Difference between revisions of "Ureteral Stent"
(→Sales) |
(→Dolcera Dashboard) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''This is a landscape report on the Ureteral stent market, including key company profiles, products, patents and relevant clinical | + | '''This is a landscape report on the Ureteral stent market, including key company profiles, products, patents and relevant clinical trials. |
''' | ''' | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=Patents= | =Patents= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Patent Search Strategy== | ==Patent Search Strategy== | ||
[[Image:Patent Search Strategy.jpg|700px]] | [[Image:Patent Search Strategy.jpg|700px]] | ||
| Line 46: | Line 48: | ||
'''Dashboard Link'''<br> | '''Dashboard Link'''<br> | ||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | ||
| − | |'''[ | + | |'''[https://www.dolcera.com/auth/dashboard/dashboard.php?workfile_id=1008 Ureteral Stent - Dashboard] ''' |
|width="100"|[[Image:dashboard_thumb.png|center|100px|]] | |width="100"|[[Image:dashboard_thumb.png|center|100px|]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
= Clinical Trials = | = Clinical Trials = | ||
| + | |||
==New trials == | ==New trials == | ||
| Line 185: | Line 188: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | =Products= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The FDA classifies a ureteric stent as follows: | The FDA classifies a ureteric stent as follows: | ||
* TITLE 21 - FOOD AND DRUGS | * TITLE 21 - FOOD AND DRUGS | ||
| Line 620: | Line 622: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Product to Clinical Trial Mapping= | = Product to Clinical Trial Mapping= | ||
| Line 631: | Line 631: | ||
= Product to Patent Mapping = | = Product to Patent Mapping = | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Product_Patent_Mapping_Screen_Shot.png|1000px|centre|thumb|'''Screenshot for the product to patent mapping(Bard and Boston)''']] | [[Image:Product_Patent_Mapping_Screen_Shot.png|1000px|centre|thumb|'''Screenshot for the product to patent mapping(Bard and Boston)''']] | ||
* Click [[Media:Product_Patent_Mapping_Bard_Boston.xls|'''Products from Boston Scientific and C R Bard ''']]to download the excel file. | * Click [[Media:Product_Patent_Mapping_Bard_Boston.xls|'''Products from Boston Scientific and C R Bard ''']]to download the excel file. | ||
| Line 641: | Line 642: | ||
=Patent-Product-Clinical Trial Mapping= | =Patent-Product-Clinical Trial Mapping= | ||
| + | |||
* To access the Dashboard you have to signup. You can do so by clicking [https://www.dolcera.com/auth/index.php/login '''here'''] | * To access the Dashboard you have to signup. You can do so by clicking [https://www.dolcera.com/auth/index.php/login '''here'''] | ||
*''Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy'' | *''Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy'' | ||
| Line 650: | Line 652: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Insights= | =Insights= | ||
| Line 772: | Line 772: | ||
| − | [[image:stentshare.jpg |center|All figures in USD million ]] | + | [[image:stentshare.jpg |thumb|center|1000px| All figures in USD million ]] |
=<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>= | =<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>= | ||
Latest revision as of 06:45, 27 July 2015
This is a landscape report on the Ureteral stent market, including key company profiles, products, patents and relevant clinical trials.
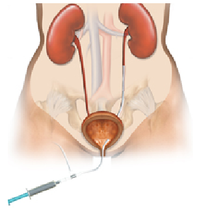
- What is it? A ureteral stent is a specially designed hollow tube, made of a flexible plastic material that is placed in the ureter.
- Need for a ureteral stent: In patients who have, or might have, an obstruction (blockage) of the kidney, an internal drainage tube called a ‘stent’ is commonly placed in the ureter, the tube between the kidney and the bladder. This is placed there in order to prevent or temporarily relieve the obstruction.
Contents
[hide]Background
Ureteral stents are used in urological surgery to maintain patency of the ureter to allow urine drainage from the renal pelvis to the bladder. These devices can be placed by a number of different endourological techniques. They are typically inserted through a cystoscope and may also be inserted intraoperatively. Indwelling ureteral stents help to reduce complications and morbidity subsequent to urological and surgical procedures. Frequently, ureteral stents are used to facilitate drainage in conjunction with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) and after endoscopic procedures. They are also used to internally support anastomoses and prevent urine leakage after surgery. Ureteral stenting may almost eliminate the urological complications of renal transplantation. An antimicrobial ureteral stent, which inhibits encrustation and bacterial colonization while maintaining patient comfort.
- Ureteral stent: resists migration, resists fragmentation, is kink resistant and radiopaque.
- Bacterial colonization: antimicrobial activity for up to two weeks.
- Patient Comfort: stent has a low coefficient of friction (value) for ease of insertion and will soften on implant at body temperature to maintain patient comfort.
Market Overview
Market for ureteral stent can be analyzed by estimating market for each of Ureteral Stent’s fundamental use. Other uses of Ureteral Stent include Post-surgical swelling/infection of uterus, Active kidney infection etc.
Interactive Mind Map
- To access the Dashboard you have to signup. You can do so by clicking here
- Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy
- Click on the red arrow adjacent to the node name to view the content for that particular node in the dashboard
- Click on the "+" sign to zoom the mindmap and "-" sign to shrink the mindmap
Patents
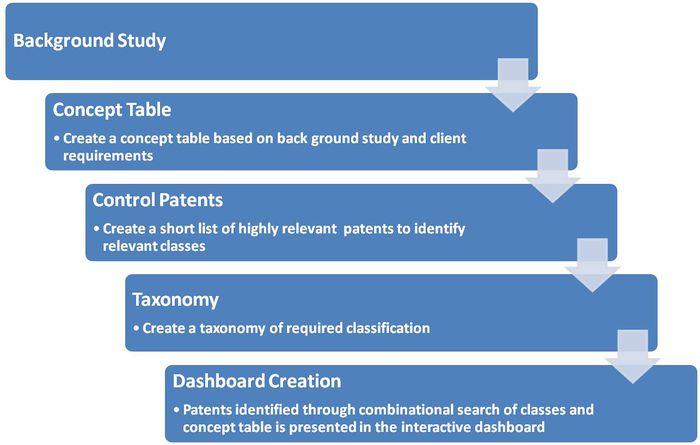
Patent Search Strategy
Dolcera Dashboard
Dashboard Link
| Ureteral Stent - Dashboard |
- Flash Player is essential to view the Dolcera Dashboard
- To access the Dashboard you have to signup. You can do so by clicking here
Clinical Trials
New trials
| |
|
| ||
| |
Assessment of Drug-Eluting Ureteral Stent on Bacterial Adherence and Biofilm Formation | Renal Calculi, Ureteral Obstruction | Ureteral Stent | Lawson Health Research Institute, Boston Scientific Corporation |
| |
Memokath® 044TW Stent for Treatment of Urethral Stricture | Urethral Stricture | Memokath stenting | Engineers & Doctors Wallsten Medical Group |
| |
Study to Determine if There Are Specific Clinical Factors to Determine Stent Encrustation | Kidney Stones | N\A | University of California, Irvine |
| |
Ureteral Stent Length and Patient Symptoms | Kidney Stones | Ureteral Stent | Emory University |
| |
Drainage of Malignant Extrinsic Ureteral Obstruction Using the Memokath Ureteral Stent | Ureteral Obstruction | Memokath 051 Ureteral Stent | Mayo Clinic Engineers & Doctors Wallsten Medical Group |
| |
A Prospective Comparison Between Ureteral Stent and Nephrostomy Tube for an Urgent Drainage of Obstructed Kidney (JJVsPCN08) | Kidney Disease | Nephrostomy tube and ureteral stent | Rabin Medical Center |
Concluded trials
| Long-term outcome of permanent urethral stents in the treatment of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia | To evaluate the long-term efficacy of a permanently implanted urethral stent in the treatment of spinally injured patients with detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia. | 13 | Detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia | Stenting is an effective alternative to sphincterotomy in the long-term, although secondary bladder neck obstruction is a frequent problem. | |
| |
Nephrostomy Tube or 'JJ' Ureteric Stent in Ureteric Obstruction: Assessment of Patient Perspectives Using Quality-of-Life Survey and Utility Analysis | Upper urinary tract obstruction is often relieved by either a percutaneous nephrostomy tube (PCN) or a ureteric stent. Both can cause considerable morbidity and reduce patient's health-related quality of life (QoL). We have compared the QoL in these 2 groups. | 34 | Upper urinary tract obstruction | Patients with 'JJ' stents have significantly more irritative urinary symptoms and a high chance of local discomfort than patients with nephrostomy tubes (PCN). However, based on the EuroQol analysis, there is no significant difference in the gross impact on the health-related QoL or the utility between these groups indicating no patient preference for either modality of treatment. |
| |
Impact of stents on urological complications and health care expenditure in renal transplant recipients: results of a prospective, randomized clinical trial. | A randomized, prospective trial to compare the incidence of early urological complications and health care expenditures in renal transplant recipients with or without ureteral stenting. | 201 | Renal transplant recipient | Using a ureteral stent at renal transplantation significantly decreases the early urinary complications of urine leakage and obstruction. However, there is a significant increase in urinary tract infections, primarily beyond 30 days after transplantation. Stent removal within 4 weeks of insertion appears advisable. |
Pre-Market Notification
Some of the companies active in the field of ureteral stents have been represented in the table below.
| |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| |
|
|
|
|
Silicone | Double pigtail with monofilament suture loop | |
| |
|
|
|
Dual Durometer Percuflex with HydroPlus Coating | Bladder loop design | | |
| |
|
|
|
Metal | Temporary stenting | | |
| |
|
|
|
Polyurethane | Spiral radially expanding stent | | |
| |
| ||||||
| |
|
|
|
Nickel-titanium shape memory alloy | Double fluted ended spiral stent | |
Products
The FDA classifies a ureteric stent as follows:
- TITLE 21 - FOOD AND DRUGS
- CHAPTER I - FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
- SUBCHAPTER H - MEDICAL DEVICES
- PART 876 - GASTROENTEROLOGY-UROLOGY DEVICES
- Subpart E - Surgical Devices
- Sec. 876.4620 - Ureteral stent.
- Classification - class II device Code of Federal Regulations
| Sr. No. | Company | Device(s) | Approval | Approval Date | Material | Technology | Indwelling Time (days) | Image |
| 1 | Allium, Israel | URS | CE Mark | Jul, 2007 | Nickel-titanium shape memory alloy covered by polymer | Self-expanding stent | ||
| 2 | Pnn Medical A/S | Memokath 051 | CE Mark | 1995 | Nickel-titanium shape memory alloy | Double fluted ended spiral stent | 240 | |
| FDA Listing | Mar, 2004 | |||||||
| 3 | Fossa Medical | Stone Sweeper | CE Mark | Sep, 2005 | Polyurethane | Radially expanding stent | 13 | |
| FDA 510(k) | Aug, 2002 | |||||||
| Open lumen stent | FDA 510(k) | Nov, 2003 | Polyurethane | Pigtail-tipped stent with ’Pusher’ | ||||
| CE Mark | Sep, 2005 | |||||||
| Expanding Ureteral Stent | FDA 510(k) | Jun, 2002 | Polyurethane | Double pigtail stent with ’Pusher’ | N/A | |||
| 4 | Boston Scientific | Contour | Percuflex - proprietary polyolefin copolymer; Hydroplus coating | Fixed and variable length; Tapered tip | 365 | |||
| Percuflex | Percuflex | Pigtail | 365 | |||||
| Polaris Ultra | FDA 510(k) | Jan, 2001 | Dual Durometer Percuflex with HydroPlus Coating; soft Nautilus Bladder Coil. | Double pigtail | 365 | |||
| Polaris Loop | FDA 510(k) | Mar, 2003 | Dual Durometer Percuflex with HydroPlus Coating | Bladder loop design | 365 | |||
| Retromax Plus | Percuflex material and Hydroplus coating | Endopyelotomy stent | Post-procedure healing | |||||
| Stretch VL Flexima | Hydroplus Coating | Variable length coil on distal and proximal ends | 90 | |||||
| Drug-Eluting Stent | Percuflex - proprietary polyolefin copolymer | Ketorolac trimethamine loaded stent | N/A | |||||
| 5 | Cook Medical | Resonance | FDA 510(k) | May, 2007 | Metal | 365 | ||
| Sof-flex | AQ® Hydrophilic Coating | Radiopaque tip and tether for repositioning | 180 | |||||
| Endo-Sof | AQ® Hydrophilic Coating | Double pigtail | 365 | |||||
| C-Flex | Double Pigtail | 180 | ||||||
| Smith Universal | Nephrostomy tube + Ureteral stent | 60 | ||||||
| Endo-Sof Radiance | Launch | Dec, 2007 | Heparin-bonded stent | |||||
| 6 | Q Urological | pAguaMedicina™ Pediatric Ureteral Stent | FDA 510(k) | Jan, 2010 | Hydrogel | Differentially larger end (no pigtail) | 30 | |
| 7 | Bioteque Corp. | Ureteral Stent Set | FDA 510(k) | Apr, 2010 | 30 | |||
| 8 | Applied Medical Resources, CA, USA | Mesh | FDA 510(k) | Jul, 2001 | Polyester mesh | Double-pigtail | N/A | |
| Silhouette | Coil-reinforced; SL-6® hydrophilic coating | Patency Device | ||||||
| Applied Standard | FDA 510(k) | Jun, 1999 | Proprietary thermoplastic elastomer material; SL-6® hydrophilic coating | Unique wall construction and enlarged drainage holes | ||||
| 7-10 endopyelotomy | Proprietary thermoplastic elastomer material; SL-6® hydrophilic coating | Dual Diameter stent | ||||||
| 9 | Bard Urological | InLay Optima | FDA 510(k) | Dec, 2004 | Silicone | Double pigtail with monofilament suture loop | 365 | |
| Bardex® Double Pigtail Soft Stent | FDA 510(k) | Jan, 2003 | Silicone | Attached with suture for ease of removal | ||||
| Fluoro-4 Silicone Ureteral Stent | Silicone/tantalum | |||||||
| Figure-4 Silicone Ureteral Stent | Silicone | Three dimensional design | ||||||
| InLay Ureteral Stent | FDA 510(k) | Dec, 1998 | Silicone | Tapered tip and lubricious hydrophilic coating | ||||
| Urinary Diversion Stent | FDA 510(k) | Apr, 1991 | Silicone | |||||
| 10 | Coloplast-Porges | Vortek | FDA 510(k) | Oct, 1998 | Silicone | Double coating for easy maneuverability as well as flexibility | ||
| Biosoft | FDA 510(k) | Oct, 1998 | Silicone | Extreme flexibility | ||||
| Polyurethane | Hard or soft Polyurethane | Designed for short-term use | 90 | |||||
| Silicone | FDA 510k) | Oct, 2002 | Silicone | Pyatiprofilnaya technology | ||||
| 11 | Teleflex Medical | Rüsch Superglide DD | FDA 510(k) | Jul, 1999 | WIRUTHAN® (polyurethane) with hydrogel coating | Directable and detachable | ||
| 12 | Gyrus ACMI/Cabot/Acromed/Circon/Surgitek | Classic closed-tip | FDA 510(k) | Dec, 1986 | Classic Closed Tip | |||
| Classic Double pigtail | FDA 510(k) | Mar, 1996 | Tecoflex® construction | Balanced-curled double pigtail design | ||||
| Double-J | FDA 510(k) | Apr, 1988 | Silicone | Double-J closed-tip | ||||
| Lithostent | Tecoflex® | Grooved design | ||||||
| Lubri-flex | FDA 510(k) | Nov, 1991 | Tecoflex® | “Rememberance” of shape with a chemically bonded wettable solution | ||||
| Multi-flex | Tecoflex® | Two durometers with helical kidney curls | ||||||
| Quadra-Coil multi-length | FDA 510(k) | Mar, 1996 | Tecoflex® | Accomodate ureteral lengths from 22cm to 28cm | ||||
| Sof-curl | Tecoflex® | Dual-durometer design and exclusive soft bladder helix | ||||||
| Uroguide | Silicone | Classic Double J with open tip | ||||||
| 13 | Ameco Medical Industries | Amecath | Nitinol; Available with hydrophilic coating | Double loop stent | Short-term and long-term | |||
| 14 | Angiomed-Movaco (C.R. Bard subsidiary) | Ureteral Stent Set | FDA 510(k) | Jan, 1987 | Nitinol | Self-expanding stent | N/A |
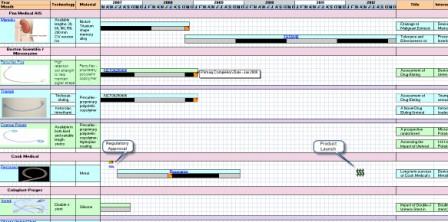
Product to Clinical Trial Mapping
Clinical Timeline Visualization
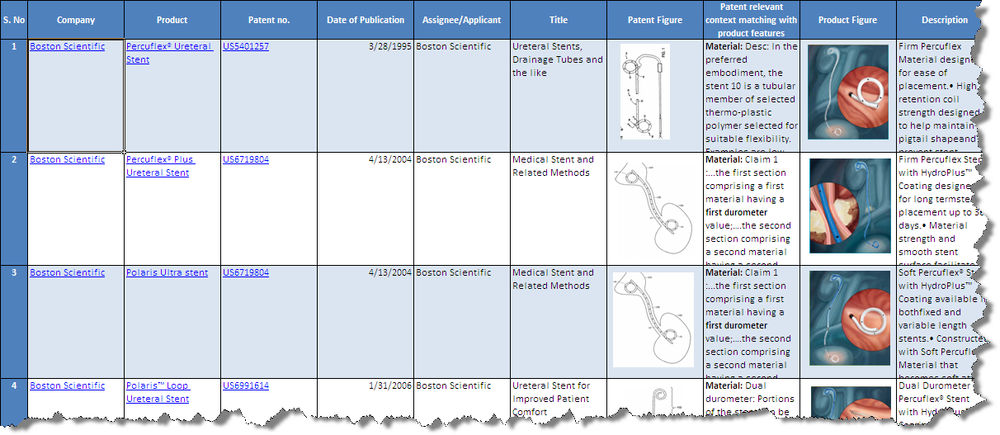
Product to Patent Mapping
- Click Products from Boston Scientific and C R Bard to download the excel file.
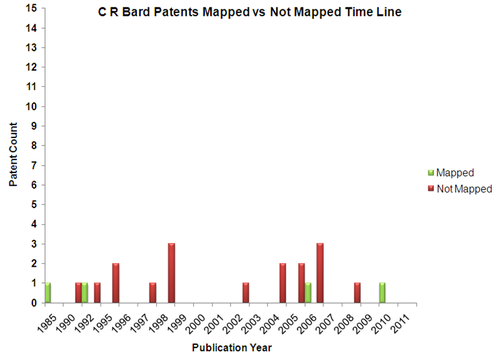
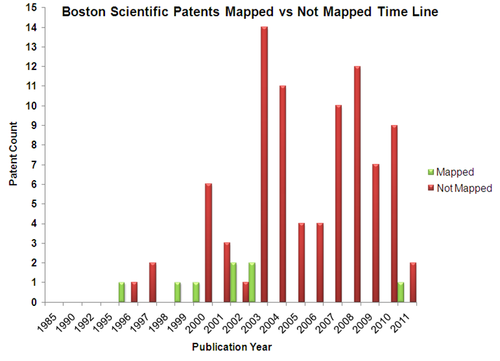
Mapped Patent vs Not Mapped Patents
Patent-Product-Clinical Trial Mapping
- To access the Dashboard you have to signup. You can do so by clicking here
- Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy
- Click on the red arrow adjacent to the node name to view the content for that particular node in the dashboard
- Click on the "+" sign to zoom the mindmap and "-" sign to shrink the mindmap
Insights
| Boston Scientific | C R BARD | ||
| Products | Portfolio | 8 Products | 6 Products |
| Material | Percuflex - Biocompatible Polymer | Silicone | |
| Coating | Hydroplus | Licensed from pHreecoat | |
| Shape | Pigtailed and More | Figure 4 and more | |
| Clinical Trials |
Current Trials | Truimph Ureteral stent - Loaded with Triclosan Currently in Phase II (Canada) |
None |
| Patents | Coating | Therapeutic / Medicinal coatings Magnetic nano particles for MRI Imaging Lubricious coatings helping easy insertion |
Therapeutic coatings |
| Structure | Multiple channels filled with therapeutic agent Multiple collapsible segments preventing fluid passing Renal coil with wick to prevent reflux Stent with beads on its surface Stent with reservoir indicating its release with change in color of urine Expandable and collapsible stent Stents with degradable barbs |
Expandable stents for reducing discomfort | |
| Material | Elastically deformable stents Biodegradable polymer based stents Porous polymer for long term implantation Stent with variable hardness |
Biodegradable polymers Shape memory alloys General polymer based |
Inference
| Boston Scientific | C R BARD |
| Relatively late entrant with patents filed post mid 90s | Early mover with patents filed in mid 80s |
| Increased patent activity since 2000 | Patent activity never gained traction |
| Large number of patents yet to be "productized" | Few patents yet to be "productized" |
| Some products undergoing clinical trails | No products undergoing clinical trails |
| Diverse range of products with variation in material and structure |
Small product portfolio |
| Seem to be strengthening they market position | Seem to be moving focus away from Ureteral stents market |
Competitive Landscape
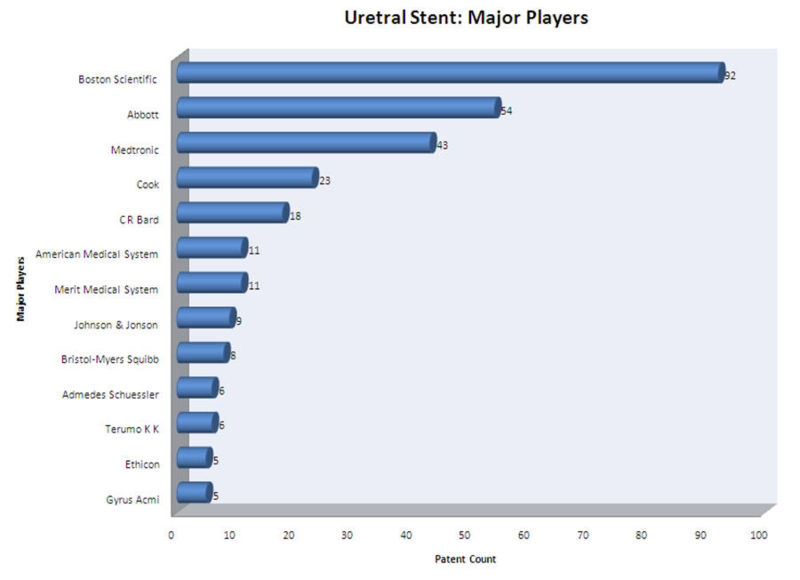
Major Players
- Boston Scientific Limited, Abbott, Medtronic and Cook Inc. are the major players in ureteral stent research field.
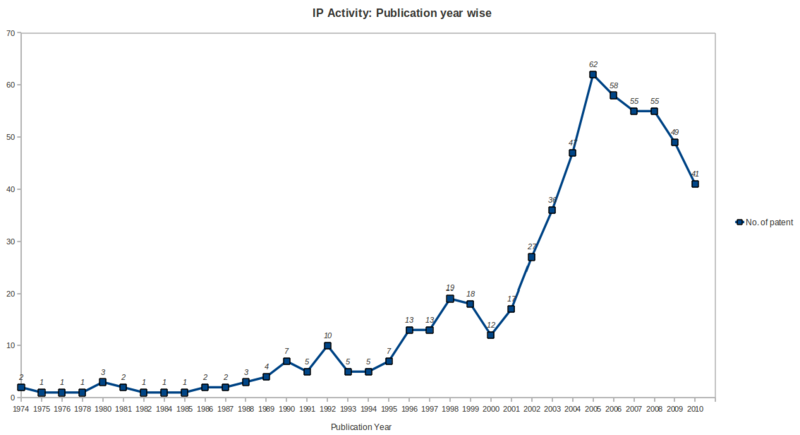
IP Activity
- Patenting activity has been high growth rate during the period 2001 to 2005 with a peak no. of patents in year 2005, followed by saturation during the period 2006 to 2008 and after that a gradual declination upto year 2010 in the ureteral stent research area.
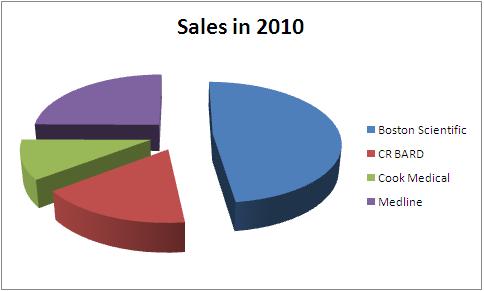
Sales
Total Sales in 2010 - 4.04 Billion USD
| Company | Total Sales in 2010 | Urological sales | Percentage share | Product portfolio |
| Boston Scientific | 7800 | 661 | 8.48 | Boston_portfolio |
| CR BARD | 2700 | 702 | 26.00 | BARD_portfolio |
| Cook Medical | 1700 | - | - | Cook_portfolio |
| Medline | 4040 | - | - | Medline_portfolio |
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs