Difference between revisions of "Oral Diabetes Drugs"
(→Conference highlights for Oral Hypoglycemic Agents) |
Manikandan (Talk | contribs) (→Contact Dolcera) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>=== | ||
| + | <p align="center"> '''This is only a sample report with brief analysis''' <br> | ||
| + | '''Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs'''</p> | ||
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align="center" " | ||
| + | |style="background:lightgrey" align = "center" colspan = "3"|'''[mailto:info@dolcera.com <span style="color:#0047AB">Buy the customized report from Dolcera</span>]''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services Patent Analytics Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/business-research-services Market Research Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools/patent-dashboard Purchase Patent Dashboard] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Landscape Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/research-processes Dolcera Processes] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/industries Industry Focus] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Search Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/alerts-and-updates Patent Alerting Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools Dolcera Tools] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
===Prevalence=== | ===Prevalence=== | ||
The prevalence of diabetes( Both type I and type II ) in U.S. during the years 1980 to 2005, increased from 5.6 million to 15.8 million (Figure 4). Especially people aged from 65 to 74 had the highest prevalence compared to other age groups (Figure 5). The prevalence of the disease was similar in both men and women till the year 1998 but from 1999, the prevalence of the disease increased highly in men compared to females (Figure 6). | The prevalence of diabetes( Both type I and type II ) in U.S. during the years 1980 to 2005, increased from 5.6 million to 15.8 million (Figure 4). Especially people aged from 65 to 74 had the highest prevalence compared to other age groups (Figure 5). The prevalence of the disease was similar in both men and women till the year 1998 but from 1999, the prevalence of the disease increased highly in men compared to females (Figure 6). | ||
| Line 281: | Line 301: | ||
===Product pipeline=== | ===Product pipeline=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Roche.jpg|thumb|center|600px|]] | ||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | ||
|align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99" colspan = "3" |<font size = "4">'''Product Pipeline'''</font> | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99" colspan = "3" |<font size = "4">'''Product Pipeline'''</font> | ||
| Line 324: | Line 346: | ||
|align = "center"|Gastrin <nowiki>+</nowiki> DPP IV Inhibitor | |align = "center"|Gastrin <nowiki>+</nowiki> DPP IV Inhibitor | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.transitiontherapeutics.com/technology/index.php Transition Therapeutics]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.transitiontherapeutics.com/technology/index.php Transition Therapeutics]</u></font> | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Preclinical |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 333: | Line 355: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Insulin sensitizer'''</font> | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Insulin sensitizer'''</font> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 350: | Line 362: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"|NCX 4016 | + | |align = "center"|NCX 4016 (Nitric Oxide donating derivative of Acetyl Salicylic acid) |
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.nicox.com/update/NCX_4016.html NicOx]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.nicox.com/update/NCX_4016.html NicOx]</u></font> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| Line 365: | Line 372: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"|NovoNorm®/Metformin | + | |align = "center"|NovoNorm® (repaglinide)/Metformin |
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.novonordisk.com/science/pipeline/rd_pipeline.asp?showid=6 Novo Nordisk]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.novonordisk.com/science/pipeline/rd_pipeline.asp?showid=6 Novo Nordisk]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"|3 | |align = "center"|3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">''' | + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Biguanides'''</font> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Gastrin <nowiki>+</nowiki> Metformin | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.transitiontherapeutics.com/technology/index.php Transition Therapeutics]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''GLP 1 Analogue / Agonists'''</font> GLP 1 Analogues have to be injected subcutaneously, Emisphere is working on an oral analogue | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Abiglutide (716155) | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.gsk.com/investors/product_pipeline/docs/pipeline.pdf glaxosmithkline]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|TH0318 | |align = "center"|TH0318 | ||
| Line 414: | Line 435: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) agonist/analogue'''</font> | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) agonist/analogue'''</font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|CS-011 (Rivoglitazone) | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Sankyo | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Metaglidasen(MBX 102) | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/26017.php Metabolex]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|MBX-2044 | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.metabolex.com/pipeline.html Metabolex]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 479: | Line 515: | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.drugs.com/nda/muraglitazar_041223.html Bristol-Myers Squibb ]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.drugs.com/nda/muraglitazar_041223.html Bristol-Myers Squibb ]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"|3 | |align = "center"|3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|R483 | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.roche.com/pages/downloads/investor/pdf/praesentations/irp050504rdd14.pdf Roche]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|PPM-204 | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.wyeth.com/research/pipeline Wyeth]</u>, <u>[http://www.invitrogen.com/downloads/Discovery_Inhibitor_Oncogenic_B-RAF.pdf Plexxikon]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 500: | Line 547: | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.osip.com/PSN010 OSI]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.osip.com/PSN010 OSI]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"| | |align = "center"| | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 516: | Line 555: | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.isispharm.com/product_pipeline.html Isis]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.isispharm.com/product_pipeline.html Isis]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"|1 | |align = "center"|1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Antisense drug for Glucocorticoid Receptor (GCCR)'''</font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 537: | Line 579: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|189075 | |align = "center"|189075 | ||
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http:// | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.gsk.com/investors/product_pipeline/docs/pipeline.pdf Glaxosmithkline]</u></font> |
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|869682 |
| − | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.gsk.com/investors/product_pipeline/docs/pipeline.pdf Glaxosmithkline]</u></font> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| Line 555: | Line 594: | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.theratech.com/en/products-therapeutic-peptides/pipeline.php Theratechnolgies]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.theratech.com/en/products-therapeutic-peptides/pipeline.php Theratechnolgies]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"| | |align = "center"| | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 586: | Line 609: | ||
|align = "center"|TRX4 | |align = "center"|TRX4 | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.btgplc.com/PartneredDevelopment/240/TRX4.html BTG]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.btgplc.com/PartneredDevelopment/240/TRX4.html BTG]</u></font> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Selective inhibitor of fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase (FBPase)'''</font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|CS-917 | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<u>[http://www.mbasis.com/pipeline/metabolic_disease.html Sankyo,Metabasis]</u> | ||
| + | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|MB07803 | ||
| + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.mbasis.com/pipeline/index.html metabasis, Daiichi Sankyo]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| Line 593: | Line 628: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|AMG 221 | |align = "center"|AMG 221 | ||
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://wwwext.amgen.com/science/pipe_AMG221.html Amgen]</u></font> | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://wwwext.amgen.com/science/pipe_AMG221.html Amgen, Biovitrum]</u></font> |
|align = "center"|1 | |align = "center"|1 | ||
| Line 607: | Line 642: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"|IPLEX | + | |align = "center"|IPLEX (Mecasermin rinfabate) |
|align = "center"|Glen Allen | |align = "center"|Glen Allen | ||
|align = "center"|Orphan Drug Status | |align = "center"|Orphan Drug Status | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Newer Meglitinides'''</font> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|Nateglinide with insulin sensitizers | |align = "center"|Nateglinide with insulin sensitizers | ||
| Line 634: | Line 660: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Islet Regeneration Factors'''</font> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|DG770 (beta cell regeneration factor) |
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www. | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.develogen.com/en/prod_pipeline.php?hnav=2&tnav=0 Develogen AG]</u></font> |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|3 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|E1 INT (Islet regeneration) |
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www. | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.transitiontherapeutics.com/technology/index.php Transition Therapeutics]</u></font> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99" colspan = "3"|<font color="#FF6600">'''Miscellaneous'''</font> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|AMG 837 (Potentiates Glucose Dependent Insulin Secretion) |
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http:// | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.amgen.com/science/pipe_amg837.html Amgen]</u></font> |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|MBX 213 |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.metabolex.com/pipeline.html Metabolex]</u></font> |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|1 |
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|R 1499 | |align = "center"|R 1499 | ||
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www. | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.roche.com/pages/downloads/investor/pdf/praesentations/irp050504rdd14.pdf Roche]</u></font> |
|align = "center"|1 | |align = "center"|1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|R1438 | |align = "center"|R1438 | ||
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www. | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.roche.com/pages/downloads/investor/pdf/praesentations/irp050504rdd14.pdf Roche]</u></font> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align = "center"|R1440 | |align = "center"|R1440 | ||
| − | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www. | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.roche.com/pages/downloads/investor/pdf/praesentations/irp050504rdd14.pdf Roche]</u></font> |
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| Line 712: | Line 711: | ||
|align = "center"|Neurocrine Biosciences | |align = "center"|Neurocrine Biosciences | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 747: | Line 731: | ||
|align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.merck.com/finance/pipeline.swf Merck]</u></font> | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.merck.com/finance/pipeline.swf Merck]</u></font> | ||
|align = "center"|2 | |align = "center"|2 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 857: | Line 786: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Product Pathways=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Product_map.jpg|thumb|center|900px| Product]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Product-map.jpg|thumb|center|900px| Product pipeline]] | ||
==Intellectual Property== | ==Intellectual Property== | ||
| Line 863: | Line 798: | ||
* '''Search scope:''' US Granted US Applications EP-A EP-B WO JP (bibliographic data only) DE-C,B DE-A DE-T DE-U GB-A FR-A; '''English Title''' | * '''Search scope:''' US Granted US Applications EP-A EP-B WO JP (bibliographic data only) DE-C,B DE-A DE-T DE-U GB-A FR-A; '''English Title''' | ||
* '''Years:''' '''Issue/Publication Date:''' >20051231 | * '''Years:''' '''Issue/Publication Date:''' >20051231 | ||
| − | * '''String:''' (Diabetes OR diabetic) AND (treatment OR treating) | + | * '''Search String:''' (Diabetes OR diabetic) AND (treatment OR treating) |
* '''Hits:''' 618/217 patents (with/with out family members) | * '''Hits:''' 618/217 patents (with/with out family members) | ||
* '''Date of search:''' 11 July 2007 | * '''Date of search:''' 11 July 2007 | ||
| Line 869: | Line 804: | ||
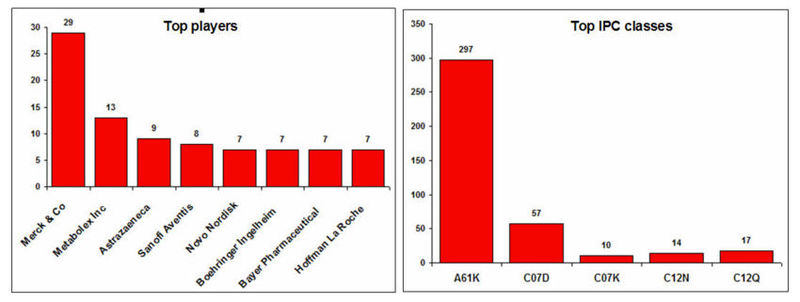
===Top players and IPC classes=== | ===Top players and IPC classes=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Diabetes- top players.jpeg|center| | + | [[Image:Diabetes- top players.jpeg|center|800 px|]] |
====IPC code definition==== | ====IPC code definition==== | ||
| Line 893: | Line 828: | ||
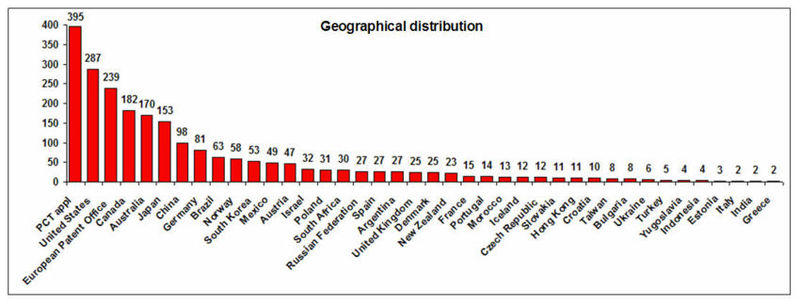
===Geographical Distribution and Treatment Approaches=== | ===Geographical Distribution and Treatment Approaches=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Diabetes -geographical.jpeg|center| | + | [[Image:Diabetes -geographical.jpeg|center|800 px|]] |
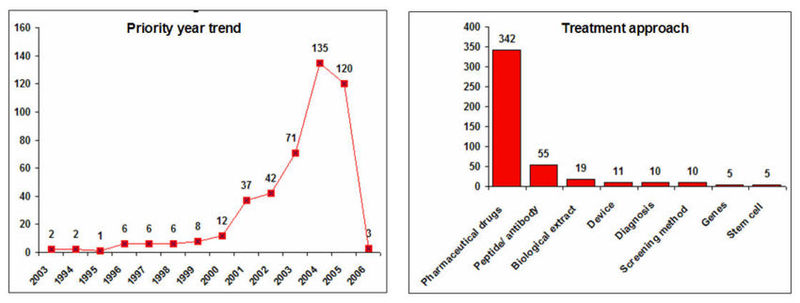
===IP activity and Treatment Approaches=== | ===IP activity and Treatment Approaches=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Diabetes -year approach.jpeg|center| | + | * Decline in the IP activity during 2005 and 2006 is due 18 months publication delay of patent document. |
| + | [[Image:Diabetes -year approach.jpeg|center|800 px|]] | ||
==Clinical Trials== | ==Clinical Trials== | ||
| Line 1,144: | Line 1,080: | ||
* [http://www.conferencealerts.com/seeconf.mv?q=ca13a3h0 7th International Diabetes Federation Western Pacific Region Congress] at Wellington, New Zealand on 30 Mar 2008. | * [http://www.conferencealerts.com/seeconf.mv?q=ca13a3h0 7th International Diabetes Federation Western Pacific Region Congress] at Wellington, New Zealand on 30 Mar 2008. | ||
* [http://debussy.hon.ch/cgi-bin/confevent?aff2+CONF07692+Diabetes_Mellitus 1st International Conference on Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes] at Czech Republic during 27 Feb to 01 Mar 2008. | * [http://debussy.hon.ch/cgi-bin/confevent?aff2+CONF07692+Diabetes_Mellitus 1st International Conference on Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes] at Czech Republic during 27 Feb to 01 Mar 2008. | ||
| − | * [http://www.goingtomeet.com/conventions/details/5301 Discovery Strategies Conference: Modeling Human Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes in Rodents] at | + | * [http://www.goingtomeet.com/conventions/details/5301 Discovery Strategies Conference: Modeling Human Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes in Rodents] at US during Aug-05-2007. |
* [http://www.goingtomeet.com/conventions/details/15113 7th International Conference for Clinical Endocrinology,Diabetes and Infertility] at Egypt during Sep-06-2007. | * [http://www.goingtomeet.com/conventions/details/15113 7th International Conference for Clinical Endocrinology,Diabetes and Infertility] at Egypt during Sep-06-2007. | ||
* [http://www.diabetes.ca/section_professionals/confindex.asp CDA/CSEM Professional Conference and Annual Meetings] at British Columbia during October 24-27, 2007. | * [http://www.diabetes.ca/section_professionals/confindex.asp CDA/CSEM Professional Conference and Annual Meetings] at British Columbia during October 24-27, 2007. | ||
| Line 1,152: | Line 1,088: | ||
# [[Oral_Diabetes_Drugs#Products:_Oral_Hypoglycemic_Agents|Oral hypoglecemic agents]] and their role in diabetes treatment. The focus was the recent meta analysis published in [http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/356/24/2457?ijkey=9288cc5edfcb35c1e7f1bd5d974d1169d64cea0b NEJM], showing increase CV mortality with Rosiglitazone. The panel consensus was that while awaiting more safety data, for now those patients who are tolerating Rosiglitazone should continue taking them, whereas newly diagnosed patients should try alternative treatment. Also all PPAR agonists should be treated as distinct entities rather than having class effect. | # [[Oral_Diabetes_Drugs#Products:_Oral_Hypoglycemic_Agents|Oral hypoglecemic agents]] and their role in diabetes treatment. The focus was the recent meta analysis published in [http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/356/24/2457?ijkey=9288cc5edfcb35c1e7f1bd5d974d1169d64cea0b NEJM], showing increase CV mortality with Rosiglitazone. The panel consensus was that while awaiting more safety data, for now those patients who are tolerating Rosiglitazone should continue taking them, whereas newly diagnosed patients should try alternative treatment. Also all PPAR agonists should be treated as distinct entities rather than having class effect. | ||
| − | # 12 different [[ | + | # 12 different [[Oral_Diabetes_Drugs#Products:_Oral_Hypoglycemic_Agents| diabetes products]] are in various stages of development, and there were about 55 abstracts talking about DPP–IV inhibitors. They are especially useful for: |
#* The elderly | #* The elderly | ||
#* Those with renal insufficiency | #* Those with renal insufficiency | ||
| Line 1,158: | Line 1,094: | ||
#[http://www.amylin.com/pipeline/symlin.cfm Amyline] analogue (Pramlinitide) was combined with Insulin for treatment of Type 2 DM and results were favorable. | #[http://www.amylin.com/pipeline/symlin.cfm Amyline] analogue (Pramlinitide) was combined with Insulin for treatment of Type 2 DM and results were favorable. | ||
# Continuous glucose monitoring using implanted glucose sensors is a step forward in evolving technology. Yet it is still very expensive and best for highly trained patients on intensive insulin therapy. | # Continuous glucose monitoring using implanted glucose sensors is a step forward in evolving technology. Yet it is still very expensive and best for highly trained patients on intensive insulin therapy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>== | ||
| + | <p align="center"> '''This is only a sample report with brief analysis''' <br> | ||
| + | '''Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs'''</p> | ||
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align="center" " | ||
| + | |style="background:lightgrey" align = "center" colspan = "3"|'''[mailto:info@dolcera.com <span style="color:#0047AB">Buy the customized report from Dolcera</span>]''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services Patent Analytics Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/business-research-services Market Research Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools/patent-dashboard Purchase Patent Dashboard] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Landscape Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/research-processes Dolcera Processes] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/industries Industry Focus] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Search Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/alerts-and-updates Patent Alerting Services] | ||
| + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools Dolcera Tools] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ==Contact Dolcera== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border:1px solid #AAA; background:#E9E9E9" align="center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="background:lightgrey" | Samir Raiyani | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Email''': [mailto:info@dolcera.com info@dolcera.com] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Phone''': +1-650-269-7952 | ||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:49, 5 August 2009
Diabetes is a disease caused by high levels of blood glucose resulting from improper production of insulin or action of insulin.
- Type 1: In this Diabetes, the cells that make the hormone insulin regulate the blood glucose are destroyed by the body immune system. This is also called as juvenile onset diabetes as it occurs mainly in children and young adults. 5%-10% of all the cases of diabetes have Type I diabetes. Clinical trials are being pursued and planned to prevent type I diabetes. This is also called as Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM).
- Type 2: In this case, either the cells do not use insulin properly or the body does not produce enough insulin. 90% - 95% of the diabetics have Type 2 diabetes. This type of disease is also called as non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and is mainly observed in people with old age, obese, family history of diabetes, history of gestational diabetes, impaired glucose metabolism, physical inactivity and race/ethnicity.
- Gestational Diabetes: Increase in the levels of blood sugar during pregnancy is called gestational diabetes.
Contents
Incidence and prevalence
Incidence
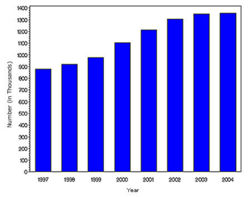
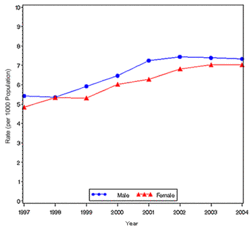
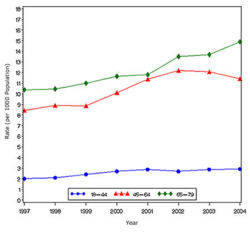
In year 2004, diabetes ( Both type I and type II ) was diagnosed in 1.4 million adults between the age of 18-79 years (Figure 1). The incidence of diabetes was lower in adults having an age between 18-44 years compared to other groups (Figure 2). From 1997 through 2004, the age adjusted incidence of diagnosed diabetes ( Both type I and type II )increased by 35% among men and 46% among women (Figure 3).
- The following table attempts to extrapolate the incidence rate for Diabetes( both type I and type II ) to the populations of various countries and regions.Cure reasearch, Statistics by Country for Diabetes
| S.NO | Country/Region | Extrapolated incidence |
| 1 | USA | 861,533 |
| 2 | Canada | 95,372 |
| 3 | Europe | 1,474,002 |
| 4 | Asia | 10,063,645 |
| 5 | Africa | 1,290,255 |
| 6 | Middle east | 1,055,809 |
| 7 | Australia and Southern Pacific | 70,138 |
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs
Prevalence
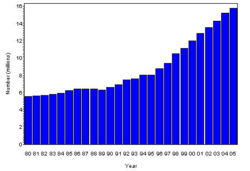
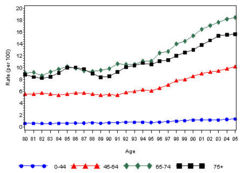
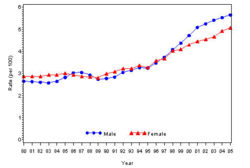
The prevalence of diabetes( Both type I and type II ) in U.S. during the years 1980 to 2005, increased from 5.6 million to 15.8 million (Figure 4). Especially people aged from 65 to 74 had the highest prevalence compared to other age groups (Figure 5). The prevalence of the disease was similar in both men and women till the year 1998 but from 1999, the prevalence of the disease increased highly in men compared to females (Figure 6).
- The following table attempts to extrapolate the prevalence rate for Diabetes( both type I and type II ) to the populations of various countries and regions.Cure reasearch, Statistics by Country for Diabetes.
| S.NO | Country/Region | Extrapolated Prevalence |
| 1 | USA | 17,273,847 |
| 2 | Canada | 1,912,227 |
| 3 | Europe | 33,882,009 |
| 4 | Asia | 201,777,550 |
| 5 | Africa | 25,393,535 |
| 6 | Middle east | 21,169,243 |
| 7 | Australia and Southern Pacific | 1,406,291 |
Market Overview
- The Insulin market in 2006 was largely dominated by two players, Novo Nordisk of Denmark and Eli Lilly of USA.
- India and China are emerging as the most potential future markets for insulin delivery devices.
- Growing at a CAGR of 14.09%, global insulin market will reach US$ 14.5 Billion by 2010 from US$ 7.5 Billion in 2005.
- Over 60% of the insulin sold in 2006 was sold in pen devices.
- Insulin pen devices dominate the market in Europe and Japan whereas syringes and pumps dominate the US market.
- There was a big improvement in the global diabetes market for innovation particularly in the field of non-invasive methods of insulin delivery, including inhalable, oral and patch technology. Source
- There are 3 key new OAD classes; PPAR agonists, GLP-1 agonists/DPP IV inhibitors, and amlinomimetic agents. High forecasted sales are anticipated in 2011 for the GLP-1 agonist Exenatide LAR and the DPP-IV inhibitor Galvus at $2,902.9m and $1,228.7m, respectively. Source
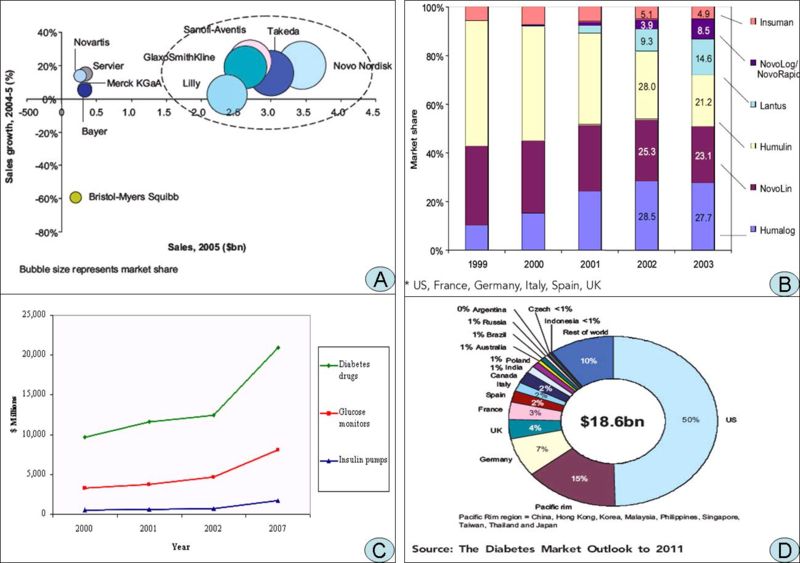
A. Competitive dynamics of the leading players in the global diabetes market, 2005 B. Global diabetes market share by geography, 2005] C. Worldwide Diabetes Market, 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2007 D. Global* market share of leading insulins (%), 1999-2003
Product Information
Products: Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
| Oral Hypoglycemic Agents | |||
| Drug | Brand | Company | Availability |
| Sulfonylureas | |||
| First Generation | |||
| Acetohexomide | Dymelor | Eli Lilly | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Chlorpropamide, Tolazamide | Diabenase | Pfizer | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Second Generation | |||
| Glyburide (Glibenclamide) | Diabeta | Aventis | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Glyburide (Glibenclamide) | Micronase | Pharmacia | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Glyburide (Glibenclamide) | Glynase | Pharmacia | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Glypizide | Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL | Pfizer | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Third Generation | |||
| Glimepride | Amaryl | Aventis | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Meglitnides | |||
| Repaglinide | Prandin | Novo Nordisk | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Nateglinide | Sralix | Novartis | US,UK, J |
| Biguanides | |||
| Metfromin | Glucophage, Glucophage XR | Bristol-Myers Squibb | US |
| Metfromin | |||
| Thiazolidinediones | |||
| Rosiglitazone | Avandia | Glaxosmithkline | US, G, UK |
| Pioglitazone | Actos | Takeda/ Eli Lilly | US, UK, G, S, J |
| Alfa-Glucosidase Inhibitors | |||
| Acarbose | Precose | Bayer | US, F, G, I, S,UK, J |
| Miglitol | Glyset | Pharmacia | US, F, G, S |
| Voglibose | Basen, Volix, Vogseal | Ranbaxy, Nihon Pharmaceutical Industry Ltd | I, J |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor | |||
| Sitgliptin | Januvia | Merck | US |
Products: Fixed Drug Combinations
| Fixed Drug Combinations | |||
| Brand Name | Drug 1 | Drug 2 | Company |
| Metaglip | Glipizide | Metformin | Bristol-Myers Squibb |
| Duetact | Glimepiride | Pioglitazone | Takeda |
| Avandaryl | Glimepiride | Rosiglitazone | GlaxoSmithKline |
| ACTOSPlusMet | Pioglitazone | Metformin | Takeda |
| Avandamet | Rosiglitazone | Metformin | GlaxoSmithKline |
| Janumet | Sitgliptin | Metformin | Merck |
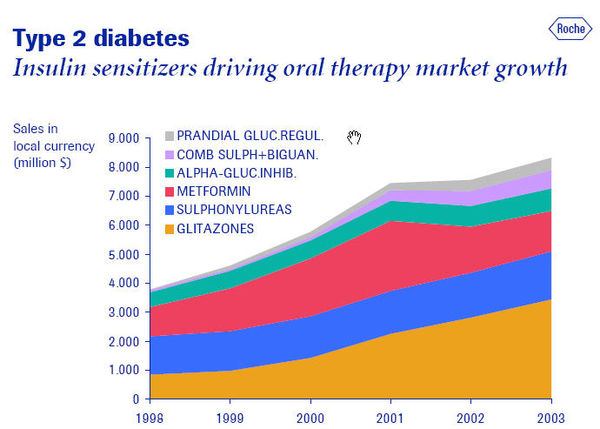
Product pipeline
| Product Pipeline | ||
| Drug | Company | Stage |
| Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitor :DPP-IV inactivates glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an important mediator of blood glucose levels following meals. DPP-IV inhibitors have been clinically shown to provide long term improvement of glucose control without the risk of hypoglycemia, and to improve the function of pancreatic beta cells, the cells responsible for the production of insulin. | ||
| ALS 2-0426 | Alantos Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Servier | 1 |
| PSN9301 | OSI | 2 |
| SYR-322 | Takeda | 3 |
| R1579 | Roche | 1 |
| vildagliptin (Galvus) | novartis | NDA submitted in March 2006 |
| MP-513 | Mitsubishi Pharma | 2 |
| Gastrin + DPP IV Inhibitor | Transition Therapeutics | Preclinical |
| Saxagliptin | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 |
| Insulin sensitizer | ||
| ISIS 113715 | Isis | 3 |
| NCX 4016 (Nitric Oxide donating derivative of Acetyl Salicylic acid) | NicOx | 2 |
| DG070 inhibitors | Develogen AG | Preclinical |
| NovoNorm® (repaglinide)/Metformin | Novo Nordisk | 3 |
| Biguanides | ||
| Gastrin + Metformin | Transition Therapeutics | 1 |
| GLP 1 Analogue / Agonists GLP 1 Analogues have to be injected subcutaneously, Emisphere is working on an oral analogue | ||
| Abiglutide (716155) | glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| TH0318 | Theratechnolgies | 1 |
| Liraglutide (NN2211) | Novo Nordisk | 3 |
| R1583 | Roche | 2 |
| Oral GLP | Emisphere Technologies | 1 |
| PC-DAC™:Exendin-4 | ConjuChem | 2 |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | Exploratory development | |
| AVE0001A | Sanofi Aventis | 2 |
| Gastrin +GLP 1 Agonist | Transition Therapeutics | 2 |
| Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) agonist/analogue | ||
| CS-011 (Rivoglitazone) | Sankyo | 2 |
| Metaglidasen(MBX 102) | Metabolex | 2 |
| MBX-2044 | Metabolex | 1 |
| AVE8134 | Sanofi Aventis | 2 |
| AVE0897 | Sanofi Aventis | 1 |
| R1439, aleglitazar | Roche | 2 |
| AVE0847 | Sanofi Aventis | 2 |
| SAR351034 | Sanofi Aventis | Preclinical |
| 376501 | Glaxosmithkline | 1 |
| 625019 | Glaxosmithkline | 1 |
| 677954 | Glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| Avandia | Glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| Avandia XR | Glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| PPAR Gamma Agonist + simvaststin | Glaxosmithkline | 3 |
| MCC-555, Netoglitazone | Mitsubishi Pharma, Novartis | |
| Muraglitzar | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 |
| R483 | Roche | 2 |
| PPM-204 | Wyeth, Plexxikon | 2
|
| Oral glucokinase activator (GKA) | ||
| PSN010 | OSI | 1 |
| R1511 | Roche | 1 |
| G protein-coupled Receptor(GPR) 119 Agonist | ||
| PSN821 | OSI | |
| Antisense drug for Glucagon Receptor (GCGR) | ||
| ISIS 325568 | Isis | 1 |
| Antisense drug for Glucocorticoid Receptor (GCCR) | ||
| ISIS 377131 | Isis | Preclinical |
| Sodium Glucose Transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor | ||
| AVE2268 | Sanofi Aventis | 2 |
| SAR 7226 | Sanofi Aventis | Preclinical |
| 189075 | Glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| 869682 | Glaxosmithkline | 2 |
| Growth hormone releasing analogue | ||
| TH 9507 | Theratechnolgies | |
| Nitric oxide (NO) blocking agent | ||
| NOX-700 | Medinox | 1 staretd in 2002 |
| Antibody | ||
| TRX4 | BTG | 2 |
| Selective inhibitor of fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) | ||
| CS-917 | Sankyo,Metabasis | 2 |
| MB07803 | metabasis, Daiichi Sankyo | 2 |
| 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11ß-HSD1) inhibitor | ||
| AMG 221 | Amgen, Biovitrum | 1 |
| Polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB, also named hnRNP) inhibitor | ||
| Serono | 1 | |
| Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 | ||
| IPLEX (Mecasermin rinfabate) | Glen Allen | Orphan Drug Status |
| Newer Meglitinides | ||
| Nateglinide with insulin sensitizers | Astellas pharmas | SNDA Filed |
| Nateglinide with biguanides | Astellas pharmas | SNDA Filed |
| Islet Regeneration Factors | ||
| DG770 (beta cell regeneration factor) | Develogen AG | 3 |
| E1 INT (Islet regeneration) | Transition Therapeutics | 2 |
| Miscellaneous
| ||
| AMG 837 (Potentiates Glucose Dependent Insulin Secretion) | Amgen | 1 |
| MBX 213 | Metabolex | 1 |
| R 1499 | Roche | 1 |
| R1438 | Roche | 2 |
| R1440 | Roche | 2 |
| PSN 357 | OSI | 1 |
| NBI 6024 | Neurocrine Biosciences | 2 |
| MK 0941 | Merck | 1 |
| MK 1642 | Merck | 1 |
| Mk 0533 | Merck | 2 |
| MK0893 | Merck | 2 |
| Insulins | ||
| Oral Insulin | Emisphere Technologies | 2 |
| Technosphere | Mannkind corporation | 3 |
| NN344 (Insulin analogue) | Novo Nordisk | 1 |
| NN5401(Insulin analogue) | Novo Nordisk | 1 |
| AERx® iDMS (Insulin Inhalation system) | Novo Nordisk | 3 |
| Inhaled insulin | Bristol Meyers Squibb | 1 |
| Inhaled insulin | Eli Lilly | 2 |
| Exubera (Inhaled insulin) | Pfizer | 4 |
| Oal Lyn (Inhaled insulin) | http://www.generex.com/products/oral-lyn/ | Approved in Ecuador |
| Nasulin | Bentley | 2 |
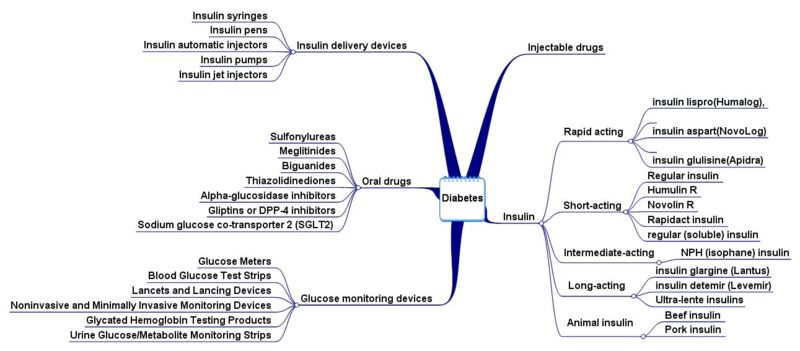
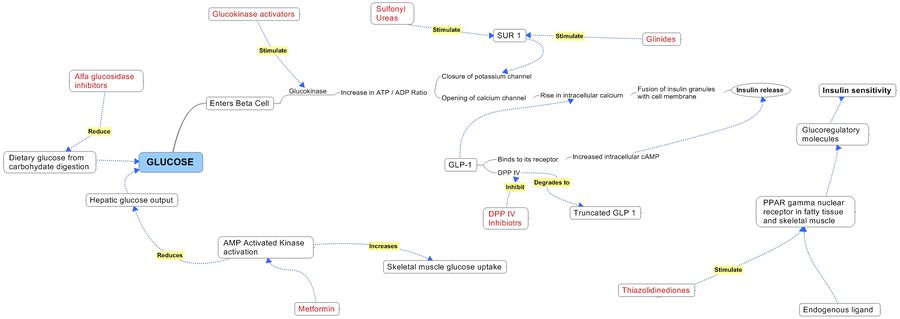
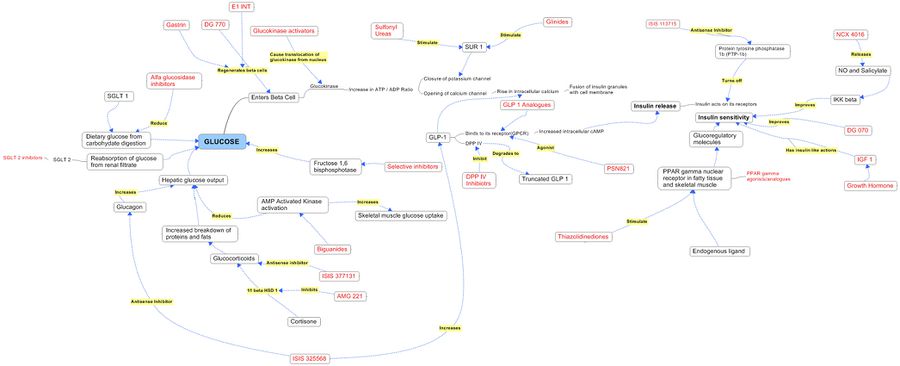
Product Pathways
Intellectual Property
Search strategy
- Database/Vendor: Micropat
- Search scope: US Granted US Applications EP-A EP-B WO JP (bibliographic data only) DE-C,B DE-A DE-T DE-U GB-A FR-A; English Title
- Years: Issue/Publication Date: >20051231
- Search String: (Diabetes OR diabetic) AND (treatment OR treating)
- Hits: 618/217 patents (with/with out family members)
- Date of search: 11 July 2007
Top players and IPC classes
IPC code definition
| A61K | Preparations for medical, dental, or toilet purposes |
| C07D | Heterocyclic compounds |
| C07K | Peptides |
| C12N | Micro-organisms or enzymes; compositions thereof |
| C12Q | Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes or micro-organisms (immunoassay); compositions or test papers therefor; processes of preparing such compositions; condition-responsive control in microbiological or enzymological processes |
Geographical Distribution and Treatment Approaches
IP activity and Treatment Approaches
- Decline in the IP activity during 2005 and 2006 is due 18 months publication delay of patent document.
Clinical Trials
Approved/On-going
| Clinical trials | ||||
| Drug | Sponsors | Description | Phase | Date of Start |
| Oral Drugs | ||||
| Cannabinoid receptor antagonist | ||||
| Rimonabant | Sanofi-Aventis | The primary objective of this study is to assess the efficacy of SR141716 (rimonabant) compared to placebo on change in HbA1c and on relative change in body weight over 52 weeks in obese type 2 diabetic patients on monotherapy inadequately controlled with oral anti-diabetic drug (sulfonylurea or ?-glucosidase inhibitor). | 3 | May-07 |
| Insulin Sensitisers | ||||
| Metaglidasen | Metabolex | 2, 3 | May-06 | |
| Thioglitazone | ||||
| Rosiglitazone maleate/metformin hydrochloride (AVANDAMET) | GlaxoSmithKline | This study will evaluate the longer-term glycemic effect of two medicines approved for initial treatment of type 2 diabetes. | 4 | Oct-06 |
| Balaglitazone | Rheoscience A/S | Balaglitazone is a thiazolidinedione derivative that is being developed as an oral anti-diabetic drug to improve blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The purpose of this study is to assess if additional treatment with balaglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes on stable insulin treatment will improve blood glucose control and decrease the daily insulin dose, but with less impact on weight gain and oedema. | 3 | Jul-07 |
| (DPP-4) inhibitor | ||||
| Vildagliptin | Novartis | This is a 24-week study to assess the efficacy on HbA1c of 100 mg vildagliptin once daily as compared to placebo as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controllled with metformin. | 3 | May-06 |
| Insulin | ||||
| Oral Insulin | NIDDK, NICHD, NIAID, NICR, ADA, JDRF | N/A | 3 | Feb-07 |
| Potassium Channel Blocker | ||||
| Diazoxide | Grill, Valdemar, M.D. | The purpose of this study is to find out if Diazoxide can partly retain insulin production in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients. | 4 | Feb-05 |
| Nutritional Agents | ||||
| Benfotiamine (Vitamin B1) | University Hospital, Aker, The Research Council of Norway | N/A | 1, 2 | Aug-05 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | NIDDK | N/A | 2 | June 2006 |
| Vitamin D | University of Tromso | The purpose of the study is to evaluate if supplementation with vitamin D in a dose of 40.000 IU per week will result in improved metablic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. | 2 | Jun-06 |
| Carnitine Supplementation | Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City,Sigma Tau Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Minimed Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacia/Upjohn Career Development Award | The purpose of this study is to determine whether type I diabetics with carnitine deficiency exhibit increased numbers of hypoglycemic (low blood sugars) events and if unrecognized hypoglycemia occurs during continuous 72-hour glucose monitoring. If they are determined to have unrecognized hypoglycemia, then oral carnitine supplementation will be given to those subjects and they will be reassessed for the number of hypoglycemic events in a 72-hour glucose monitoring. | Oct-04 | |
| Antiinflammatory | ||||
| Salsalate | NIDDK,National Institutes of Health Clinical Center | This study, conducted at the Phoenix Indian Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, will determine whether reducing subclinical inflammation lessens insulin resistance in healthy, obese volunteers. | 4 | Mar-03 |
| Angiotensin (AT 2) Antagonist/blocker | ||||
| Olmesartan | Daiichi Sankyo Inc | N/A | 3 | Oct-04 |
| MBX-2044 | Metabolex | The purpose of this study is to collect important information regarding the glucose-lowering efficacy of MBX-2044 and the safety of MBX-2044 (especially weight gain and edema) in diabetics. It will also provide important information about the appropriate doses to be used in subsequent longer-term studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MBX-2044 alone and in combination with other anti-diabetic agents. | 2 | Oct-06 |
| PF-00734200 | Pfizer | The purpose of this Phase 2a study is to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability, of multiple parallel doses of PF-00734200 following oral administration to adult human subjects with T2DM who currently are on a stable dose of metformin. | 2 | Jun-07 |
| CP-945,598 | Pfizer | The purpose of this study is to determine if CP-945,598 is effective in the treatment of obesity in type 2 diabetic patients | 3 | Nov-06 |
| WelChol® (colesevelam) | Daiichi Sankyo Inc | This study is designed to assess the potential mechanism of action by which WelChol® (colesevelam) may improve blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes | 2 | May-05 |
| Aleglitazar and Actos® | Hoffmann-La Roche | This study will compare the effects of aleglitazar and Actos®, added to preexisting oral antihyperglycemic therapy and/or diet and exercise, on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes, and normal or mildly impaired renal function. | 2 | June 2007 |
| BI 1356 BS | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals | The objective of this monotherapy study is to investigate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of 3 doses of BI 1356 BS compared to placebo over 12 weeks of treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and insufficient control of thier blood glucose. In addition, there will be an open-label treatment arm with metformin. The hypothesis of the trial is that the test drug, BI 1356 BS will lead to better control of blood glucose compared to placebo after 12 weeks of treatment. | 2 | May-06 |
| BMS-512148 | Bristol-Myers Squibb | The purpose of this clinical research study is to learn if BMS-512148, added to insulin and one or two anti-diabetes medications (metformin and/or pioglitazone or rosiglitazone), can help reduce the blood sugar levels compared to insulin and one or two anti-diabetes medications (metformin and/or pioglitazone or rosiglitazone) alone, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. | 2, 3 | October 2006 |
| Parenteral routes | ||||
| Insulins | ||||
| Insuline glargine | Sanofi-Aventis | Purpose ogf this study is to determine rhe first dose and titration of basal insulin | 4 | May-06 |
| Basal Insulin Plus Insulin Glulisine | Sanofi-Aventis | To evaluate the efficacy of a single injection of glulisine before the main meal added to insulin glargine plus oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs) compared to insulin glargine plus OADs in Type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with basal insulin plus OADs. | 4 | Jul-06 |
| Inhaled Insulin (Exubera) | Pfizer | To assess the impact on glucose control by inhaled insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not well controlled on 2 or more oral anti-diabetic agents | 3 | Mar-06 |
| Insulin Inhalation Powder | Eli Lilly and Company | This is a phase 3, open-label, randomized study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the Lilly/Alkermes inhaled insulin system compared to injected pre-meal insulin in non-smoking patients with type 2 diabetes. Patients will be treated for 24 months with a 2-month follow-up period. | 3 | Apr-06 |
| Levemir | Novo Nordisk | This trial aims for a comparison of the effect on glycaemic control in subjects with type 2 diabetes under both established Western algorithm and Korean practical algorithm, given in combination with oral diabetic drug(s) | 4 | Aug-07 |
| Pulsatile IV Insulin | Florida Atlantic University | The purpose of this study is to determine if restoring normal metabolic function in patients with either type I or type II diabetes can improve the impact of the consequences of diabetic complications on the overall quality of life of diabetic patients. Patients are treated once a week with pulsatile intravenous insulin therapy mimicking normal insulin secretion. | 2, 3 | Mar-03 |
| Incretin Minetic | ||||
| Exenatide With Basal Insulin | Amylin Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly | This is a phase 3 trial designed to compare the effects of twice daily exenatide plus oral antidiabetic agents (OADs) and once-daily insulin glargine plus OADs with respect to glycemic control, as measured by hemoglobin A1c, with minimum weight gain, in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes on OADs. | 3 | Jun-06 |
| Exenatide | Baylor College of Medicine, NIH | The purpose of this study is to see if giving exenatide and insulin before a meal would lower blood sugars after the meal. | 4 | Mar-07 |
| Exenatide Plus Metformin vs. Insulin Aspart Plus Metformin | Amylin Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly | This study in Germany is designed to compare the effects of twice-daily exenatide plus metformin and twice-daily premixed human insulin aspart plus metformin with respect to glycemic control, as measured by HbA1c, combined with the percentage of patients with at least one treatment-emergent hypoglycemic episode. Patients will be treated with study therapy for approximately 26 weeks. | 3 | Feb-07 |
| Sitigliptin | Merck Frosst Canada Ltd, University of British Columbia | 2 | Nov-06 | |
| Antibodies | ||||
| hOKT3gamma1 (Ala-Ala) | NIAID | hOKT3gamma1 (Ala-Ala) is a man-made antibody that is commonly used to prevent organ rejection. The purpose of this study is determine whether hOKT3gamma1 (Ala-Ala) can halt the progression of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. | 2 | Sep-05 |
| Anti-CD20 (rituximab) | NIDDK, NICHD, NIAID, NICR, ADA, JDRF | This study will investigate the use of rituximab to see if it can help lower the number of immune B cells thereby preventing the destruction of any remaining insulin producing beta cells that remain at diagnosis. | 2, 3 | Dec-06 |
| Surgical | ||||
| Islet Cell Transplants | Weill Medical College of Cornell University | 1 | Aug-03 | |
Conferences
- Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin Action and Resistance at Breckenridge, Colorado from January 22 - 27, 2008
- Diabetes UK Annual Professional Conference 2008 at Glasgow from 05 Mar 2008 09:00 to 07 Mar 2008 17:00
- 7th International Diabetes Federation Western Pacific Region Congress at Wellington, New Zealand on 30 Mar 2008.
- 1st International Conference on Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes at Czech Republic during 27 Feb to 01 Mar 2008.
- Discovery Strategies Conference: Modeling Human Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes in Rodents at US during Aug-05-2007.
- 7th International Conference for Clinical Endocrinology,Diabetes and Infertility at Egypt during Sep-06-2007.
- CDA/CSEM Professional Conference and Annual Meetings at British Columbia during October 24-27, 2007.
Conference Update: American Diabetic Association 2007
Conference highlights for Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
- Oral hypoglecemic agents and their role in diabetes treatment. The focus was the recent meta analysis published in NEJM, showing increase CV mortality with Rosiglitazone. The panel consensus was that while awaiting more safety data, for now those patients who are tolerating Rosiglitazone should continue taking them, whereas newly diagnosed patients should try alternative treatment. Also all PPAR agonists should be treated as distinct entities rather than having class effect.
- 12 different diabetes products are in various stages of development, and there were about 55 abstracts talking about DPP–IV inhibitors. They are especially useful for:
- The elderly
- Those with renal insufficiency
- Heart failure patients
- Amyline analogue (Pramlinitide) was combined with Insulin for treatment of Type 2 DM and results were favorable.
- Continuous glucose monitoring using implanted glucose sensors is a step forward in evolving technology. Yet it is still very expensive and best for highly trained patients on intensive insulin therapy.
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs
Contact Dolcera
| Samir Raiyani |
|---|
| Email: info@dolcera.com |
| Phone: +1-650-269-7952 |