Rise in IP filing and product trials in 5G Backhaul
Backhaul Network:
- Backhaul (back-net or backbone or transport network) in cellular networks connects the base stations to the core network and consists mostly of dedicated fiber, copper, microwave and occasionally satellite links.
- Mobile backhaul deployment impacts mobile interface as well as contributes to overall performance of the network.
5G Backhaul:
- With the advent of 5G opening doors to host of new services, the increasing exchange of data in the network will further be taking place. It is hence desired that a well working inter connections are necessary for the mobile networks to operate properly which in turn will be needing support from the transport and packet network and will form the mobile backhaul network (MBH).
- In 5G network, backhaul is the connection between gNBs and 5G core networks. Frequency range up to 100GHz can be considered for 5G Backhaul which is set by the ITU standards.
- Denser placement of base stations is required in high-frequency (mmWave frequency) deployments. The main challenge in network densification is the site acquisition costs and fiber deployment. For this reason, wireless backhauling is an attractive replacement for fiber.
Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB):
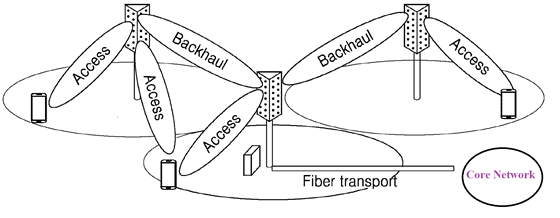
- In IAB, the access link (Base station to base station or Base station to UE) and backhaul link (Base station to core network) share the same wireless standard technology. The center base station uses the same spectrum or wireless channel to provide backhaul connection to the other two base stations as well as to serve the mobiles in its coverage.
Fig 1: Architecture of IAB
- IAB can be deployed through both in-band and out-band relaying and can be used in both indoor and outdoor networks. In-band relaying uses the same carrier frequency in access and backhaul links whereas Out-band relaying uses different carrier frequency in access and backhaul links.
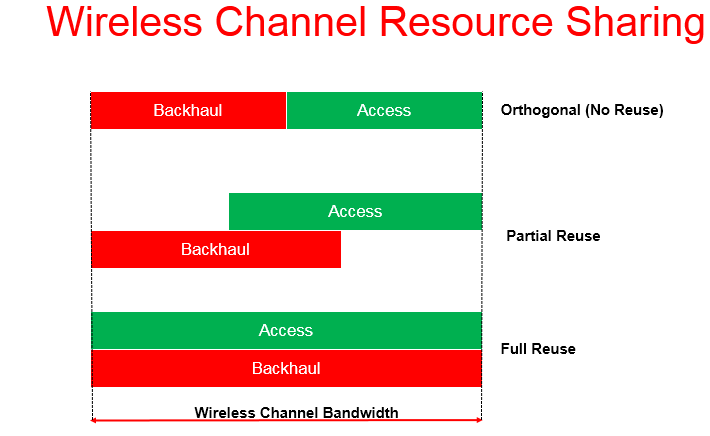
- The sharing options of the wireless channel resources are Time, Frequency and Space.The summation of the available resource is fixed for access and backhaul links which can be dynamically partitioned between access and backhaul links to meet the instantaneous demand of UEs across the network. Non-adjacent access and backhaul links can share the same bandwidth without interference. This enables efficient re-use of radio resources.
Fig 2:Wireless Channel resource sharing
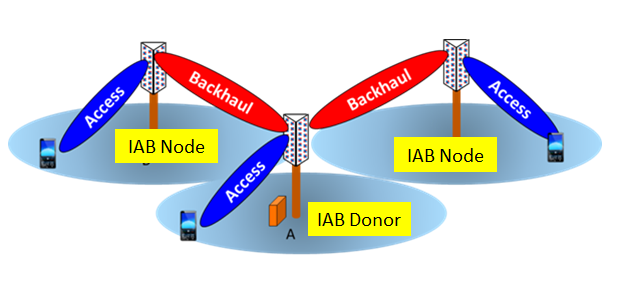
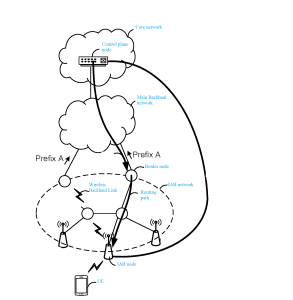
- In the context of IAB, there are two kinds of nodes that are identified as components of a RAN as defined in the TR 38.874.
- IAB donor: RAN node which provides UE’s interface to core network and wireless backhauling functionality to IAB nodes.
- IAB node: RAN node that supports wireless access to UEs and wirelessly backhauls the access traffic.
Fig 3: IAB architecture (IAB donor and IAB node)
Pros of IAB:
- High spectrum efficiency – Reuse of time, frequency and space resources between access and backhaul.
- Higher cost efficiency – As it uses the same radio hardware unit.
- Higher performance – Dynamic optimization of resource across access and backhaul.
Cons of IAB:
- Access backhaul interference
- Complex scheduling of the channel resources – across access and backhaul.
Technology Solutions for IAB:
- The potential solutions for efficient operation of integrated access and wireless backhaul for NR are listed below
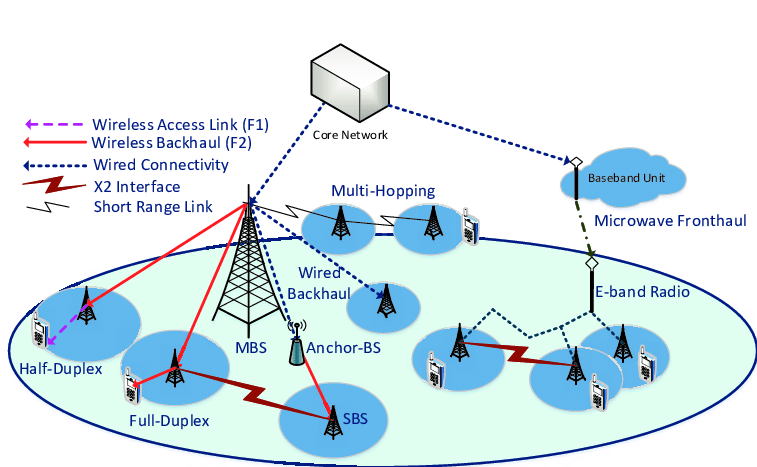
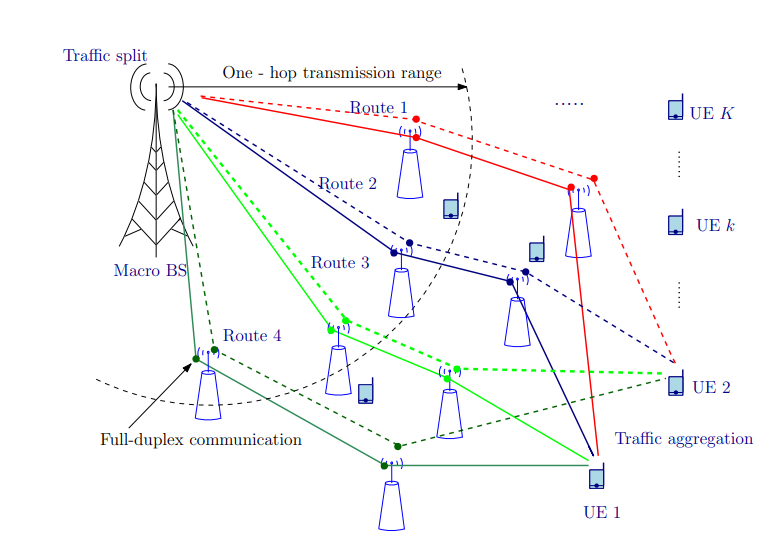
Multi-hop Backhauling: It is hop-by-hop propagation of signalling to support low latency scheduling. Dense multi-hop networks provide several paths that can be used to increase robustness of the network. It enables flexible range extension. But the maximum number of hops in a deployment depends on many factors such as frequency, cell density, propagation environment, and traffic load. Therefore it is better to have flexibility in the hop count
Fig 4.Multi-hop backhauling of 5G small cells
Fig 5.Illustration of multi-hop backhauling
Scalable networks: Backhaul architectures and techniques to enable easy expansion and up gradation of network to meet strategic and demand based needs. Instead of building new structures, installing additional fiber and cable, network connectivity can be obtained by using high-bandwidth, millimeter-wave communications and existing power line infrastructure.
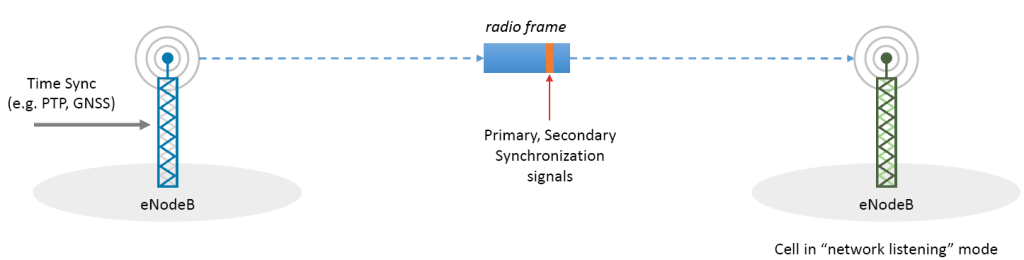
Over the air (OTA) synchronization: Timing, frequency or phase synchronization between relay nodes of backhaul network uses Precision Time Protocol (PTP) or Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).The “network listening” cell gets synchronized to the radio frames coming from the nearby cell which is a synchronized node as shown in the figure. It is very essential to support TDD system and some potential features which need network synchronization. It enables the detection of movement, location and proximity of the UE or relay nodes. If the location of the node is not known, it is used in determining the location.Therefore it allows successful communication between nodes in a network.
Fig 6.OTA synchronization
Flexible Deployment: IAB-node integration for both Stand-alone(SA) and Non-standalone(NSA) It is important to enable the utilization of existing LTE infrastructure for NR deployment.
- SA mode: using only one radio access technology.
- NSA mode: combines multiple radio access technologies.
Topology Management: IAB topology is adapted in order to maintain service continuity (e.g., when a backhaul link is degraded or lost), or for load balancing purposes (e.g., to avoid congestion). It improves the optimal performance of the backhaul link.
Fig 7.Topology management
List of 3GPP Documents related to IAB:
| Document Number | Title | Publication Date | Company | Key Concepts |
| RP-182329 | Enhancements to support NR backhaul links | 10/12/2019 |
Qualcomm |
1. Multi-hop Backhauling 2. Specification of IAB-node architecture. 3. Enhancements to gNB. 4. Efficient operation for both in-band and out-of-band relaying. 5. Flexible deployment |
| RP-190712 | Integrated Access and Backhaul for NR | 3/18/2019 | ||
| R1-1805274 | Evaluation Methodology for NR IAB | 4/16/2018 | Samsung | 1. Physically fixed relays 2. In-band and out-of-band scenarios. 3. NR access over NR backhaul 4. Support of multiple backhaul hops 5. Topology adaptation |
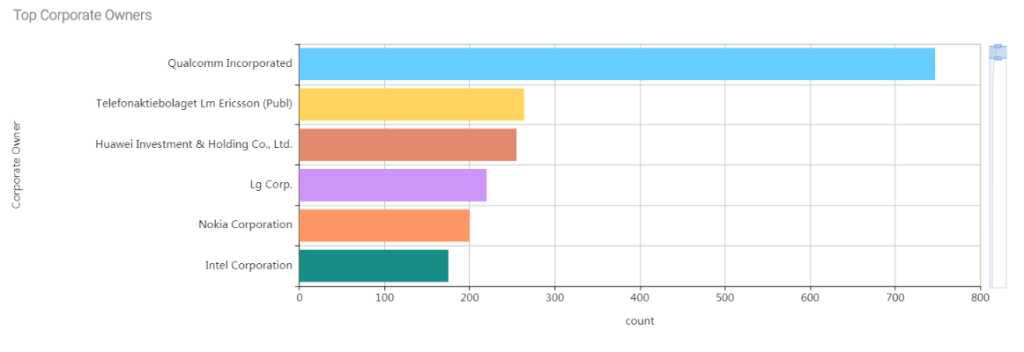
List of top IP filing companies:
Major IP filing companies in backhaul are Qualcomm, Ericsson, Huawei, LG Corp and Nokia Corp.
The above chart is based on Dolcera PCS tool search results of 5G Backhaul technology.
Examples of 5G Backhaul patents:
| Company | Patent No. | Priority Date | Title | Technology |
|
Qualcomm |
US20190109745A1 | 10/09/2017 | Timing and frame structure in an integrated access backhaul (iab) network | Multi-hop Backhauling |
| US10136359B2 | 06/30/2015 | Traffic flow migration in backhaul networks | Topology management | |
| US20190132807A1 | 10/30/2017 | Techniques and apparatuses for resource-specific power control in 5g | Power control in 5G various aspects | |
|
Ericsson |
WO2019057279A1 | 09/20/2017 | Method and apparatus for traffic management in a self-backhauled network by using capacity requests | Traffic management between access and backhaul links |
| US20190191398A1 | 07/17/2015 | Synchronization of Wireless Base Stations | Over The Air synchronization | |
|
Huawei Investment and Holding Co., Ltd |
US9642146B2 | 06/05/2013 | System and method for an agile wireless access network | Radio access network management |
| WO2015042966A1 | 09/30/2013 | Backhaul link establishment method, apparatus and system | Backhaul link establishment method | |
|
LG Corp |
US10212678B2 | 11/20/2013 | Method and apparatus for network synchronization | Network synchronization |
| WO2018182286A1 | 03/30/2017 | Method for performing path reselection in wireless communication system and apparatus therefore | Path reselection in wireless communication system |
Products:
Top infrastructure vendors have started launching their 5G backhaul product portfolio. Some of the products are:
| S.no | Company | Product Type | Date | Remarks |
| 1 | Huawei | Backhaul | Aug-17 | It provides solutions of smoothly upgrading bandwidths from 1 Gbps to 2 Gbps to 5 Gbps to 10 Gbps, enables continuous evolution of microwave sites |
| 2 | Huawei | WDM | Feb-18 | The Centralized WDM fronthaul solution uses innovative colorless optical modules to simplify site delivery and operation and maintenance |
| 3 | Huawei | FO OTN | Feb-18 | The active FO OTN fronthaul solution supports up to 15 channels of service access, hitless switching, and integrated access for multiple services. |
| 4 | Huawei | Microwave backhaul | Feb-18 | In backhaul scenarios, 5G microwave series products are able to offer 10 Gbps high data rate and 25 µs low latency when traditional microwave frequency bands are used |
| 5 | Ericsson | Microwave backhaul | Dec-18 | The portfolio includes small cell backhaul solutions using the V-band (60GHz). |
| 6 | Nokia | Broadband Anyhaul | Feb-19 | A proof of concept of Nokia Broadband Anyhaul 25G Passive Optical Network (PON) demonstrates the viability of building on existing fiber infrastructure to offer 25 Gbps speeds |
| 7 | Ericsson | Mini Link 6200 | Feb-19 | Mini-Link 6200 is the first long haul system on the market to cater for 5G transport. It brings the 5G transport outside the urban area – with market leading capacities over long distances, up to 10 Gbps over 35 km |
| 8 | Nokia | Wavence Microwave | Feb-19 | Portfolio supports carrier aggregation to combine frequency bands in the traditional uWave or mmWave frequencies or even with existing third-party microwaves to achieve 5G-ready microwave throughput beyond 10 Gbps |
| 9 | Cisco, Colt Technology Services | Backhaul | Mar-19 | Colt has deployed Cisco’s segment routing and Ethernet VPN architecture to enable network operators to be more flexible in how they deliver bandwidth at scale based on characteristics like data rates, latency requirements, and the impact on fiber efficiency. |
Trials and Demonstrations:
Telecom operators in partnership with infrastructure vendors have started conducting 5G backhaul trials & demonstrations. Some of the trials & demonstrations can be listed as:
| S.no | Companies | Date | Country | Details |
| 1 | China Telecom, CCS | May-14 | China | CCS with China telecom trialed small cell backhaul |
| 2 | KT, NEC | Apr-16 | Japan | KT and NEC successfully test 5G backhaul solution utilising E-band spectrum |
| 3 | Vodafone, Huawei | Feb-18 | Germany | Vodafone and Huawei test applicability of IP microwave backhaul for 5G |
| 4 | NTT Docomo, Huawei | May-18 | Japan | Docomo, Huawei demo backhaul tech for 5G networks |
| 5 | Vodafone | Nov-18 | Italy | Vodafone trials SDN-powered microwave backhaul |
| 6 | Ericsson, Deutsche Telekom | Jan-19 | Greece | Ericsson attained a data transmission rate of 40Gbps during a trial of millimetre-wave (mmWave) wireless backhaul in partnership with Deutsche Telekom. |
| 7 | BT, CCS | Feb-19 | UK | CCS links with BT for trial of gigabit backhaul |
| 8 | Vodafone, Telesat | May-19 | UK | First demo of 5G backhaul via LEO satellite |
| 9 | Ericsson, Deutsche Telekom | May-19 | Greece | Attained data transmission rate of 100 Gbps |
Conclusion:
- Multi-hop backhaul, OTA synchronisation, topology management, scalable and flexible networks are the key technology areas in 5G Backhaul
- Qualcomm, Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia and LG are top IP holding companies in 5G Backhaul
- Microwave and Fiber networks are currently used in products that are implementing 5G Backhaul technology
- Vodafone, Ericsson and Deutsche Telecom are continuously doing trails in 5GBackhaul technology


 中文
中文