMS | (((Microelectromechanical) OR (Micro ADJ ((System*1 ADJ Technology) OR (Electromechanical))) OR (MEMS) OR (BioMEMS) OR (Bio ADJ2 MEMS) OR (Microtechnology) OR (Micro ADJ Electro ADJ Mechanical)) OR (Drug ADJ2 Pump) OR (Micro ADJ2 Pump*1) OR(Micro ADJ2 Needle*) OR (Micro ADJ2 Osmotic*) OR Micropump* OR Microneedle* OR Microosmotic* OR (Lab ADJ on ADJ a ADJ chip)OR (Lab ADJ2 Micro ADJ2 Chip)) | Title/Abstract/Claims | 1836-2009 | 24396 |
| 2 | NEMS | (Nanoelectromechanical OR NEMS OR (Nano ADJ Electromechanical) OR (Nano ADJ Electro ADJ Mechanical) OR BioNEMS OR (Bio ADJ2 NEMS) OR (Nano ADJ Pump*1) OR Nanopump OR (Nano ADJ2 Needle*1) OR Nanoneedle*1) | Title/Abstract/Claims | 1836-2009 | 474 |
| 3 | Drug Delivery | (Drug OR Pharmaceutic*2 OR Medic*5) Near10 (Deliver*4 OR Inject*4 OR Perfus*3 OR Infus*3 OR Diffus*3 OR Releas*) | Full Spec | 1836-2009 | 336156 |
| 4 | Sensor/Communication | (*sensor) OR (Sensor*1) OR Communicat*3 OR Telemetry OR (Bio ADJ2 IT) OR (Bio ADJ2 Information) | Title/Abstract/Claims | 1836-2009 | 3257001 |
| 5 | Final Query | (1 OR 2) AND 3 AND 4 | 1225(531 unique patents) | ||
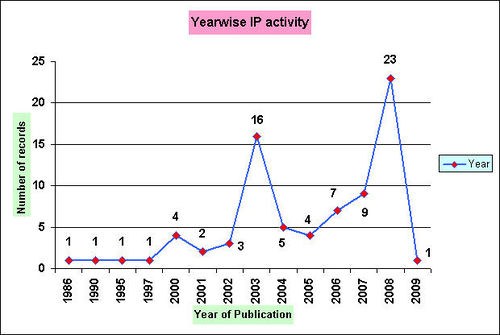
IP Activity
Year wise IP activity
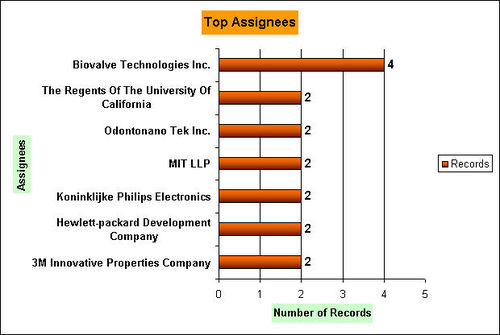
Top Assignees
Other assignees with one record
It can be inferred from the graph that out of the 78 ON target patents Biovalve Technologies Inc. is the Top Assignee in the Smart drug delivery system based on MEMS/NEMS
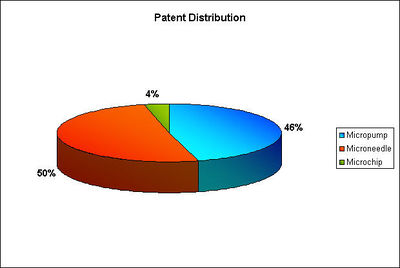
Patent Distribution
Analysis sheets
On target records
Off target records
Dashboard link
| Dashboard |
Contact Dolcera
Samir Raiyani
201 A South Delaware St. #306 San Mateo, CA 94401 USA Phone: +1-650-269-7952 Fax: +1-866-690-7517 info@dolcera.com